JavaScript(三)
History对象的方法
back:加载上一个URL
forward:加载下一个URL
go:前进至指定的URL( go(1)等同于forward go(-1)等同于back() )
Location对象的属性和方法:
href:获取当前浏览器的URL
reload():重载当前URL
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
//添加图片
<img src="1.jpg" onclick="forwardPage()" style="cursor: pointer;">
<br>
//添加按钮
<input type="button" value="刷新" name="" onclick="refresh()">
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
//location.href用于跳转页面
window.location.href = "http://www.baidu.com";
//页面跳转的方法
function forwardPage(){
location.href = "http://www.taobao.com";
}
//重新加载页面的方法
function refresh(){
//重新加载当前的地址
location.reload();
}
</script>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 应避免给超链接添加onclick事件,因为超链接本身就是点击操作,功能就会重复 -->
<!-- 后退按钮 -->
<a href="javascript:pageBack()" style="margin-right: 20px">后退</a>
<br>
<!-- 前进按钮 -->
<a href="javascript:pageForward()" style="margin-left: 20px">前进</a>
<!-- 复选框 -->
<select onchange="changePage()" id="selPage">
<option value="none">-请选择-</option>
<!-- 跳转至红色页面 -->
<option value="red.html">red</option>
<!-- 跳转至橙色页面 -->
<option value="orange.html">orange</option>
<!-- 跳转至黄色页面 -->
<option value="yellow.html">yellow</option>
</select>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
//获取下拉列表框
var sel = document.getElementById("selPage");
function changePage(){
//获取选中项的值(如果没有写value值就会获取文本节点的值‘请选择’)
//console.log(sel.value);
//如果是选中的是有效的项
if(sel.value != "none"){
//根据选项的值进行页面跳转
location.href = sel.value;
}
}
function pageForward(){
//前进浏览过的缓存页面
window.history.forward();
}
function pageBack(){
//后退之前浏览过的页面
window.history.back();
}
</script>
HTML中的常见样式:

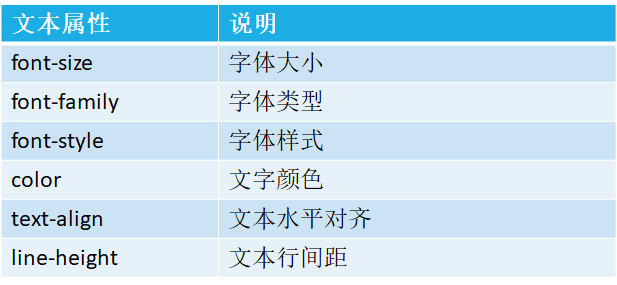
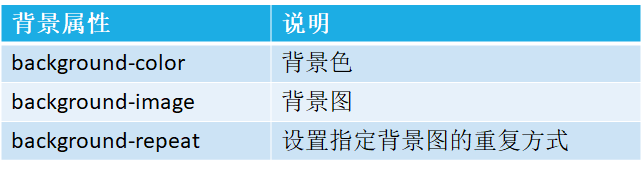
css样式基本示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<style type="text/css">
/*文本相关样式*/
.d1{
color: red;
font-size: 20px;
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
letter-spacing: 10px;
/*font-family: "宋体";*/
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
text-decoration: underline;
width:200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: gray;
}
/*背景样式*/
.d2{
background-image: url(image/1.jpg);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
/*background-size: cover;*/
/*background-position: center;*/
background-position: 50px 10px;
width: 460px;
height: 290px;
background-color: gray;
}
/*盒子模型相关样式*/
.d3{
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
border: 5px solid blue;
padding-left: 20px;
margin-top: 100px;
}
.d4{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkred;
border-radius: 50%;//圆
}
.container{
width: 600px;
border: 5px solid;
}
.container div{
width: 200px;
float: left;
height: 300px;
}
/*清除浮动效果*/
.clear:after{
clear:both;
display: block;//块级元素
content:"";
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="d1">文本样式</div>
<hr>
<div class="d2"></div>
<hr>
<div class="d3">内容</div>
<div class="d4"></div>
<!-- div布局 -->
<div class="container clear">
<div style="background-color: red"></div>
<div style="background-color: darkred"></div>
<div style="background-color: orange"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
根据JavaScript脚本访问样式:
对象.style.键(样式名称)=“值”
修改div层的宽高和背景颜色:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="d1"></div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
//获取d1标签
var d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
//使用style属性访问样式集合
d1.style.width = "360px";
d1.style.height = "190px";
d1.style.backgroundColor = "red";</script>
修改div的字体大小和背景图:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="d1">文字内容</div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
//获取d1标签层
var d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
//设置标签内的文字大小设为20px
d1.style.fontSize = "20px";
//设置标签的背景图
d1.style.backgroundImage = "url(image/1.jpg)";
</script>
通过脚本访问已有的类样式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<style type="text/css">
.d2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid blue;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="d2"></div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
//使用脚本访问类样式
var d2 = document.getElementById("d2");
d2.className = "d2";//填入样式名称
</script>
使用脚本设置按钮的样式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" id="btn" name="">
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
//获取按钮
var btn = document.getElementById("btn");
//使用脚本设置按钮的样式
btn.style.width = "82px";
btn.style.height = "23px";
btn.style.backgroundImage = "url(image/back1.jpg)";
//去掉边框
btn.style.border = "none";
//鼠标进入
btn.onmouseenter = function(){
//修改背景图
btn.style.backgroundImage = "url(image/back2.jpg)";
}
//鼠标离开
btn.onmouseleave = function(){
btn.style.backgroundImage = "url(image/back1.jpg)";
}
</script>
通过JavaScript获取读写行内样式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="d1" style="width:200px; height:200px;background-color:darkred" ></div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
var d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
//js访问的样式是可以进行读写
//获取层的宽度
//该方式只能访问到行内的样式,或者是js作用的样式
console.log(d1.style.width);
//在原宽度上增加50px
var width = parseInt(d1.style.width);
d1.style.width = width+50+"px";
</script>
通过JavaScript获取读写外部样式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<style type="text/css">
.d1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkred;
/*overflow: scroll;*/
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="d1" style="" class="d1"></div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
var d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
//获取外部作用的样式(内嵌式样式、外部样式表作用的样式)传入的是获取到的元素对象:获取元素对象的样式
var style = window.getComputedStyle(d1);
console.log(style.width);
//获取宽度的其他方式
//返回number,这两个属性都是只读的
//clientWidth获取标签的实际宽度
console.log(d1.clientWidth);
//offsetWidth获取标签包含滚动条、边框的宽度
console.log(d1.offsetWidth);
</script>
改变div层的位置:
1.position:absolute;再配合top和left
2.margin 修改两个元素之间的距离(不建议用,因为会改变相对位置,影响布局)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<style type="text/css">
.d1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkred;
/*overflow: scroll;*/
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="d1" style="" class="d1"></div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
var d1 = document.getElementById("d1");
//获取浏览器的大小 ,不同的浏览器需要根据document.body或者document.documentElement访问
//获取浏览器宽度
console.log(document.body.clientWidth);
//获取浏览器的高度
console.log(document.body.clientHeight);
console.log(document.body.clientHeight);
console.log(document.documentElement.clientWidth); console.log(document.documentElement.clientHeight);
//每隔十毫秒就移动1像素 function move(){ console.log(parseInt(style.left)); d1.style.left = parseInt(style.left)+1+"px"; window.setTimeout("move()",10); } //move(); window.onresize = function(){ console.log("窗体大小发生了变化"); } </script>







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!