SQL语句入门
SQL语句入门
MySQL的连接管理
自带的连接工具
mysql
# mysql
-u :user指定MySQL的用户
-p :password指定mysql用户的密码
-S :socket指定主机ip地址
-h :host指定主机ip地址
-e:exec执行SQL语句
-P :port指定端口
--protocol=name :指定连接方式
mysqladmin
mysqldump
第三方连接工具(客户端)
Navicat
SQLmanager
SQLyog
MySQL启动关闭流程
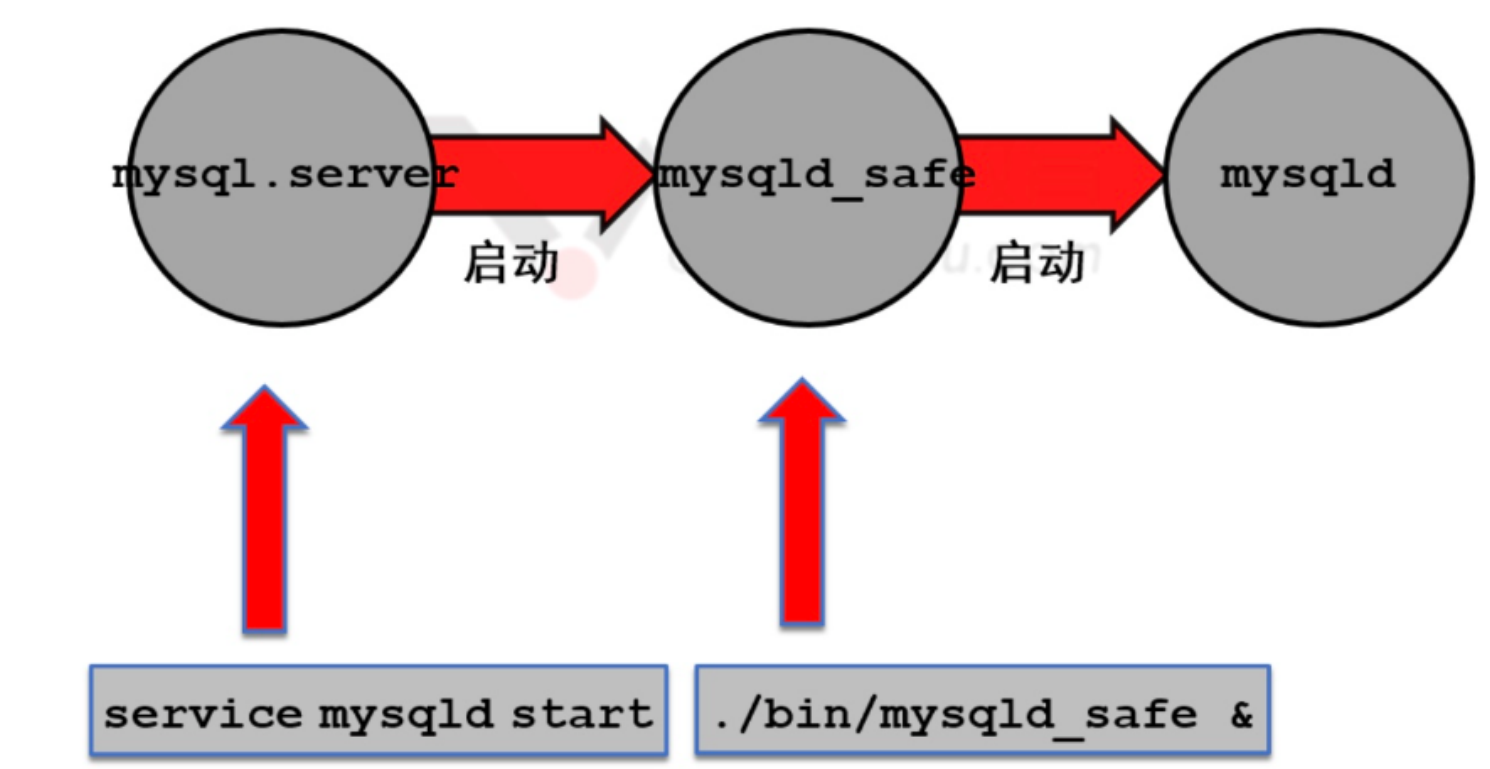
启动
/etc/init.d/mysqld start
systemctl start mysqld
mysqld_safe --选项
关闭
/etc/init.d/mysqld stop
systemctl stop mysqld
mysqladmin -uroot -s /data/3309/data/3309.sock shutdown
kill -9 pid ?
killall mysqld ?
pkill mysqld ?
MySQL实例初始化配置
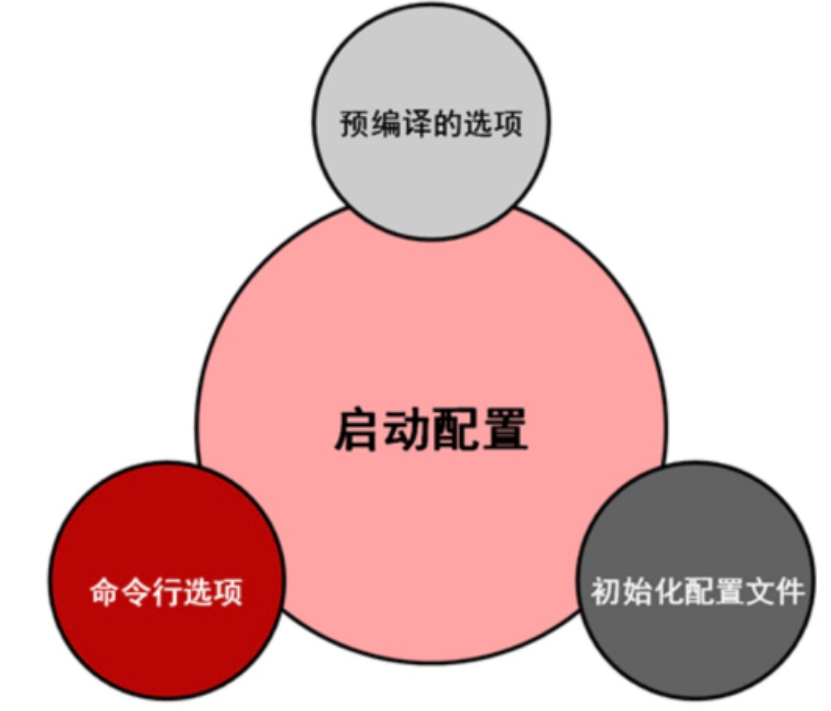
1.预编译
2.命令行
3.配置文件(读取顺序)
- /etc/my.cnf
- /etc/mysql/my.cnf
- $basedir/my.cnf
- --defaults-extra-file=/opt/my.cnf
- ~/.my.cnf
# 优先级
~/.my.cnf > --defaults-extra-Ũle=/opt/my.cnf > $basedir/my.cnf > /etc/mysql/my.cnf >
/etc/my.cnf
# 注意: 如果启动MySQL加了-defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf选项,其他位置的配置文件都不读取
# cmake:
socket=/application/mysql/tmp/mysql.sock
# 命令行
--socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
# 配置文件:
/etc/my.cnf中[mysql]标签:socket=/opt/mysql.sock
# default参数:
--defaults-file=/tmp/a.txt配置文件中[mysqld]标签下:socket=/tmp/test.sock
/application/mysql/tmp/mysql.sock
/tmp/mysql.sock
/opt/mysql.sock
/tmp/test.sock
mysqld --defaults-file=/tmp/a.txt --socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
/tmp/mysql.sock
# 结论
默认配置,优先级
1.命令行
2.配置文件
- ~/.my.cnf
- --defaults-extra-file=/opt/my.cnf
- $basedir/my.cnf
- /etc/mysql/my.cnf
- /etc/my.cnf
3.编译安装
初始化配置的作用
- 影响实例的启动 (mysqld)
- 影响到客户端的连接
[mysqld] [server] # 这两个标签下的配置,都是来影响服务端启动的
[mysql] [mysqladmin] [mysqldump] # 这几个标签影响对应的客户端命令
[client] # 这个标签,影响所有的客户端命令
注意:修改客户端配置,不需要重启mysql,修改服务端配置[mysqld] 需要重启mysql
[mysqld]
skip_name_resolve
basedir=/application/mysql
datadir=/application/mysql/data
server_id=10
socket=/opt/mysql.sock
[client]
user=root
password=abc
socket=/opt/mysql.sock
MySQL的SQL语句
客户端命令
mysql
# 查看命令帮助
? \? help \h
# 查看状态
staus \s
# 退出
exit quit \q
# 结束当前的SQL语句
\c
# ctrl + c
MySQL5.6中:退出MySQL
MySQL5.7中:结束当前SQL语句,类似于\c
# 在MySQL中执行系统命令
system \!
# 临时将操作纪律到指定的文件中
tee \T
tee /tmp/mysql.log
\T /tmp/mysql.log
# 切换数据库
use \u
sue mysql
\u mysql
# 导入数据
source \.
source /tmp/zh.sql
\. /tmp/zh.sql
# 格式化(key:value)方式,显示数据
\G
select * from mysql.user\G
# 客户端配置,显示当前所在数据库及登录用户
[client]
prompt="\u@\h:\d>"
mysqladmin
mysqladmin password '密码' # 修改密码或者设置密码
mysqladmin shutdown # 关闭mysql
mysqladmin ping # 检测mysql是否存活
mysqladmin status # 检查mysql的状态
mysqladmin variables # 查看mysql默认配置 (内置变量)
mysqladmin create 库名 # 在库外面删除数据库
mysqladmin reload # 重新舰载数据库
mysqladmin flush-log # 刷新授权表
# 注意: 有密码 -u -p
SQL层的SQL语句
什么是SQL语句
结构化的查询语句 标准:SQL-92
SQL语句的分类
- DDl
# DDL
Database Definition Language
数据 定义 语言
# 开发规范
1.表名不能大写,数字开头,16个字符串
2.表名和业务有关
3.drop 语句禁止
4.选择合适的数据类型
5.必须要有主键
6.列劲量非空约束
7.减少外键约束
8.必须设置存储引擎和字符集
9.列必须要有注释
10.对于非负数设置数据类型约束--无符号
## 库
# 增
语法:
Syntax:
CREATE {DATABASE | SCHEMA} [IF NOT EXISTS] db_name
[create_option] ...
create_option: [DEFAULT] {
CHARACTER SET [=] charset_name
| COLLATE [=] collation_name
}
create database 库名;
create schema 库名;
create database 库名 character set utf8;
create database 库名 charset utf8;
create database if not exists 库名 charset utf8;
collate utf8_bin;
# 删
drop database 库名;
# 改
修改字符集
alter database zh charset latin1;
## DQL查看数据库的字符集
mysql> show create database sb;
## 表
# 增
create table 表名(字段1 数据类型 约束,字段2 数据类型 约束)
建表,至少要给的是 字段名称和数据类型
create table sb.student(id int not null primary key auto_increment,name varchar(10),age tinyint,gender enum('0','1'));
# 数据类型
int: 整数 -2^31 ~ 2^31 -1
varchar: 字符串类型 (变长)
char:字符类型 (定长)
tinyint: 最小整数 -128 ~ 127
enum:枚举类型
enum('A','B','C','D')
datetime: 时间类型 年月日时分秒
# 约束
not null :非空
primary key: 主键(唯一且非空的) 一张表只能有一个主键
auto_increment: 自增 (此类必须是:primary key或者unique key)
unique key: 唯一键,单独的唯一键 + not null
default:默认值
unsigned:无符号(非负)
comment:注释
create table zls.student5(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '学号',
name varchar(10) not null comment '学生姓名',
age tinyint unsigned not null default 18 comment '学生年龄',
gender enum('0','1') not null default '1' comment '学生性别');
-
DML
增
Data Manipulation language 数据 操作 语言 所有的DML都是操作表内容的 # 插入单条数据库 insert into stu(name,gender,age,data,phone,bir,id) value('zh','f','255','2002-08-10','133',NOW(),1); # 插入多数数据 insert into stu(name,gender,age) value('zh','f',255,),('zh2','f',244); # 默认字段不加 insert into stu(name,bir,phone) value('liquanyi',NOW(),'138'); # 不规范写法 insert stuvalue(7,'liangkang',18,'m',NOW(),'139',NOW());删
# 使用delete删除一定要加条件 delete from student; # 不要这样删 # 加条件 delete from student where name='xxx'; # 全部删除 delete from student where 1=1; # 注意:一般在删除数据是,我们会根据唯一性的字段,进行删除改
# 使用update一定要加条件 update update student set id=3 where name='xxx'; 1.给表中,加一个状态列 alter table student add status enum('0','1') default '1'; 2.使用update删除数据 update student sed status='0' where name='zh'; 3.查询的时候,使用where条件查询 select * from student where ststus='1'; # 注意:update修改数据库用户的密码,要是flush private;修改其他数据,不需要 -
DCL
Database Control Language 数据 控制 语言 # 赋予权限 5.6和5.7区别: 5.7老版本:grant赋予权限,如果该用户不存在,则无法创建, 5.6和5.7新版本可以直接创建用户,5.6和5.7新版本可以直接创建用户 grant all on *.* to test@'%' identified by '123'; grant 权限,权限 on 库.表 to 用户@'主机域' identified by '密码'; max_queries_per_hour 3 ## 限制该用户一小时内,只能查询3次 max_updates_per_hour 1 ## 限制用户一小时,只能执行一次update max_connections_per_hour 1 # 限制用户,一小时内只能连接一次数据库 max_user_connections 1 ## 限制用户,只能同时一个用户连接 grant option; # 回收权限 revoke revoke 权限 on 库.表 from 用户@'主机域'; revoke delete on *.* from zh@'%'; -
DQL
Database Query Language 数据 查询 语言 # show show database; # 查看数据库 show tables; # 查看表 show tables from sb; # 查看数据库下的表,不用切换数据库 show create database 库名; # 查看建表语句,也是为了查看注释 show create table 库名.表名; # 查看建表语句,也是为了查看注释(不用切换数据库) show grants for 用户名@'主机域'; # 查看授权语句,也是为了查看用户的权限 show variables; # 查看所有内置变量(默认配置) show variables like '%server%'; # 模糊查询(过滤) show variables like '%server'; # 模糊查询 show processlist; # 查看后台执行的sql语句 show full processlist; # 查看完整的后台执行的sql语句 show collation; # 查看所有校验规则 show charset; # 查看所有字符集以及该字符集默认校验规则 # desc desc 库.表 # 查看表结构 查看执行计划 # select wget http://test.driverzeng.com/MySQL_File/world.sql source /root/world.sql # select 常用简单查询 select * from city; # 查看该表中所有的字段的记录(所有数据) select id,name from city; # 查看指定字段的所有记录 # select 行级查询(翻页功能) select id,name from city limit 10; select id,name from city limit 180,60; # 翻页功能,从181开始查60个 # select 条件查询 select * from city where countrycode='CHN'; select * from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA'; select * from city where countrycode='CHN' and distryct='jiangxi' # 条件查询结合行级查询 select * from city where countrycode='CHN' and district='jiangxi' limit 10; # select 模糊查询 select * from city where countrycode like '%H' or countrycode='JPN'; # select 排序查询 order by select * from where countrycode='CHN' order by population; # 顺序排序 select * from where countrycode='CHN' order by population desc; # 倒叙排序 select * from city order by population; # 不加条件 顺序排序 select * from city order by population desc; # 不加条件倒序排序 # select 范围查询 select * from city where population > 10000; > < >= <= <> != # in select * from city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA'); # or select * from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA'; # union all 联合查询 select * from city where countrycode='CNH' union all select * from city where countrycode='USA'; # select 分组查询 group by group by + 聚合函数 聚合函数 max(): 最大值 min():最小值 sum():求和 avg():求平均数 count():统计 1.遇到统计想函数 2.形容词前group by 3.函数中央是名词 4.列名select后添加 # 统计世界上每个国家的总人口 select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode; # 统计中国各个省的人口数 select district,sum(population) from city where countrycode='CHN' group by district; # 同级每个国家的城市数量 select countrycode,count(name) from city group by countrycode;slesct高级用法
传统连接
# 传统连接 链表查询的前提是:两张表必须要有关联的字段 # 世界上小于100人的人口城市是哪个国家的 select country.name as '国家',city.name as '城市',city.population as '城市人口数' from city,country where city.countrycode=country.code and city.population < 100; +----------+-----------+------------+ | 国家 | 城市 | 城市人口数 | +----------+-----------+------------+ | Pitcairn | Adamstown | 42 | +----------+-----------+------------+ # 世界上大于100000000人口数量的尝试在哪个城市,说什么语言? select country.name as 国家,city.name as 城市名,city.population as 人口数量, countrylanguage.countrycode from city,country,countrylanguage where city.countrycode=country.code and country.code=countrylanguage.countrycode and city.population > 10000000;自连接
# 自连接 natural join 自动找到等价条件,前提:两张表的等价条件字段名必须一样 city 国家代码:countrycode country 国家代码:code countrylanguage 国家代码:countrycode # 说english的城市有哪些,他们的国家代码是什么? select city.name,city.countrycode,countrylanguage.language,city.population from city natural join countrylanguage where countrylanguage.language='english'; # 每个国家有几种城市说英语,他们的国家代码是什么? select city.countrycode,countrylanguage.language,count(city.name) from city natural join countrylanguage where countrylanguage.language='english' group by countrycode; # 每个国家有几种城市说英语,他们的国家代码是什么?按城市数量排序 select city.countrycode,countrylanguage.language,count(city.name) from city natural join countrylanguage where countrylanguage.language='english' group by countrycode order by count(city.name);内连接(join on)
select 字段1,字段2,字段3 from 表1 jion 表2 on 等价条件 where 自己的条件; # 每个国家有几个城市说英语,他们的国家代码是什么? select city.countrycode as '国家代码',count(city.name) as '城市数量',countrylanguage.language as '语言' from city join countrylanguage on city.countrycode=countrylanguage.countrycode where countrylanguage.language='english' group by city.countrycode; # 世界上大于100000000人口数量的城市在那个国家,说什么语言? 表1 jion 表2 on 等价条件A jion 表3 on 等价条件B select country.name as 国家,city.population as 人口数量,countrylanguage.language as 语言 from country join city on country.code=city.countrycode join countrylanguage on country.code=countrylanguage.countrycode where city.population > 10000000; join on # 注意:大表在前,小表在后外连接
# 左外连接 left join select city.name,city.countrycode,country.name from city left join country on city.countrycode=country.code and city.population<100; # 右连接 right join select city.name,city.countrycode,country.name from city right join country on city.countrycode=country.code and city.population<100;
连接查询
#范围查询OR语句
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA';
#范围查询IN语句
select * from city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA');
#替换为
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' union all select * from city where countrycode='USA';
union:去重合并
union all:不去重
使用情况: union<union all
视图:view
触发器:trigger
字符集设置
操作系统设置字符集
# centos6
[root@db03 ~]# source /etc/sysconfig/i18n
[root@db03 ~]# echo $LANG
en_US.UTF-8
# centos7
[root@db03 ~]# vim /etc/locale.conf
LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
[root@db03 ~]# echo $LANG
en_US.UTF-8
作业
mysql> create table sb.student3( id int primary key auto_increment comment '学号',name varchar(10) not null comment '姓名', age tinyint unsigned not null default 18 comment '年龄',gender enum('0','1') not null default '1' comment '性别', bir date not null comment '出生日期',cometime datetime not null comment '到校时间');
+----------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | 18 | |
| gender | enum('0','1') | NO | | 1 | |
| bir | date | NO | | NULL | |
| cometime | datetime | NO | | NULL | |
+----------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
作业2
# linux50 字符集:utf8 校验规则:utf8_general_ci
create database if not exists linux50 charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
# 创建表名:student(学生表)
mysql> create table student(sno int not null primary key comment '学号', sname varchar(10) not null comment '学生姓名', sage tinyint unsigned not null comment '学生年龄', ssex enum('0','1') not null default '1' comment '学生性别', sbirthday datetime comment '学生生日', class varchar(10) not null comment '学生班级');
# 将自己班级小组所有人员信息插入到student表中(数据自定义)
mysql> insert into student(sno,sname,sage,ssex,sbirthday,class) value(1,'周恒',18,'1',NOW(),'2期'),(2,'计磊',99,'0',NOW(),'2期'),(3,'王成',99,'0',NOW(),'2期'),(4,'罗伟',99,'0',NOW(),'2期');
# 创建表名:course(课程表)
create table course(cno int(20) not null primary key comment '课程号',
cname varchar(10) not null comment '课程名称',
ton varchar(10) not null comment '教师编号');
# 将数学、语文、英语学科插入到课程表中(数据自定义)
insert into course(cno,cname,ton) value(1,'英语','001'),(2,'语文','002'),(3,'数学','003');
# 创建表名:score(成绩表)
create table score(
sno int(20) not null comment '学号',
cno int(20) not null comment '课程号',
mark float(4,1) not null comment '成绩');
# .将分数插入到成绩表中(数据自定义)
insert into score(sno,cno,mark) value(1,'1','100.0'),(1,'2','100.0'),(3,'1','10.0');
# 创建表名:teacher(教师表)
create table teacher(
tno int(20) not null primary key comment '教师编号',
tname varchar(10) not null comment '老师姓名',
tage tinyint unsigned not null comment '老师年龄',
tsex enum('0','1') not null default '1' comment '老师性别',
prof varchar(10) comment '老师职称',
depart varchar(10) not null comment '老师部门');
# .将曾导、徐导、李导信息插入教师表中(数据自定义)
insert into teacher(tno,tname,tage,tsex,prof,depart) value(001,'曾志高翔',18,'1','教学总监','语言系'),(002,'徐亮伟',50,'1','讲师','文学系'),(003,'李永宜',80,'1','助教','科学系');
作业3
#1.查询student表中的所有记录的sname、ssex和class列
mysql> select sname,ssex,class from student;
#2.查询教师所有的单位即不重复的depart列。
mysql> select distinct depart from teacher;
#3.查询student表的所有记录
mysql> select * from student;
#4.查询score表中成绩在60到80之间的所有记录。
mysql> select * from score where mark <= 80 and mark >= 60;
#5.查询score表中成绩为85,86或88的记录。
mysql> select * from score where mark=85 or mark=86 or mark=88;
#6.查询student表中1班或性别为“女”的同学记录
mysql> select * from student where ssex='0' or class='1';
#7.以class降序查询Student表的所有记录。
mysql> select * from student order by class desc;
#8.以cno升序、mark降序查询Score表的所有记录
mysql> select * from score order by mark desc,cno;
#9.查询2班的学生人数
mysql> select class,count(sname) from student where class='2期' group by class;
#10.查询”曾志高翔“教师任课的学生成绩。
select student.sname,score.mark
from student natural join score
where score.cno='1';
#11.查询语文课程所有男生的成绩并且查出对应课程的教师名,职称,及所在部门。
select course.cname,student.sname,score.mark,teacher.tname,teacher.prof,teacher.depart from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno join teacher on teacher.tno=course.ton where course.cno=2;
#12.把11题查出的成绩按照降序排序。
select course.cname,student.sname,score.mark,teacher.tname,teacher.prof,teacher.depart from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno join teacher on teacher.tno=course.ton where course.cno=2 order by score.mark desc;





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!