如何在Linux下建立包含lua vm的unit test framwork
0 引言
lua是一种语法极为灵活、扩展性极强的“胶水语言”, 在使用lua/lua capi时常常会写出一些容易出错的code. 因此,有必要建立以lua vm为基础的unit test帮助程序员及早地发现bug,提高代码的质量。为此,有三件事情需要做。
1 编译配置googletest/googlemock环境
1.1 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13513905/how-to-set-up-googletest-as-a-shared-library-on-linux
1.2 为什么要选择gtest
(1) gtest可以帮助我们编写独立可复制的测试用例。在gtest中,每个测试用例(TEST(classname, functionName))都被一个独立的对象调用,因此即使一组测试用例中的一个运行失败了,其他的测试用例也可以正常跑完。
(2)gtest可以帮助我们编写组织结构良好、反映代码结构的测试用例。gtest使用test suites将测试结果组织到一起。从逻辑上来说,相关的测试应当被放在同一组test suite中。换句话说, Test() 的第一个参数应该是一样的。举例:
///< tested function
int Factorial(int n); // Returns the factorial of n
///< gtest code
// Tests factorial of 0.
TEST(FactorialTest, HandlesZeroInput) {
EXPECT_EQ(Factorial(0), 1);
}
// Tests factorial of positive numbers.
TEST(FactorialTest, HandlesPositiveInput) {
EXPECT_EQ(Factorial(1), 1);
EXPECT_EQ(Factorial(2), 2);
EXPECT_EQ(Factorial(3), 6);
EXPECT_EQ(Factorial(8), 40320);
}
在上面的例子中, HandlesZeroInput 和 HandlesPositiveInput 都属于 FactorialTest 这个test suite.
(3)gtest是跨平台的,可以跨平台复用代码。
(4)gtest可以在一次运行中提供尽量多的信息。当一个测试用例跑挂了,gtest不会中断。反之,它会一直跑一直跑,跑到所有测试用例都跑完,并且把所有测试用例的运行情况一次性输出。这样可以保证每次运行都能得到足够多的信息,并且可以一次修完。
(5)gtest可以帮助我们很多自动化的事情。一旦一个测试用例被定义完成了,gtest就被主动帮助我们管理这些测试用例。不需要用户一个一个地去跑。
(6)gtest很快。通过fixture中的subroutine机制,可以复用跨测试用例中共享的资源并且只需要调用 SetUp() 和 TearDown() 一次,在此情况下还能使得测试用例独立于这些资源。test fixture 举例如下:
///< class to be tested.
template <typename E> // E is the element type.
class Queue {
public:
Queue();
void Enqueue(const E& element);
E* Dequeue(); // Returns NULL if the queue is empty.
size_t size() const;
...
};
///< gtest code: prepare a fixture class
class QueueTest : public ::testing::Test {
protected:
void SetUp() override {
q0_.Enqueue(1);
q1_.Enqueue(2);
q2_.Enqueue(3);
}
// void TearDown() override {}
Queue<int> q0_;
Queue<int> q1_;
Queue<int> q2_;
};
///< gtest code: write TEST_F() part
TEST_F(QueueTest, IsEmptyInitially) {
EXPECT_EQ(q0_.size(), 0);
}
TEST_F(QueueTest, DequeueWorks) {
int* n = q0_.Dequeue();
EXPECT_EQ(n, nullptr);
n = q1_.Dequeue();
ASSERT_NE(n, nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(*n, 1);
EXPECT_EQ(q1_.size(), 0);
delete n;
n = q2_.Dequeue();
ASSERT_NE(n, nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(*n, 2);
EXPECT_EQ(q2_.size(), 1);
delete n;
}
- googletest constructs a
QueueTestobject (let’s call itt1). t1.SetUp()initializest1.- The first test (
IsEmptyInitially) runs ont1. t1.TearDown()cleans up after the test finishes.t1is destructed.- The above steps are repeated on another
QueueTestobject, this time running theDequeueWorkstest.
1.3 在同一个测试用具内共用测试资源: http://google.github.io/googletest/advanced.html#sharing-resources-between-tests-in-the-same-test-suite
class FooTest : public testing::Test { protected: // Per-test-suite set-up. // Called before the first test in this test suite. // Can be omitted if not needed. static void SetUpTestSuite() { // Avoid reallocating static objects if called in subclasses of FooTest. if (shared_resource_ == nullptr) { shared_resource_ = new ...; } } // Per-test-suite tear-down. // Called after the last test in this test suite. // Can be omitted if not needed. static void TearDownTestSuite() { delete shared_resource_; shared_resource_ = nullptr; } // You can define per-test set-up logic as usual. void SetUp() override { ... } // You can define per-test tear-down logic as usual. void TearDown() override { ... } // Some expensive resource shared by all tests. static T* shared_resource_; }; T* FooTest::shared_resource_ = nullptr; TEST_F(FooTest, Test1) { ... you can refer to shared_resource_ here ... } TEST_F(FooTest, Test2) { ... you can refer to shared_resource_ here ... }
2 编译配置lua5.0
2.1 download src file: https://www.lua.org/ftp/lua-5.0.3.tar.gz
2.2 make
2.3 write testing code:
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> extern "C" {///< It is very important to wrap related header files into this cracket, or you will get some error message as below. #include "mylua/lua.h" #include "mylua/lauxlib.h" #include "mylua/lualib.h" } int main(void) { char buff[256] = "print(\"hello world!\n\")"; int error; lua_State* L = lua_open(); /* opens Lua */ luaopen_base(L); /* opens the basic library */ luaopen_table(L); /* opens the table library */ luaopen_io(L); /* opens the I/O library */ luaopen_string(L); /* opens the string lib. */ luaopen_math(L); /* opens the math lib. */ while (fgets(buff, sizeof(buff), stdin) != NULL) { error = luaL_loadbuffer(L, buff, strlen(buff), "line") || lua_pcall(L, 0, 0, 0); if (error) { fprintf(stderr, "%s", lua_tostring(L, -1)); lua_pop(L, 1); /* pop error message from the stack */ } } lua_close(L); return 0; }
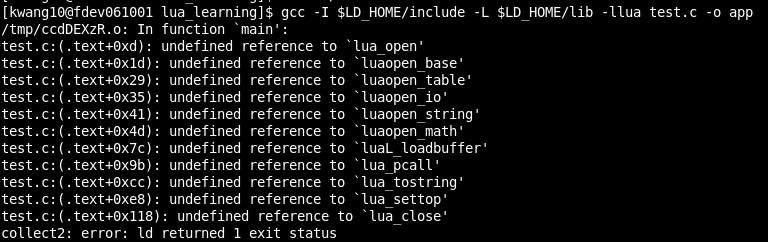
2.3 use g++ to build:
g++ test.c -I $LD_HOME/include -L $LD_HOME/lib -llua -llualib -o app
3 集成测试
2.1 编写luaC 类
//lua_c.hh #ifndef _LUA_C_HH_ #define _LUA_C_HH_ #include <vector> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <cstring> extern "C" { #include "mylua/lua.h" #include "mylua/lauxlib.h" #include "mylua/lualib.h" } class LuaC { public: LuaC() { d_avr = 0.0; d_sum = 0; } void ComAvrSum(const std::vector<int>& vec); void print() { std::cout << "avr = " << d_avr << std::endl; std::cout << "sum = " << d_sum << std::endl; } double getAvr() { return d_avr; } double getSum() { return d_sum; } private: double d_avr; int d_sum; }; #endif ///< _LUA_C_HH_
//lua_c.cc #include "lua_c.hh" lua_State* InitLua() { lua_State* L = lua_open(); /* opens Lua */ luaopen_base(L); /* opens the basic library */ luaopen_table(L); /* opens the table library */ luaopen_io(L); /* opens the I/O library */ luaopen_string(L); /* opens the string lib. */ luaopen_math(L); /* opens the math lib. */ return L; } static int foo(lua_State* L) { int n = lua_gettop(L); /* number of arguments */ lua_Number sum = 0; int i; for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (!lua_isnumber(L, i)) { lua_pushstring(L, "incorrect argument to function `average'"); lua_error(L); } sum += lua_tonumber(L, i); } lua_pushnumber(L, sum / n); /* first result */ lua_pushnumber(L, sum); /* second result */ return 2; /* number of results */ }; void LuaC::ComAvrSum(const std::vector<int>& vec) { lua_State* L = InitLua(); lua_register(L, "average", foo); ///< method 1: lua_register std::string buff = "avr, sum = average("; for (size_t i = 0; i < vec.size() - 1; ++ i) { buff += std::to_string(vec[i]) + ", "; } buff += std::to_string(vec[vec.size()-1]) + ")"; std::cout << "buff = " << buff << std::endl; int error; error = luaL_loadbuffer(L, buff.c_str(), strlen(buff.c_str()), "average") || lua_pcall(L, 0, 0, 0); ///< first load, and second call if (error) { fprintf(stderr, "%s", lua_tostring(L, -1)); lua_pop(L, 1); // pop error message from the stack } lua_getglobal(L, "avr"); d_avr = lua_tonumber(L, -1); lua_pop(L, 1); lua_getglobal(L, "sum"); d_sum = lua_tonumber(L, -1); lua_pop(L, 1); }
2.2 编写测试函数
// Test_Lua_C.cc
#include "gtest/gtest.h" #include "lua_c.hh" TEST(Lua_C, ComAvrSum) { LuaC aa; std::vector<int> vec; vec.push_back(33); aa.ComAvrSum(vec); aa.print(); EXPECT_EQ(33, aa.getSum()); EXPECT_EQ(33, aa.getAvr()); vec.push_back(33); aa.ComAvrSum(vec); aa.print(); EXPECT_EQ(66, aa.getSum()); EXPECT_EQ(33, aa.getAvr()); }
2.3 编译
g++ Test_Lua_C.cc lua_c.cc -I $LD_HOME/include -L $LD_HOME/lib -lgtest -lgtest_main -lpthread -llua -llualib -o app -std=c++11
running
[==========] Running 1 test from 1 test case. [----------] Global test environment set-up. [----------] 1 test from Lua_C [ RUN ] Lua_C.ComAvrSum buff = avr, sum = average(33) avr = 33 sum = 33 buff = avr, sum = average(33, 33) avr = 33 sum = 66 [ OK ] Lua_C.ComAvrSum (0 ms) [----------] 1 test from Lua_C (0 ms total) [----------] Global test environment tear-down [==========] 1 test from 1 test case ran. (0 ms total) [ PASSED ] 1 test.
Done !


