【笔记】PyTorch快速入门:简单的神经网络模型
神经网络
神经网络是一些层或者模块,对数据进行处理。
torch.nn提供了诸多构造神经网络的模块,模块化的结构方便了管理复杂结构。
接下来以在FashionMNIST上构造一个图像分类器为例。
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
准备训练设备
有GPU用GPU,没有用CPU
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(f"Using {device} device")
定义网络的类
我们的网络从nn.Module继承来
class NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear_relu_stack = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 10),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.flatten(x)
logits = self.linear_relu_stack(x)
return logits
然后创建一个实例(对象),把它放到device上
model = NeuralNetwork().to(device)
print(model)
跑一下的结果
Using cpu device
NeuralNetwork(
(flatten): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
(linear_relu_stack): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): ReLU()
(4): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
结果是返回值的softmax,这是个10维的概率,找最大的就是预测结果
X = torch.rand(1, 28, 28, device=device)
logits = model(X)
pred_probab = nn.Softmax(dim=1)(logits)
y_pred = pred_probab.argmax(1)
print(f"Predicted class: {y_pred}")
模型的layers
以3张28x28的图像为例,分析它在network里的状态
input_image = torch.rand(3,28,28)
print(input_image.size())
'''
torch.Size([3,28,28])
'''
nn.Flatten
Flatten顾名思义,扁平化,用于将2维tensor转为1维的
flatten = nn.Flatten()
flat_image = flatten(input_image)
print(flag_image.size())
'''
torch.Size([3,784])
'''
nn.Linear
Linear,做线性变换的
layer1 = nn.Linear(in_features=28*28,out_features=20)
hidden1 = layer1(flag_image)
print(hidden1.size())
'''
torch.Size([3,20])
'''
nn.ReLU
非线性激活函数,在Linear层后,增加非线性,让神经网络学到更多的信息
hidden1 = nn.ReLU()(hidden1)
nn.Sequential
Sequential,序列的,类似于把layers一层一层摆着
seq_modules = nn.Sequential(
flatten,
layer1,
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(20, 10)
)
input_image = torch.rand(3,28,28)
logits = seq_modules(input_image)
nn.Softmax
最后一层的结果返回一个在[-inf,inf]的值logits,通过softmax层后,映射到[0,1]
这样[0,1]的值可以作为概率输出,dim指定和为1的维度
softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
pred_probab = softmax(logits)
模型的参数
这些layers是参数化的,就是说在训练中weights和biases不断被优化
以下的代码输出这个模型里的所有参数值
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
print(name,param.size(),param[:2])
自动求导
训练神经网络的时候,最常用的是反向传播,模型参数根据loss functoin的梯度进行调整。
为了求梯度,也就是求导,我们使用torch.autograd。
考虑就一个layer的网络,输入x,参数w和b,以及一个loss function,也就是
import torch
x = torch.ones(5) # input tensor
y = torch.zeros(3) # expected output
w = torch.randn(5, 3, requires_grad=True)
b = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
z = torch.matmul(x, w)+b
loss = torch.nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(z, y)
Tensors, Functions and Computational Graph
考虑这个过程的Computational Graph,如下
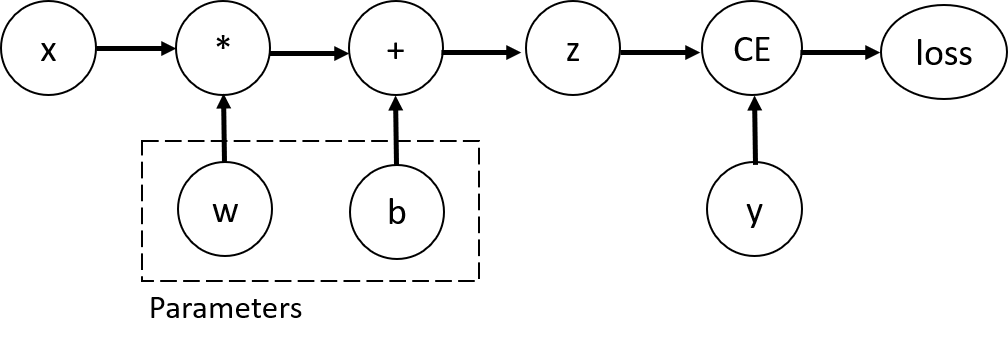
这个一定是DAG(有向无环图)
为了计算loss在w和b方向上的梯度,我们给他们设置requires_grad
w.requires_grad_(True)
b.requires_grad_(True)
Functions实际上是对象,有计算正向值和反向导数的成员。
print(z.grad_fn)
print(loss.grad_fn)
计算梯度
我们要计算Loss对w和b的偏导,只需要使用
loss.backward()
然后就得到了
print(w.grad)
print(b.grad)
注意:
- 我们只能计算图里叶子的梯度,内部的点不能算
- 一张图只能计算一次梯度,要保留节点的话,backward要传
retain_graph=True
import torch
x = torch.randn((1,4),dtype=torch.float32,requires_grad=True)
y = x ** 2
z = y * 4
print(x)
print(y)
print(z)
loss1 = z.mean()
loss2 = z.sum()
print(loss1,loss2)
loss1.backward() # 这个代码执行正常,但是执行完中间变量都free了,所以下一个出现了问题
print(loss1,loss2)
loss2.backward() # 这时会引发错误
所以要把loss1的那行改成
loss1.backward(retain_graph=True)
不计算梯度
有些时候我们不需要计算梯度,比如模型已经训好了,只需要正向用
这个时候算梯度就很拖累时间,所以要禁用梯度
z = torch.matmul(x, w)+b
print(z.requires_grad)
with torch.no_grad():
z = torch.matmul(x, w)+b
print(z.requires_grad)
'''
True
False
'''
另一个办法是用.detach()
z = torch.matmul(x, w)+b
z_det = z.detach()
print(z_det.requires_grad)
'''
False
'''
tensor输出和雅克比积
如果函数的输出是tensor,就不能简单算梯度了
结果是一个矩阵(其实就是依次遍历x和y的分量,求偏导)
PyTorch不计算J的原始值,而是给一个\(v\),计算\(v^T\cdot J\),输出接口是统一的
具体来说,把v当参数传进去
inp = torch.eye(5, requires_grad=True)
out = (inp+1).pow(2)
out.backward(torch.ones_like(inp), retain_graph=True)
本文来自博客园,作者:GhostCai,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ghostcai/p/16209200.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号