票务阶段考试
1、计算器布局
分析:计算器窗口主要由上下两部分组成,使用Frame默认的BorderLayout布局方式。北部使用Panel装载-一 个保存计算结果的文本框;中部使用Panel装载计算器的20个按钮,采用GridLayout布局。为了维持布局方式,禁止改变Frame的大小。将计算器20个按钮上的符号初始化在一个 String字符串中,创建按钮时从中截取相应的字符。构建GUI时通常这样划分代码:将组件定义为属性;在构造方法中构建组件;自定义init()方法设置布局;在show()方法中设置GUI的显示属性。
书上源码有错误,错误代码:

修正后,正确代码:
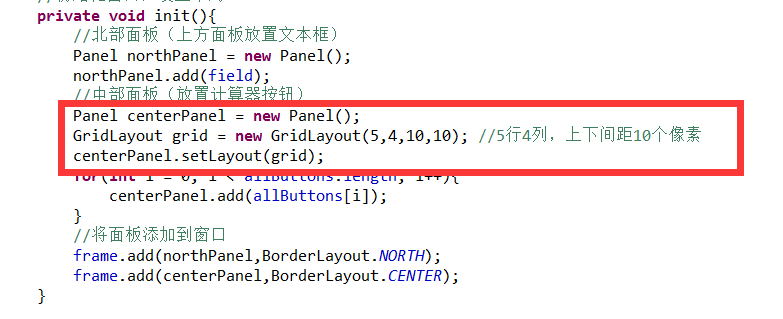
源码如下:
1 import java.awt.*; 2 3 public class AWTCalculation { 4 5 //全局变量 6 private Frame frame; 7 private TextField field; 8 private Button[] allButtons; 9 10 //构造方法用于创建组件并对其初始化 11 //生成并初始化对象 12 public AWTCalculation(){ 13 frame = new Frame("票务专用计算器"); //设置窗口名称 14 field = new TextField(20); //20表示文本宽度,此文本框只接收20个字符 15 allButtons = new Button[20]; //20个按钮 16 String str = "←C√±789/456*123-0.=+"; 17 for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){ 18 allButtons[i] = new Button(str.substring(i,i+1)); //substring()字符串截取函数 19 } 20 } 21 //初始化窗口,设置布局 22 private void init(){ 23 //北部面板(上方面板放置文本框) 24 Panel northPanel = new Panel(); 25 northPanel.add(field); 26 //中部面板(放置计算器按钮) 27 Panel centerPanel = new Panel(); 28 GridLayout grid = new GridLayout(5,4,10,10); //5行4列,上下间距10个像素 29 centerPanel.setLayout(grid); 30 for(int i = 0; i < allButtons.length; i++){ 31 centerPanel.add(allButtons[i]); 32 } 33 //将面板添加到窗口 34 frame.add(northPanel,BorderLayout.NORTH); 35 frame.add(centerPanel,BorderLayout.CENTER); 36 } 37 38 //设置窗口的显示属性 39 public void showMe(){ 40 init(); 41 frame.pack(); //设置窗口的最佳大小 42 frame.setLocation(300,200); //设置窗口显示初始位置 43 frame.setResizable(true); //允许改变窗口的大小,false禁止改变大小 44 frame.setVisible(true); //显示窗口 45 } 46 47 public static void main(String[] args){ 48 new AWTCalculation().showMe(); 49 } 50 }
运行结果:
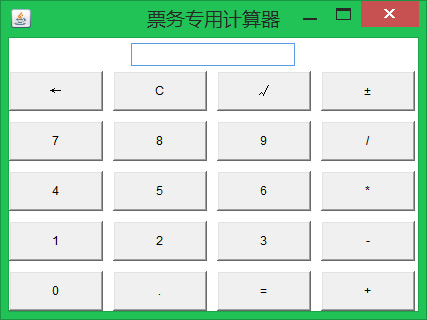
2、工资计算
某学校教师的工资=基本工资+课时补贴。教授的基本工资为5000元,每学时补贴70元;副教授的基本工资为3500元,每学时补贴60元;讲师的基本工资为2600元,每学时补贴55元。已知每个教师的学时数,请编程计算每个教师的每月工资数目。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Stady { 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); 5 System.out.println("*********** 工资计算 ***********\n*"); 6 System.out.print("*\t1.计算教授工资;"); 7 System.out.println("\t *"); 8 System.out.print("*\t2.计算副教授工资;"); 9 System.out.println(" *"); 10 System.out.print("*\t3.计算讲师工资; *\n*"); 11 System.out.println("\t\t *"); 12 for(int i=0;i<31;i++){ 13 System.out.print("*"); 14 if(i==30) 15 System.out.print("\n"); 16 } 17 int temp; 18 while(true){ 19 System.out.print("请选择:"); 20 temp = scan.nextInt(); 21 switch(temp){ 22 case 1: 23 System.out.print("请输入教授学时:"); 24 int time0 = scan.nextInt(); 25 System.out.println("教授每月工资数目:"+ (5000 + 70 * time0) ); 26 break; 27 case 2: 28 System.out.print("请输入副教授学时:"); 29 int time1 = scan.nextInt(); 30 System.out.println("副教授每月工资数目:"+ (3500 + 60 * time1) ); 31 break; 32 case 3: 33 System.out.print("请输入讲师学时:"); 34 int time2 = scan.nextInt(); 35 System.out.println("讲师每月工资数目:"+ (2600 + 55* time2) ); 36 break; 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 }
3、公里计价
编写一个北京地铁按公里计价的程序。计价规则为: 6km (含)内3元; 6~12km(含4元;12-22km(含)5元;22~32km(含)6元;32km以上每加1元可乘坐20km.
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Price { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 System.out.print("输入距离:"); 6 Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in); 7 int distance = scn.nextInt(); 8 int price; 9 if(distance <= 6 && distance > 0){ 10 price = 3; 11 } 12 else if(distance <= 12){ 13 price = 4; 14 } 15 else if(distance <= 22){ 16 price = 5; 17 } 18 else if(distance <= 32){ 19 price = 6; 20 } 21 else{ 22 if((distance - 32) % 20 != 0){ 23 price = 6 + (distance - 32) / 20 + 1; //没满20Km,按20Km计算 24 } 25 else{ 26 price = 6 + (distance - 32) / 20; 27 } 28 } 29 System.out.printf("price=%d\n", price); //格式化输出 30 } 31 }
4、数据加密
某个公司传送数据时采用加密方式,数据是四位整数,加密规则如下:每位数字都加上5,然后用和除以10的余数代替该数字,再将第一位和第四位交换,第二位和第三位交换。
1 public class Encode { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 int number = (int)(Math.random() * 10000) + 1000; //随机生成四位数 4 System.out.println("加密前:" + number); 5 int a = (number % 10 + 5) % 10; //个位 6 number /= 10; 7 int b = (number % 10 + 5) % 10; //十位 8 number /= 10; 9 int c = (number % 10 + 5) % 10; //百位 10 number /= 10; 11 int d = (number % 10 + 5) % 10; //千位 12 13 //交换1、4位 14 int temp = a; 15 a = d; 16 d = temp; 17 18 //交换2、3位 19 temp = b; 20 b = c; 21 c = temp; 22 System.out.println("加密后:" + d + c + b + a); 23 } 24 }
5、约瑟夫环
解约瑟夫问题。约瑟夫问题是一个 出现在计算机科 学和数学中的经典问题,可以这样描述:N个人围成一圈,从第一个开始报数,每报数到M的人出列,然后从下一一个人开始重新报数,直到最后剩下一个人。编写程序,打印出列的顺序以及最后剩下人的序号。例如N=6,M=5,出列的顺序:5,4,6,2,3,剩下1。
1 public class Josephus { 2 3 /** 4 * 约瑟夫问题 5 * 6 */ 7 static int N = 6; 8 static int M = 5; 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 boolean[] person = new boolean[N+1]; //默认为false 12 13 int count=N; 14 int now=1; 15 int next=1; 16 while(count>1){ 17 if(person[now]==false){//未被杀死的报数 18 if(next==M){ 19 person[now]=true; //杀死 20 System.out.print(" " + now); 21 count--; 22 next=1; //从1开始报数 23 }else{ 24 next++; //继续报数 25 } 26 } 27 if(now==N){ 28 now=1; 29 }else{ 30 now++; 31 } 32 } 33 34 for(int i=1; i<person.length; i++){ 35 if(person[i]==false){ 36 System.out.println("\n" + "最后剩下" + i); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 }

