狂神说笔记——CSS3快速入门10
CSS3快速入门
1.什么是CSS
1.什么是CSS
- Cascading Style Sheet 层叠样式表。
- CSS:表现(美化网页)。
- 字体,颜色,边距,高度,宽度,背景图片,网页定位,网页浮动。
2.CSS发展史
- CSS 1.0:1994年 10月提出;
- CSS 2.0:DIV(块)+CSS,HTML与CSS结构分离的思想,网页变得简单,SEO;
- CSS 2.1:浮动,定位;
- CSS 3.0:圆角、阴影、动画…浏览器兼容性。
3.快速入门

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>CSS3快速入门</title>
<!-- 规范:<style>可以编写CSS的代码,每一个声明最好以“;”结尾
语法:
选择器{
声明1;
声明2;
声明3;
}
-->
<style>
h1{
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS3测试</h1>
</body>
</html>
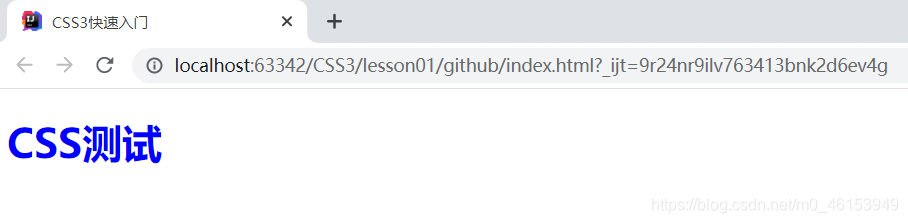
- 建议使用这种规范(单独写一个css文件,用link标签引入css文件效果) 。


CSS的优势:
- 内容和表现分离;
- 网页结构表现统一,可以实现复用;
- 样式十分的丰富;
- 建议使用独立于html的css文件;
- 利用SEO,容易被搜索引擎收录!
CSS的3种常用导入方式。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>CSS3快速入门</title>
<!--外部样式-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
<style>
<!--内部样式-->
h1{
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--优先级:就近原则——行内样式 > 内部样式 > 外部样式-->
<!--行内样式:在标签元素中,编写一个style属性,编写样式即可-->
<h1 style="color: aquamarine">CSS3测试</h1>
</body>
</html>
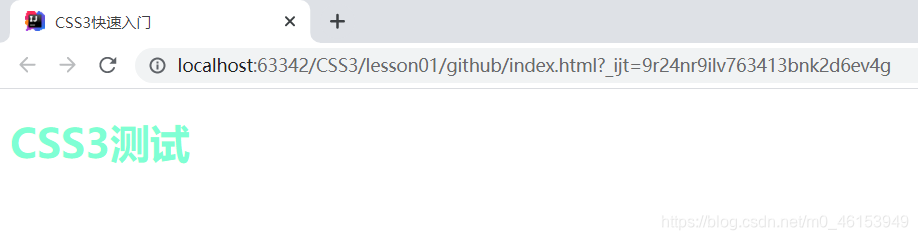
-
拓展:外部样式两种方法。
-
链接式——HTML
<!--外部样式--> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"> -
导入式—— @import是CSS2.1特有的!
<!--导入式--> <style> @import url("css/style.css"); </style>
-
2.CSS选择器
- 作用:选择页面上的某一个后者某一类元素。
1.基本选择器
- 标签选择器——选择一类标签。
- 格式:标签名{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>标签</title>
<style>
h1{
color: orange;
background: beige;
border-radius: 10px;
}
h3{
color: aquamarine;
background: chocolate;
border-radius: 10px;
}
p{
font-size: 80px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>标签选择器</h1>
<p>Android</p>
<h3>前端-CSS3</h3>
</body>
</html>
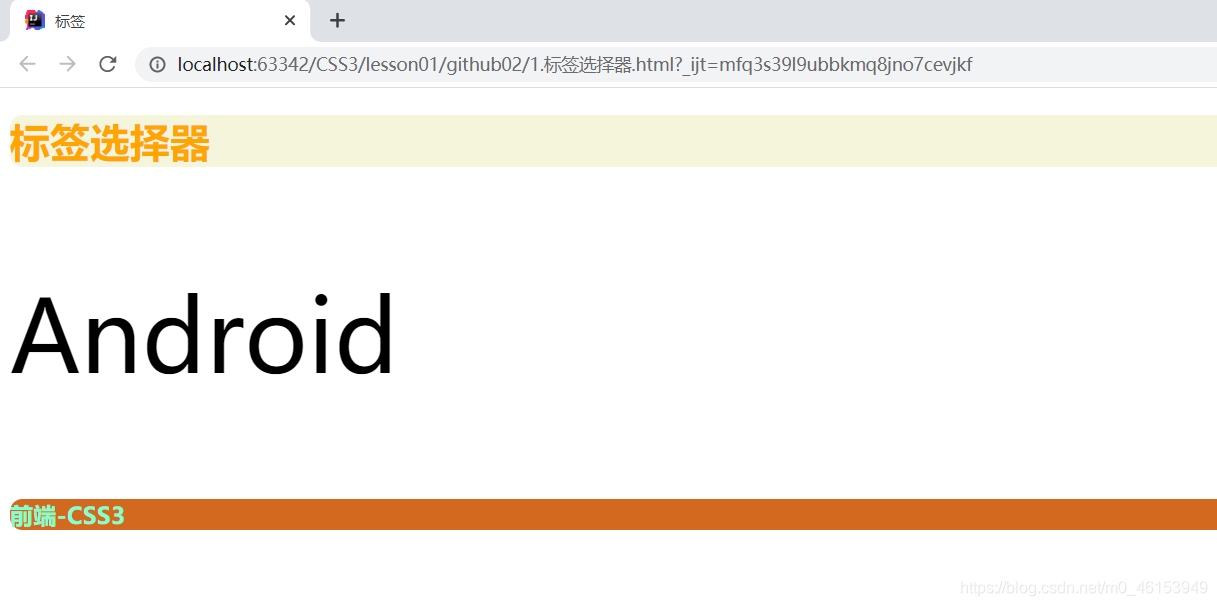
- 类选择器class——选择所有class一致的标签,跨标签。
- 格式:.类名{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>类选择器</title>
<style>
/*
类选择器的格式: .class的名称{}
好处:可以多个标签归类,是同一个class,可以复用!
*/
.test01{
color: darkorange;
}
.test02{
color: cadetblue;
}
.test03{
color: cornflowerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="test01">类选择器:Test01</h1>
<h1 class="test02">类选择器:Test02</h1>
<h1 class="test03">类选择器:Test03</h1>
<p class="test03">类选择器:Test04</p>
</body>
</html>

- id选择器——全局唯一
- 格式:#id名{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*
id选择器: id必须保证全局唯一
#id名称{}
不遵循就近原则,优先级是固定的
id选择器 > class类选择器 > 标签选择器
*/
#git02{
color: darkorange;
}
#git03{
color: cadetblue;
}
#git01{
color: cornflowerblue;
}
h1{
color: darkseagreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="git01" class="git02">id选择器:git01</h1>
<h1 id="git02" class="git02">id选择器:git02</h1>
<h1 class="git03">id选择器:git03</h1>
<h1 id="git03" class="git01">id选择器:git01</h1>
<h1>id选择器:git03</h1>
</body>
</html>
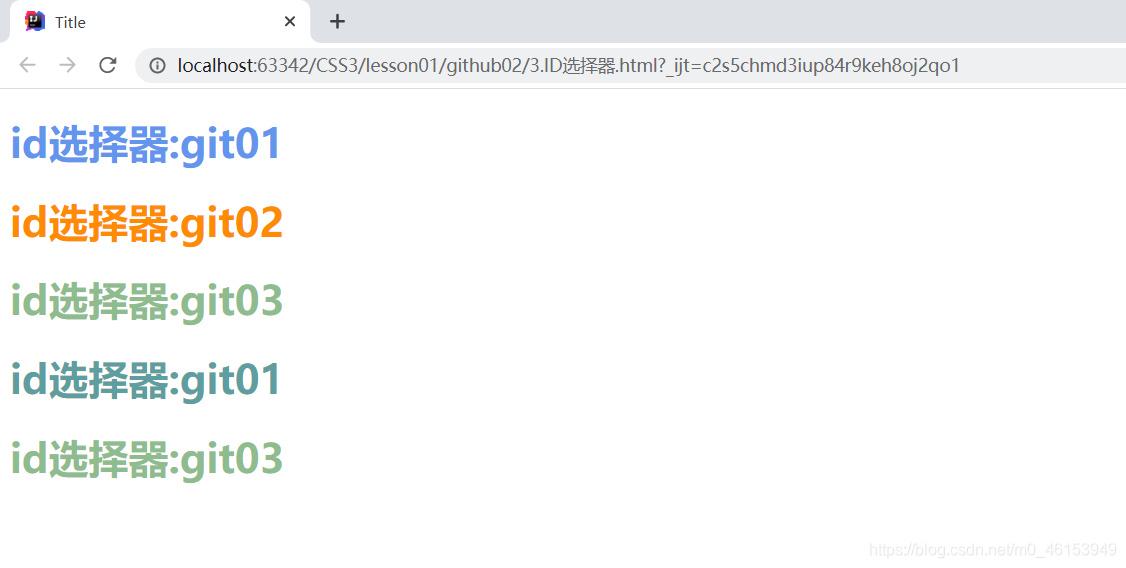
- 优先级:id > class > 标签。
2.层次选择器
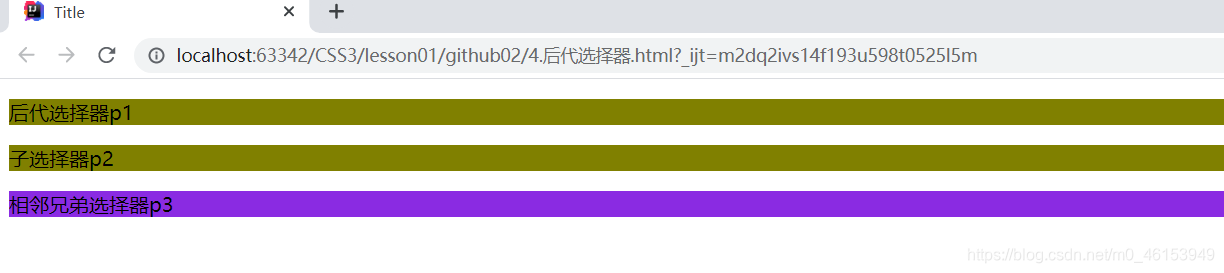
- 后代选择器:在某个元素的后面。
- 子选择器:一代。
- 相邻的兄弟选择器:同辈。
- 通用选择器。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*
后代选择器
*/
body p{
background: deeppink;
}
/*
子选择器
*/
body>p{
background: olive;
}
/*
相邻兄弟选择器:只选择一个,相邻向下
*/
.active+p{
background: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>后代选择器p1</p>
<p class="active">子选择器p2</p>
<p>相邻兄弟选择器p3</p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*
后代选择器
*/
body p{
background: deeppink;
}
/*
子选择器
*/
/*body>p{*/
/* background: olive;*/
/*}*/
/*
相邻兄弟选择器:只选择一个,相邻向下
*/
.active+p{
background: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>后代选择器p1</p>
<p class="active">子选择器p2</p>
<p>相邻兄弟选择器p3</p>
</body>
</html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*
后代选择器
*/
body p{
background: deeppink;
}
/*
子选择器
*/
/*body>p{*/
/* background: olive;*/
/*}*/
/*
相邻兄弟选择器:只选择一个,相邻向下
*/
.active+p{
background: blueviolet;
}
/*
通用兄弟选择器,当前选中元素的向下的所有兄弟元素
*/
.active2~p{
background: dodgerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>后代选择器p1</p>
<p class="active">子选择器p2</p>
<p>相邻兄弟选择器p3</p>
<p class="active2">通用兄弟选择器p4</p>
<p>通用兄弟选择器p5</p>
</body>
</html>

3.结构伪类选择器
- 伪类
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪类选择器</title>
<style>
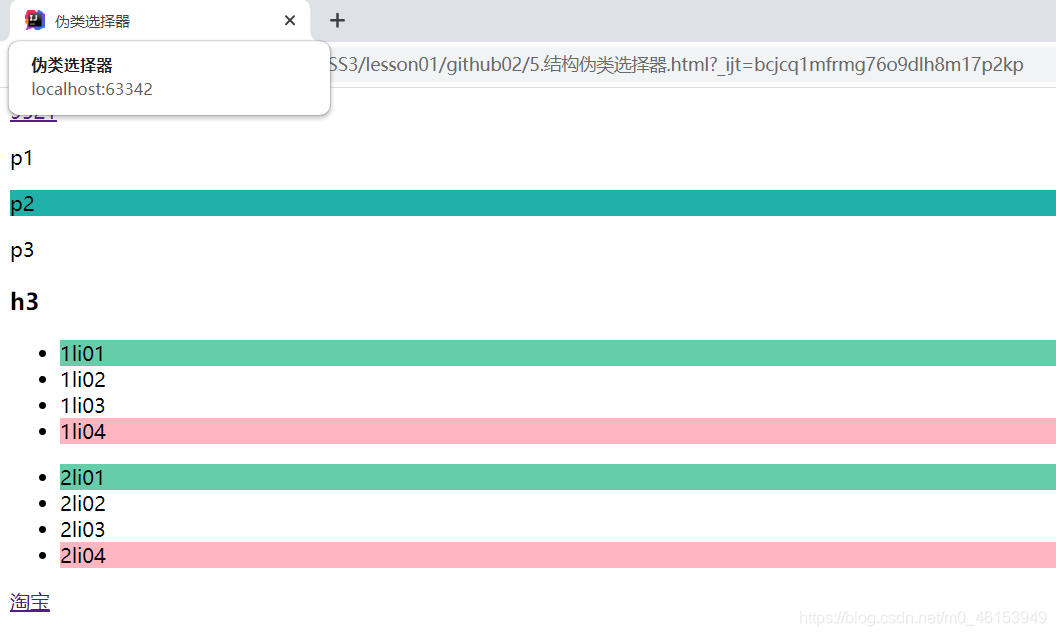
ul li:first-child{
/*
ul的第一个子元素
*/
background: mediumaquamarine;
}
ul li:last-child{
/*
ul的最后一个子元素
*/
background: lightpink;
}
/*
选中p1:定位到父元素,选择当前的第一个元素
选择当前P元素的父级元素,选中父级元素的第一个,并且是当前元素才生效!
*/
p:nth-child(1){
background: greenyellow;
}
p:nth-of-type(2){
/*
选中父元素下的第二个p元素
*/
background: lightseagreen;
}
a:hover{
color: royalblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="">9521</a>
<p>p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<h3>h3</h3>
<ul>
<li>1li01</li>
<li>1li02</li>
<li>1li03</li>
<li>1li04</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li>2li01</li>
<li>2li02</li>
<li>2li03</li>
<li>2li04</li>
</ul>
<a href="https://www.taobao.com/">淘宝</a>
</body>
</html>
4.属性选择器(常用)
- id + class 结合
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性选择器</title>
<style>
.demo a{
float: left;
display: block;
height: 50px;
width: 50px;
border-radius: 10px;
background: aquamarine;
text-align: center;
color: gray;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 5px;
line-height:50px;
font: bold 20px/50px Arial;
}
/*
属性名,属性名 = 属性值(正则)
= 表示绝对等于
*= 表示包含
^= 表示以...开头
$= 表示以...结尾
存在id属性的元素
a[]{}
*/
a[id]{
background: deeppink;
}
a[id=first]{
/*
id=first的元素
*/
background: greenyellow;
}
a[class*="links"]{
/*
class 中有links的元素
*/
background: green;
}
a[href^=http]{
/*
选中href中以http开头的元素
*/
background: aquamarine;
}
a[href$=pdf]{
/*
选中href中以http开头的元素
*/
background: aquamarine;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="demo">
<a href="https://www.taobao.com/" class="links item first" id="first">淘宝</a>
<a href="" class="links item active" target="_blank " title="test">链接</a>
<a href="img/hello.html" class="links item">网页</a>
<a href="img/str1.png" class="links item">png</a>
<a href="img/str2.jpg" class="links item">jpg</a>
<a href="abc" class="links item">链2</a>
<a href="/fy.pdf" class="links item">pdf</a>
<a href="/quit.pdf" class="links item">pdf2</a>
<a href="dump.doc" class="links item">doc</a>
<a href="kiko.doc" class="links item last">doc2</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>

3.美化网页
1.为什么要美化网页
- 有效的传递页面信息
- 美化网页,页面漂亮才能吸引客户
- 凸显页面的主题
- 提高用户的体验
span标签:重点要突出的字,使用span标签套起来
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>美化网页</title>
<style>
#title{
font-size: 25px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
编程语言:<span id="title">Java</span>
</body>
</html>

2.字体样式
- font-family:字体
- font-size:字体大小
- font-weight:字体粗细
- color:字体颜色
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
font-family: "Arial Black";
color: dodgerblue;
}
h1{
font-size: 25px;
}
.p1{
font-weight: 600;
color: chocolate;
}
</style>
</head>
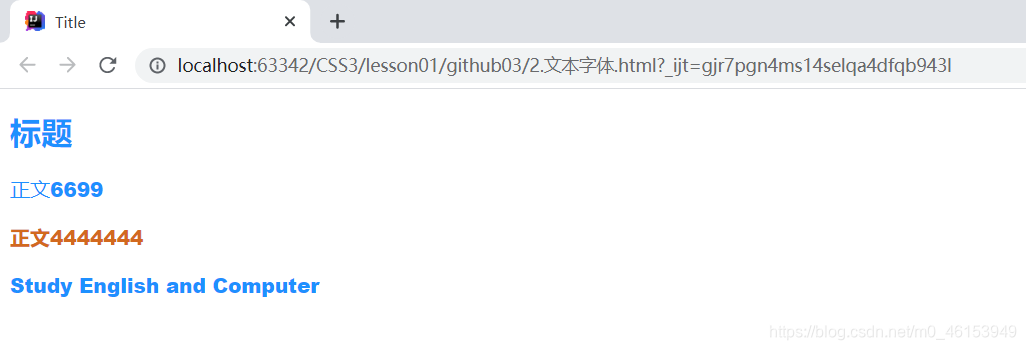
<body>
<h1>标题</h1>
<p>正文6699</p>
<p class="p1">正文4444444</p>
<p>Study English and Computer</p>
</body>
</html>
- 常用写法。
/* 也可以填px,但不能超过900,相当于bloder */
font-weight:bolder;
/*常用写法:*/
font:oblique bloder 12px "楷体"
3.文本样式
- 颜色–>color:agb / rgba()
- 文本对齐方式–>text-align:center;
- 首行缩进–>text-indent:2em;
- 行高–>line-height:300px;
- 下划线–>text-decoration;
/*下划线*/
text-decoration:underline
/*中划线*/
text-decoration:line-through
/*上划线*/
text-decoration:overline
/*超链接去下划线*/
text-decoration:none
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
h1{
color: rgba(0,255,255,0.9);
text-align: center;
}
.p1{
text-indent:2em;
}
.p3{
line-height:300px;
background: mediumaquamarine;
height: 300px;
}
/*下划线*/
.l1{
text-decoration: underline;
}
/*中划线*/
.l2{
text-decoration: line-through;
}
/*上划线*/
.l3{
text-decoration: overline;
}
/*超链接去下划线*/
a{
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
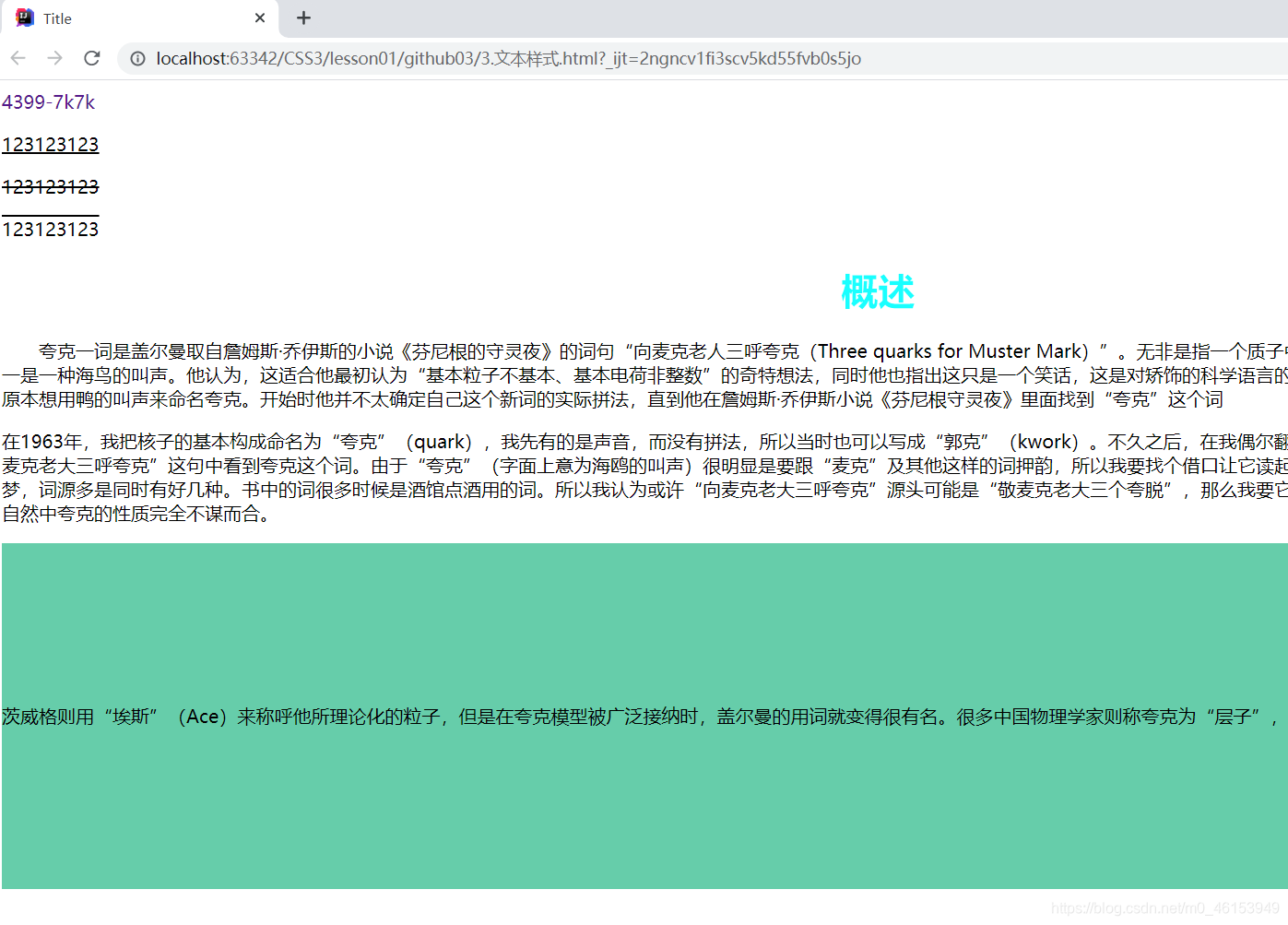
<body>
<a href="">4399-7k7k</a>
<p class="l1">123123123</p>
<p class="l2">123123123</p>
<p class="l3">123123123</p>
<h1>概述</h1>
<p class="p1">
夸克一词是盖尔曼取自詹姆斯·乔伊斯的小说《芬尼根的守灵夜》的词句“向麦克老人三呼夸克(Three quarks for Muster Mark)”。无非是指一个质子中有三个夸克。另外夸克在该书中具有多种含义,其
中之一是一种海鸟的叫声。他认为,这适合他最初认为“基本粒子不基本、基本电荷非整数”的奇特想法,同时他也指出这只是一个笑话,这是对矫饰的科学语言的反抗。另外,也可能是出于他对鸟类的喜爱。 [7]
盖尔曼原本想用鸭的叫声来命名夸克。开始时他并不太确定自己这个新词的实际拼法,直到他在詹姆斯·乔伊斯小说《芬尼根守灵夜》里面找到“夸克”这个词
</p>
<p>
在1963年,我把核子的基本构成命名为“夸克”(quark),我先有的是声音,而没有拼法,所以当时也可以写成“郭克”(kwork)。不久之后,在我偶尔翻阅詹姆斯·乔伊斯所著的《芬尼根守灵夜》时,我在“向麦克老大三呼夸克”这句中看到夸克这个词。由于“夸克”(字面上意为海鸥的叫声)很明显是要跟“麦克”及其他这样的词押韵,所以我要找个借口让它读起来像“郭克”。但是书中代表的是酒馆老板伊厄威克的梦,词源多是同时有好几种。书中的词很多时候是酒馆点酒用的词。所以我认为或许“向麦克老大三呼夸克”源头可能是“敬麦克老大三个夸脱”,那么我要它读“郭克”也不是完全没根据。再怎么样,字句里的三跟自然中夸克的性质完全不谋而合。
</p>
<p class="p3">
茨威格则用“埃斯”(Ace)来称呼他所理论化的粒子,但是在夸克模型被广泛接纳时,盖尔曼的用词就变得很有名。很多中国物理学家则称夸克为“层子”,在台湾地区亦曾翻译“亏子”,但并不普遍使用。
</p>
</body>
</html>
- 图片、文字水平对齐。
img,span{
vertical-align: middle;
}
4.文本阴影和超链接伪类
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*超链接有默认的颜色*/
a{
text-decoration: hotpink;
color: #000000;
}
/*鼠标悬浮的状态*/
a:hover{
color: dodgerblue;
}
/*鼠标按住未释放的状态*/
a:active{
color:green
}
/*点击之后的状态*/
a:visited{
color:mediumpurple;
}
/*
text-shadow:5px 5px 5px 颜色
第一个参数:表示水平偏移
第二个参数:表示垂直偏移
第三个参数:表示模糊半径
第四个参数:表示颜色
*/
#price{
text-shadow: #eaff29 5px 5px 5px;
}
/*固定阴影*/
a:link{
background: bisque;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#">
<img src="img/harf.jpg" width="400" height="200" alt="">
</a>
<p>
<a href="#">Java博客</a>
</p>
<p id="price">
<a href="#">哇哈哈</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>

5.列表ul、li
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link href="css/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="nav">
<h2 class="title">全部商品分类</h2>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="#">图书</a>
<a href="#">影视</a>
<a href="#">家电</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">配件</a>
<a href="#">手机</a>
<a href="#">数码</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">电脑</a>
<a href="#">办公</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">家居</a>
<a href="#">家装</a>
<a href="#">厨具</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">服饰鞋帽</a>
<a href="#">个性化妆</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">礼品箱包</a>
<a href="#">钟表</a>
<a href="#">珠宝</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">食品饮料</a>
<a href="#">保健食品</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">彩票</a>
<a href="#">旅行</a>
<a href="#">充值</a>
<a href="#">票务</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- CSS规则。
#nav{
width: 300px;
background: beige;
}
.title{
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
text-indent: 2em;/*缩进*/
line-height: 35px;
background: gold;
}
/*ul li*/
/*
list-style:
non 去掉实心圆
circle 空心圆
square 正方形
*/
/*nav替换效果*/
/*ul{
background: antiquewhite;
}*/
ul li{
height: 30px;
list-style: none;
text-indent: 1em;
}
a{
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 14px;
color: darkorange;
}
a:hover{
color: dodgerblue;
text-decoration: underline;
}

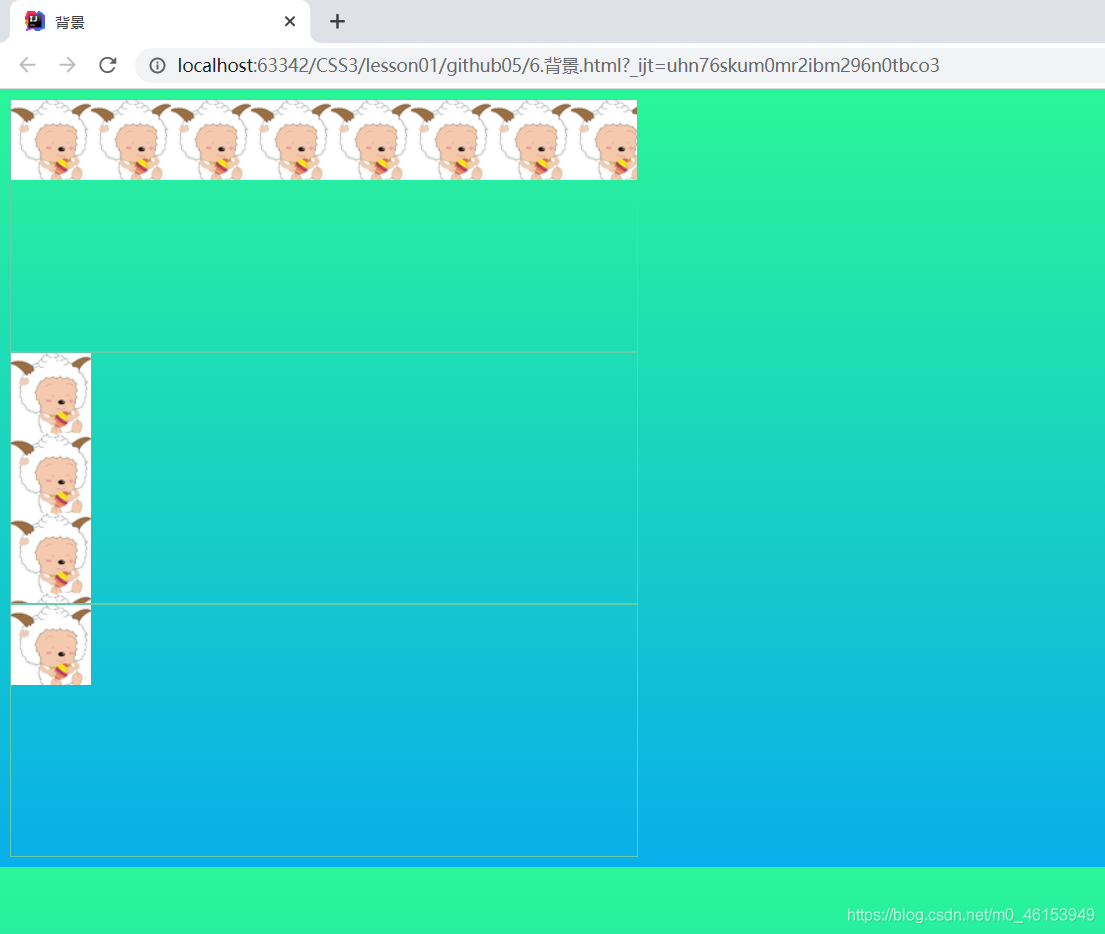
6.背景
-
背景颜色:background
-
背景图片。
background-image:url(""); /* 默认是全部平铺的 */ background-repeat:repeat-x; /* 水平平铺 */ background-repeat:repeat-y; /* 垂直平铺 */ background-repeat:no-repeat; /* 不平铺 */
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>背景</title>
<style>
div{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid mediumaquamarine;
background-image: url("img/str.png");
/* 默认是全部平铺的 */
}
/*水平平铺*/
.div1{
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
/*垂直平铺*/
.div2{
background-repeat: repeat-y;
}
/*不平铺*/
.div3{
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</body>
</html>

7.渐变
- 渐变背景网址:https://www.grabient.com
- 径向渐变、圆形渐变。
body{
background-color: #0cd7f3;
background-image: linear-gradient(43deg, #0093E9 0%, #80D0C7 46%, #23F549 100%);
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>背景</title>
<style>
body{
background-color: #08AEEA;
background-image: linear-gradient(0deg, #08AEEA 0%, #2AF598 100%);
}
div{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid mediumaquamarine;
background-image: url("img/str.png");
/* 默认是全部平铺的 */
}
/*水平平铺*/
.div1{
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
/*垂直平铺*/
.div2{
background-repeat: repeat-y;
}
/*不平铺*/
.div3{
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</body>
</html>
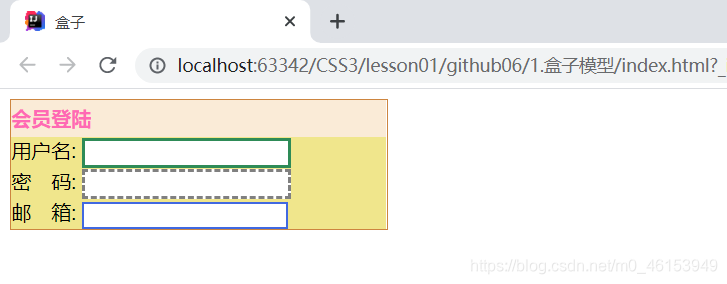
4.盒子模型
1.什么是盒子模型

- margin:外边距;
- padding:内边框;
- border:边框;
2.边框
-
border:粗细 样式 颜色
- 边框的粗细;
- 边框的样式;
- 边框的颜色。
-
html空格代码
名称 描述   ; 不断行的空白(1个字符宽度) &ensp ; 半个空白(1字符宽度) &emsp ; 一个空白(2个字符宽度) &thinsp ; 窄空白(小于1个字符宽度)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>盒子</title>
<style>
/*body总有一个默认的外边距为0*/
/*h1,ul,li,a,body{*/
/* margin: 0;*/
/* padding: 0;*/
/* text-decoration: none;*/
/*}*/
/*border:粗细 样式 颜色*/
#box{
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid peru;
}
h2{
font-size: 16px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
line-height: 30px;
margin: 0;
color: hotpink;
}
form{
background: khaki;
}
div:nth-of-type(1) input{
border: 3px solid seagreen;
}
div:nth-of-type(2) input{
border: 3px dashed gray;
}
div:nth-of-type(3) input{
border: 2px solid royalblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<h2>会员登陆</h2>
<form action="#">
<div>
<span>用户名:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>密 码:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>邮 箱:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
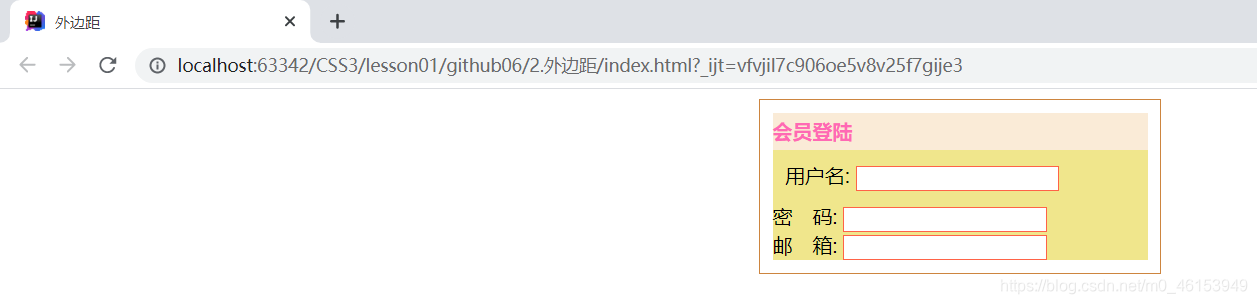
3.外边距
- margin-left/right/top/bottom–>表示四边,可分别设置,也可以同时设置如下 .
/* 分别表示上、右、下、左;从上开始顺时针 */
margin:0 0 0 0
/* 例1: 居中 auto表示左右自动 */
margin:0 auto
/* 例2:表示上、右、下、左都为4px */
margin:4px
/* 例3: 表示上为10px,左右为20px,下为30px */
margin:10px 20px 30px
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>外边距</title>
<style>
#box{
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid peru;
margin: 0 auto;
}
h2{
font-size: 16px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
line-height: 30px;
margin: 0;
color: hotpink;
}
form{
background: khaki;
}
input{
border: 1px solid tomato;
}
div:nth-of-type(1){
padding: 10px; /* 内边距10px */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<h2>会员登陆</h2>
<form action="#">
<div>
<span>用户名:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>密 码:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>邮 箱:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- 盒子的计算方式:
- margin+border+padding+内容的大小。
- 总结:
- body总有一个默认的外边距 margin:0
- 常见操作:初始化。
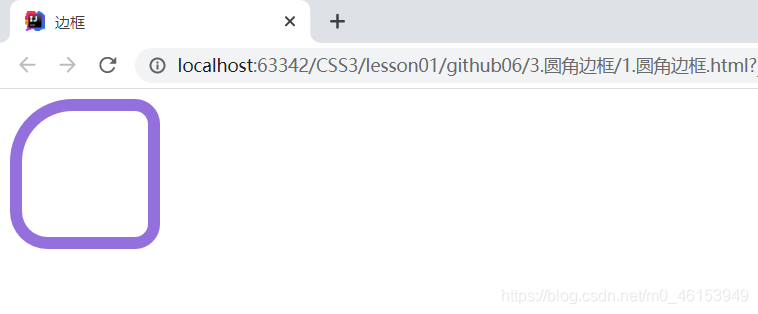
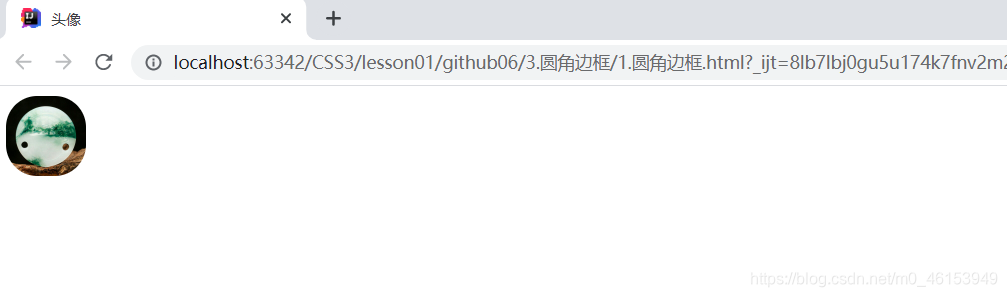
4.圆角边框
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>边框</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 10px solid mediumpurple;
/* 一个border-radius只管一个圆的1/4 */
border-radius: 50px 20px 20px 30px;
/* 左上 右上 右下 左下 ,顺时针方向 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>头像</title>
<style>
img{
border-radius: 25px; /*圆角矩形25px*/
width: 64px;
height: 64px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="img/pot.jpg" alt="#">
</body>
</html>
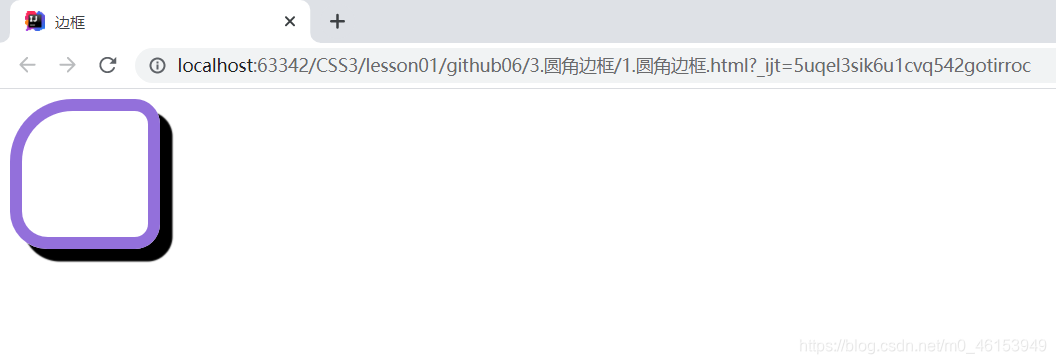
5.盒子阴影
box-shodow:10px 10px 1px black;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>边框</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 10px solid mediumpurple;
/* 一个border-radius只管一个圆的1/4 */
border-radius: 50px 20px 20px 30px;
/* 左上 右上 右下 左下 ,顺时针方向 */
}
#box{
box-shadow: 10px 10px 1px black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box"></div>
</body>
</html>
5.浮动
1.标准文档流

- 块级元素:独占一行
h1~h6 、p、div、 列表…
- 行内元素:不独占一行
span、a、img、strong
- 注: 行内元素可以包含在块级元素中,反之则不可以。
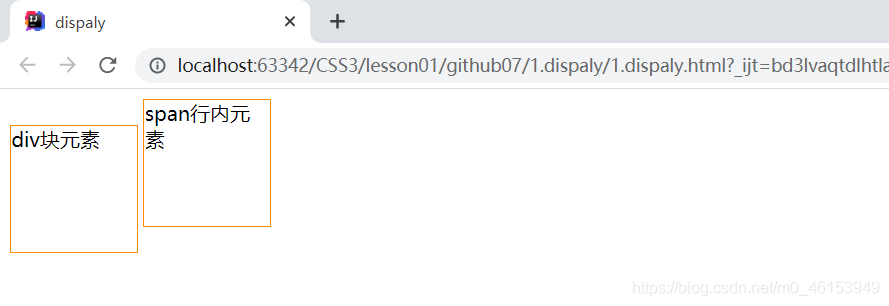
2.dispaly
- block:块元素;
- inline:行内元素;
- inline-block:是块元素,但是可以内联,在一行;
- 这也是一种实现行内元素排列的方式,但是我们很多情况用float。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dispaly</title>
<style>
/*
block: 块元素
inline: 行内元素
inline-block: 块元素,但是可以内联
none: 隐藏
*/
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
display: inline-block;
}
span{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
display: inline-block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div块元素</div>
<span>span行内元素</span>
</body>
</html>
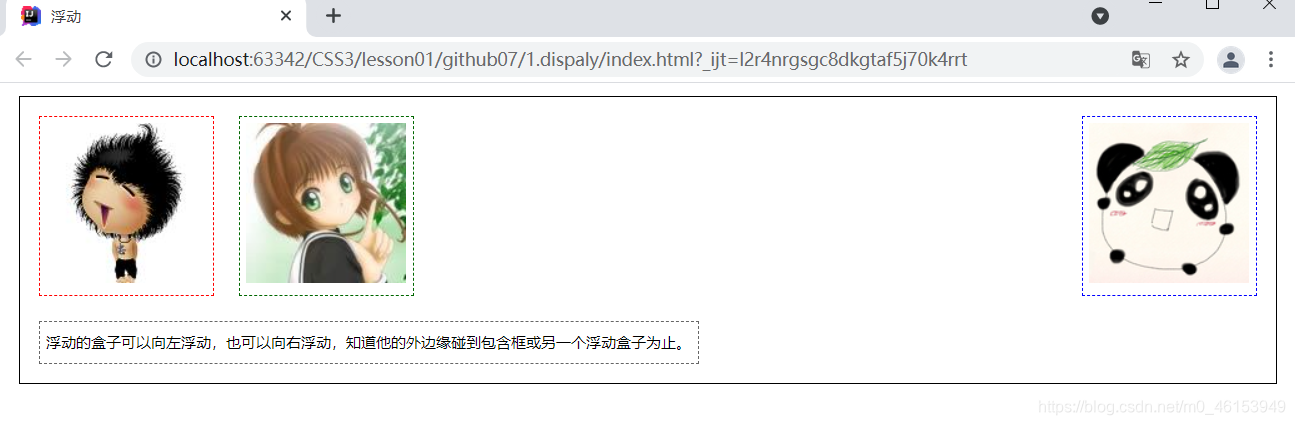
3.float:left/right
- clear: both
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>浮动</title>
<link href="css/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div class="layer01"><img src="img/str1.jpeg" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer02"><img src="img/str2.jpg" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer03"><img src="img/str3.jpeg" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer04">
浮动的盒子可以向左浮动,也可以向右浮动,知道他的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动盒子为止。
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
}
#father{
border: 1px #000 solid;
}
.layer01{
border: 1px #F00 dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;
}
.layer02{
border: 1px #00F dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: right;
}
.layer03{
border: 1px #060 dashed;
display: inline-block;
}
.layer04{
border: 1px #666 dashed;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 23px;
display: inline-block;
clear: both;
}
4.父级边框塌陷的问题
-
clear:
- right:右侧不允许有浮动元素;
- left:左侧不允许有浮动元素;
- both:两侧不允许有浮动元素;
- none:
-
解决塌陷问题方案:
- 方案一:增加父级元素的高度;
#father{ border:1px #000 solid; height:800px; }- 方案二:增加一个空的div标签,清除浮动。
<div class = "clear"></div>
<style>
.clear{
clear:both;
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
</style>
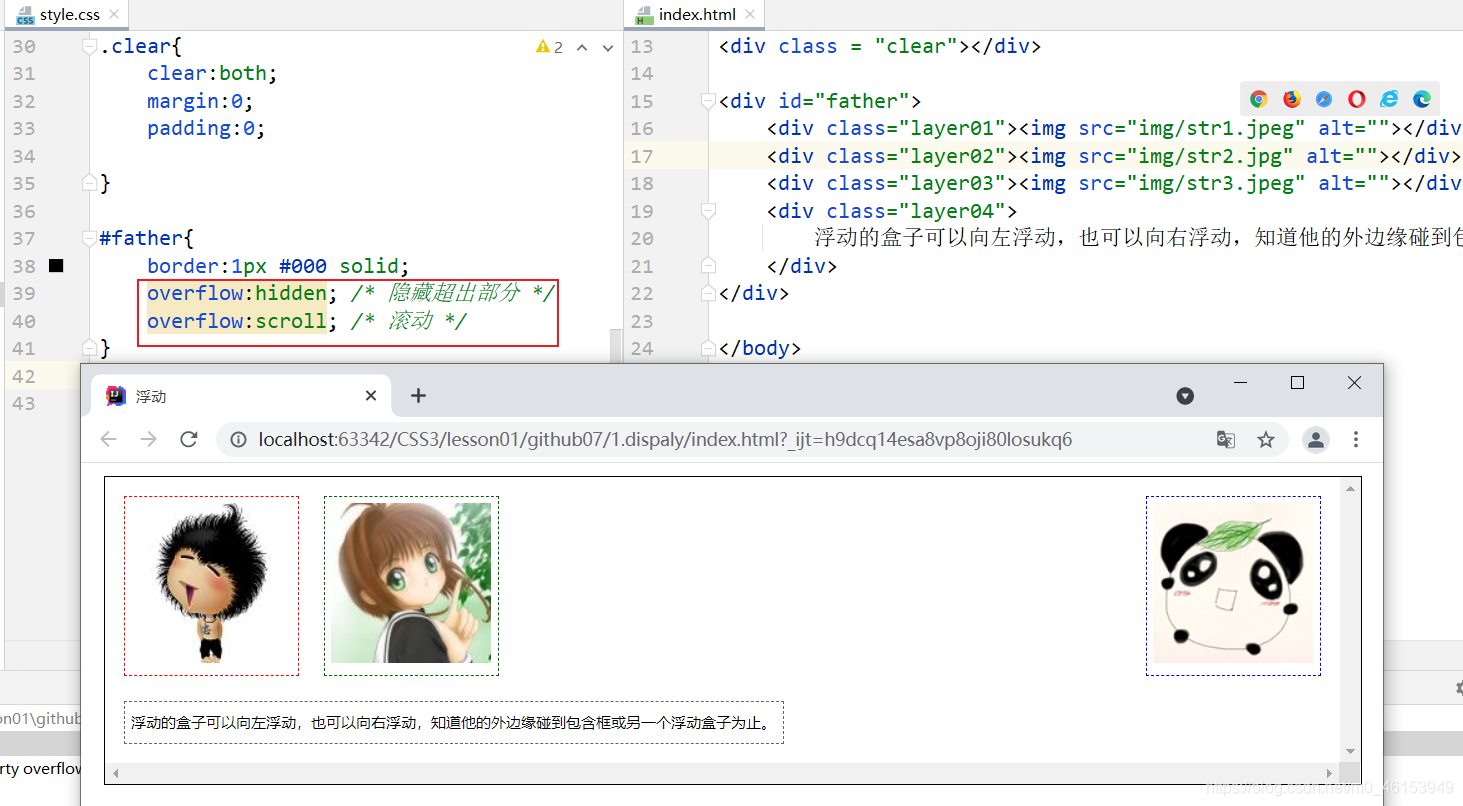
- 方案三:在父级元素中增加一个overflow属性。
overflow:hidden; /* 隐藏超出部分 */
overflow:scroll; /* 滚动 */
- 方案四:父类添加一个伪类:after。
#father:after{
content:'';
display:block;
clear:both;
}
-
小结:
- 浮动元素增加空div----> 简单、代码尽量避免空div;
- 设置父元素的高度-----> 简单,但是元素假设有了固定的高度,可能就会超出范围;
- overflow----> 简单,下拉的一些场景避免使用;
- 父类添加一个伪类:after(推荐)----> 写法稍微复杂,但是没有副作用,推荐使;
display与float对比:
- display:方向不可以控制;
- float:浮动起来的话会脱离标准文档流,所以要解决父级边框塌陷的问题。。
6.定位
1.相对定位
- 相对定位:positon:relstive;
- 相对于原来的位置,进行指定的偏移,相对定位的话,它仍然在标准文档流中!原来的位置会被保留。
top:-20px; /* 向上偏移20px */
left:20px; /* 向右偏移20px */
bottom:10px; /* 向上偏移10px */
right:20px; /* 向左偏移20px */
- 案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>路径</title>
<style>
/* 相对路径: 相对于自己原来的位置进行偏移 */
body{
padding: 20px;
}
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 25px;
}
#father{
border: #6646f3 1px solid;
padding: 0;
}
#first{
border: #ff38f5 1px solid;
background-color: #e83970;
position: relative; /* 相对定位:上下左右*/
top: -20px; /* 向上偏移20px */
left: 20px; /* 向右偏移20px */
}
#second{
border: #3ad518 1px solid;
background-color: #08e0fc;
}
#third{
background-color: #5075f8;
border: #fcb346 1px solid;
position: relative;
bottom: 10px; /* 向上偏移10px */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div id="first">第一个盒子</div>
<div id="second">第二个盒子</div>
<div id="third">第三个盒子</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

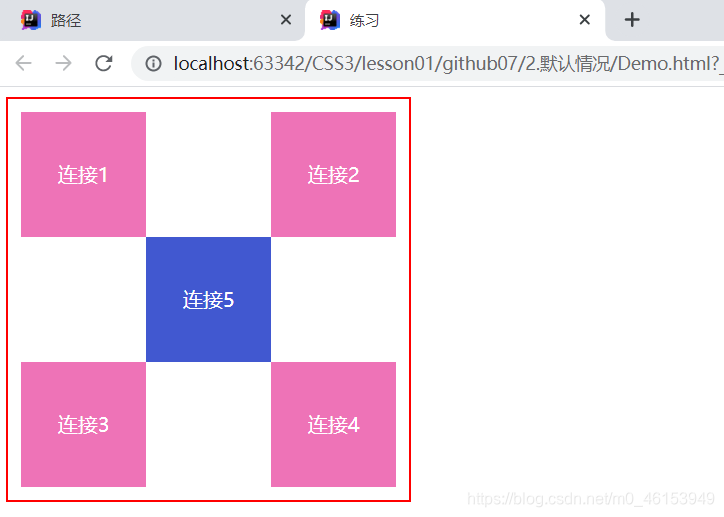
- 练习
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>练习</title>
<style>
#box{
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
border: 2px red solid;
padding: 10px;
}
a{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: #ee73b7;
color: white;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
line-height: 100px; /* 设置行距100px */
display: block; /* 设置方块 */
}
a:hover{
background: #4158D0;
}
.a2,.a4{
position: relative;
left: 200px;
top: -100px;
}
.a5{
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: -300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div class="a1"><a href="#">连接1</a></div>
<div class="a2"><a href="#">连接2</a></div>
<div class="a3"><a href="#">连接3</a></div>
<div class="a4"><a href="#">连接4</a></div>
<div class="a5"><a href="#">连接5</a></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
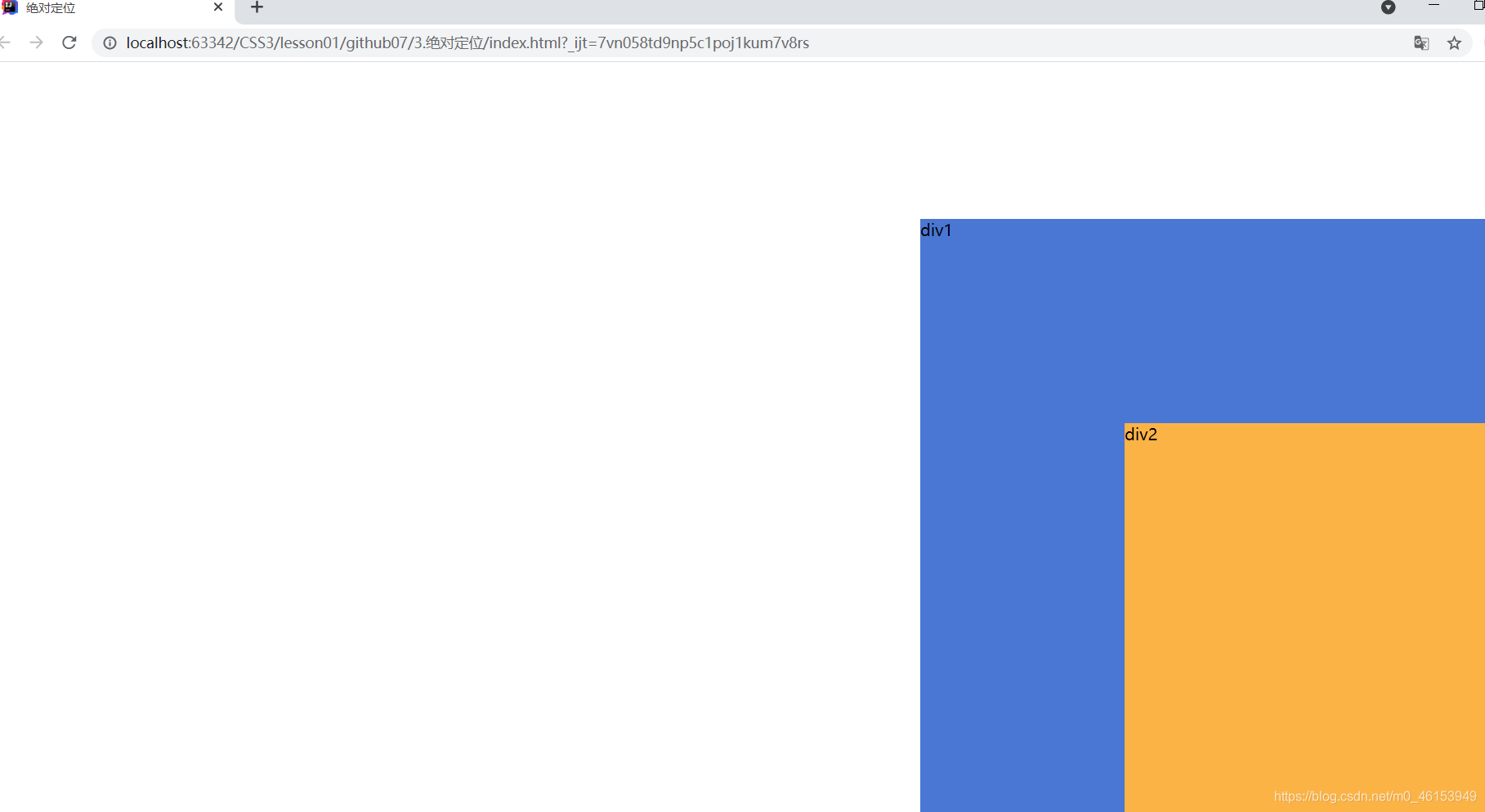
2.绝对定位与固定定位
- 定位:基于xxx定位,上下左右;
- 没有父级元素定位的前提下,相对于浏览器定位;
- 假设父级元素存在定位,我们通常会相对于父级元素进行偏移;
- 在父级元素范围内移动。
- 总结:相对一父级或浏览器的位置,进行指定的偏移,绝对定位的话,它不在标准文档流中,原来的位置不会被保留。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
body{
height: 1000px;
}
div:nth-of-type(1){
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
background-color: #4a77d4;
position: absolute; /* absolute 绝对定位 */
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
div:nth-of-type(2){
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #fcb346;
position: fixed; /* fixed 固定定位 */
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div1</div>
<div>div2</div>
</body>
</html>
3.z-index及透明度
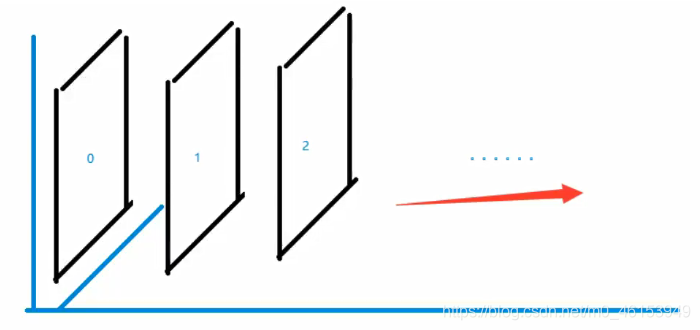
- 图层-z-index:默认是0,最高无限~999。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>透明度</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" type="text/css">
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="content">
<ul>
<li><img src="img/ntr.jpeg" alt=""></li>
<li class="tipText">Java后端学习</li>
<li class="tipBg"></li>
<li>时间:1202-06-15</li>
<li>地点:水星基地核心仓</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- CSS源码
#content{
width: 450px;
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
overflow: hidden;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 25px;
border: 1px solid #1079f6;
}
ul,li{
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
list-style: none;
}
/* 父级元素相对定位 */
#content ul{
position: relative;
}
.tipText,.tipBg{
position: absolute;
width: 380px;
height: 25px;
top:216px
}
.tipText{
color: #ffffff;
z-index: 999;
}
.tipBg{
background: #33f13d;
opacity: 0.5; /* 背景透明度 */
filter: alpha(opacity=50);
}

7.网页动画
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>HTML5 Canvas模拟飞机航班线路动画DEMO演示</title>
<style>
*{margin:0;padding:0;}
canvas {
background:#111;
background-size:cover;
display:block;
}
body{overflow: hidden;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
window.requestAnimFrame=function(){return window.requestAnimationFrame||window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame||window.mozRequestAnimationFrame||function(a){window.setTimeout(a,1E3/60)}}();
$ = {};
$.util = {
rand: function( min, max ) {
return Math.random() * ( max - min ) + min;
},
randInt: function( min, max ) {
return Math.floor( Math.random() * ( max - min + 1 ) ) + min;
},
norm: function( val, min, max ) {
return ( val - min ) / ( max - min );
},
lerp: function( norm, min, max ) {
return ( max - min ) * norm + min;
},
map: function( val, sMin, sMax, dMin, dMax ) {
return $.util.lerp( $.util.norm( val, sMin, sMax), dMin, dMax );
},
clamp: function( val, min, max ) {
return Math.min( Math.max( val, Math.min( min, max ) ), Math.max( min, max ) );
},
distance: function( p1, p2 ) {
var dx = p1.x - p2.x,
dy = p1.y - p2.y;
return Math.sqrt( dx * dx + dy * dy );
},
angle: function( p1, p2 ) {
return Math.atan2( p1.y - p2.y, p1.x - p2.x );
},
inRange: function( val, min, max ) {
return val >= Math.min( min, max ) && val <= Math.max( min, max );
},
pointInRect: function( x, y, rect ) {
return $.util.inRange( x, rect.x, rect.x + rect.width ) &&
$.util.inRange( y, rect.y, rect.y + rect.height );
},
pointInArc: function( p, a ) {
return distance( p, a ) <= a.radius;
},
setProps: function( obj, props ) {
for( var k in props ) {
obj[ k ] = props[ k ];
}
},
multicurve: function( points, ctx ) {
var p0, p1, midx, midy;
ctx.moveTo(points[0].x, points[0].y);
for(var i = 1; i < points.length - 2; i += 1) {
p0 = points[i];
p1 = points[i + 1];
midx = (p0.x + p1.x) / 2;
midy = (p0.y + p1.y) / 2;
ctx.quadraticCurveTo(p0.x, p0.y, midx, midy);
}
p0 = points[points.length - 2];
p1 = points[points.length - 1];
ctx.quadraticCurveTo(p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y);
}
};
$.init = function() {
// setup
$.c = document.createElement( 'canvas' );
$.ctx = $.c.getContext( '2d' );
document.body.appendChild( $.c );
// collections
$.ports = [];
$.planes = [];
// events
window.addEventListener( 'resize', $.reset, false );
window.addEventListener( 'click', $.reset, false );
$.reset();
$.step();
};
$.reset = function() {
// dimensions
$.cw = $.c.width = window.innerWidth;
$.ch = $.c.height = window.innerHeight;
$.dimAvg = ( $.cw + $.ch ) / 2;
// type / font
$.ctx.textAlign = 'center';
$.ctx.textBaseline = 'middle';
$.ctx.font = '16px monospace';
// options / settings
$.opt = {};
$.opt.portCount = 6;
$.opt.planeCount = 80;
$.opt.portSpacingDist = $.dimAvg / $.opt.portCount;
$.opt.holdingDist = 5;
$.opt.approachDist = 80;
$.opt.planeDist = 20;
$.opt.pathSpacing = 15;
$.opt.pathCount = 40;
$.opt.avoidRadius = 30;
$.opt.avoidMult = 0.025;
// collections
$.ports.length = 0;
$.planes.length = 0;
// delta
$.lt = Date.now();
$.dt = 1;
$.et = 0;
$.tick = 0;
// setup ports
for( var i = 0; i < $.opt.portCount; i++ ) {
$.ports.push( new $.Port() );
}
// setup planes
for( var i = 0; i < $.opt.planeCount; i++ ) {
$.planes.push( new $.Plane() );
}
};
$.Port = function() {
this.x = $.util.rand( $.cw * 0.1, $.cw * 0.9 );
this.y = $.util.rand( $.ch * 0.1, $.ch * 0.9 );
while( !this.validSpacing() ) {
this.x = $.util.rand( $.cw * 0.1, $.cw * 0.9 );
this.y = $.util.rand( $.ch * 0.1, $.ch * 0.9 );
}
};
$.Port.prototype.validSpacing = function() {
var spaced = true,
i = $.ports.length;
while( i-- ) {
var otherPort = $.ports[ i ];
if( $.util.distance( otherPort, this ) < $.opt.portSpacingDist ) {
spaced = false;
break;
}
}
return spaced;
};
$.Port.prototype.update = function( i ) {
var j = $.planes.length;
this.approachingCount = 0;
while( j-- ) {
var plane = $.planes[ j ];
if( plane.destIndex == i && plane.approaching ) {
this.approachingCount++;
}
}
};
$.Port.prototype.render = function( i ) {
$.ctx.beginPath();
$.ctx.arc( this.x, this.y, 3 + ( this.approachingCount + 5 ), 0, Math.PI * 2 );
$.ctx.fillStyle = 'hsla(120, 90%, 80%, ' + ( 0.35 + Math.sin( $.et / 20 ) * 0.2 ) + ')';
$.ctx.fill();
$.ctx.fillStyle = '#fff';
$.ctx.fillText( this.approachingCount, this.x, this.y - 30 );
};
$.Plane = function( opt ) {
this.originIndex = $.util.randInt( 0, $.ports.length - 1 );
this.origin = $.ports[ this.originIndex ];
this.path = [];
this.x = this.origin.x;
this.y = this.origin.y;
this.vx = $.util.rand( -0.35, 0.35 );
this.vy = $.util.rand( -0.35, 0.35 );
this.vmax = 1;
this.accel = 0.01;
this.decel = 0.96;
this.angle = 0;
this.approaching = false;
this.holding = false;
this.setDest();
};
$.Plane.prototype.setDest = function() {
if( this.destIndex != undefined ) {
this.originIndex = this.destIndex;
this.origin = $.ports[ this.originIndex ];
}
this.destIndex = $.util.randInt( 0, $.ports.length - 1 );
while( this.destIndex == this.originIndex ) {
this.destIndex = $.util.randInt( 0, $.ports.length - 1 );
}
this.dest = $.ports[ this.destIndex ];
this.approaching = false;
this.holding = false;
}
$.Plane.prototype.update = function( i ) {
this.ox = this.x;
this.oy = this.y;
if( $.tick % $.opt.pathSpacing == 0 ) {
this.path.push( { x: this.x, y: this.y } );
}
if( this.path.length > $.opt.pathCount ) {
this.path.shift();
}
this.angle = $.util.angle( this.dest, this );
this.speed = ( Math.abs( this.vx ) + Math.abs( this.vy ) ) / 2;
if( !$.util.pointInRect( this.x, this.y, { x: 0, y: 0, width: $.cw, height: $.ch } ) ) {
this.vx *= this.decel;
this.vy *= this.decel;
}
if( this.speed > 0.1 ) {
if( $.util.distance( this.dest, this ) < $.opt.approachDist ) {
this.vx *= this.decel;
this.vy *= this.decel;
this.approaching = true;
}
}
if( $.util.distance( this.dest, this ) < $.opt.holdingDist ) {
this.holding = true;
this.setDest();
}
this.vx += Math.cos( this.angle ) * this.accel;
this.vy += Math.sin( this.angle ) * this.accel;
if( this.speed > this.vmax ) {
this.vx *= this.decel;
this.vy *= this.decel;
}
this.x += this.vx * $.dt;
this.y += this.vy * $.dt;
};
$.Plane.prototype.render = function( i ) {
if( this.approaching ) {
$.ctx.strokeStyle = 'hsla(0, 80%, 50%, 1)';
} else {
$.ctx.strokeStyle = 'hsla(180, 80%, 50%, 1)';
}
$.ctx.beginPath();
$.ctx.moveTo( this.x, this.y );
var angle = $.util.angle( { x: this.ox, y: this.oy }, this );
$.ctx.lineWidth = 2;
$.ctx.lineTo(
this.x - Math.cos( angle ) * ( 3 + this.speed * 2 ),
this.y - Math.sin( angle ) * ( 3 + this.speed * 2 )
);
$.ctx.stroke();
var pathLength = this.path.length;
if( pathLength > 1) {
$.ctx.strokeStyle = 'hsla(0, 0%, 100%, 0.15)';
$.ctx.lineWidth = 1;
$.ctx.beginPath();
if( pathLength >= $.opt.pathCount ) {
var angle = $.util.angle( this.path[ 1 ], this.path[ 0 ] ),
dx = this.path[ 0 ].x - this.path[ 1 ].x,
dy = this.path[ 0 ].y - this.path[ 1 ].y,
dist = Math.sqrt( dx * dx + dy * dy ),
x = this.path[ 0 ].x + Math.cos( angle ) * ( dist * ( ( $.tick % $.opt.pathSpacing ) / $.opt.pathSpacing ) ),
y = this.path[ 0 ].y + Math.sin( angle ) * ( dist * ( ( $.tick % $.opt.pathSpacing ) / $.opt.pathSpacing ) );
} else {
var x = this.path[ 0 ].x,
y = this.path[ 0 ].y
}
$.ctx.moveTo( x, y );
for( var i = 1; i < pathLength; i++ ) {
var point = this.path[ i ];
$.ctx.lineTo( point.x, point.y );
}
$.ctx.lineTo( this.x, this.y );
$.ctx.stroke();
}
};
$.step = function() {
requestAnimFrame( $.step );
// clear
$.ctx.globalCompositeOperation = 'destination-out';
$.ctx.fillStyle = 'hsla(0, 0%, 0%, 1)';
$.ctx.fillRect( 0, 0, $.cw, $.ch );
$.ctx.globalCompositeOperation = 'lighter';
// collections
var i;
i = $.ports.length; while( i-- ) { $.ports[ i ].update( i ) }
i = $.planes.length; while( i-- ) { $.planes[ i ].update( i ) }
i = $.ports.length; while( i-- ) { $.ports[ i ].render( i ) }
i = $.planes.length; while( i-- ) { $.planes[ i ].render( i ) }
// delta
var now = Date.now();
$.dt = $.util.clamp( ( now - $.lt ) / ( 1000 / 60 ), 0.001, 10 );
$.lt = now;
$.et += $.dt;
$.tick++;
};
$.init();
</script>
</body>
</html>

8.总结

CSS3快速入门完结🎉🎉🎉
深入学习,请参考:Web前端HTML5&CSS3初学者零基础入门全套完整版
欢迎查阅


