对MobileNet网络结构的解读
引言
近几年来,CNN在ImageNet竞赛的表现越来越好。为了追求分类准确度,模型越来越深,复杂度越来越高,如深度残差网络(ResNet)其层数已经多达152层。但是在真实场景中如移动或者嵌入式设备,大而复杂的模型是难以被应用的。模型过于庞大会面临内存不足的问题,其次模型的过于复杂也使得响应速度过慢,很难达到实时要求。
目前的研究主要分为两个方向:一是对训练好的的复杂模型进行压缩得到小模型;二是直接设计小模型并进行训练。不管怎样,其目的都是在保持模型性能(accuracy)的前提下降低模型大小(parameters size),同时提升速度(speed)。MobileNet属于后者,是Google提出的一种小巧而高效的CNN模型。
Depthwise separable convolution
MobileNet的基本单元是深度级可分离卷积(depthwise separable convolution),这种结构其实已经在inception中使用。深度级可分离卷积其实是将一个卷积分解成两个更小的卷积:depthwise convolution和 pointwise convolution,如图1所示。Depthwise convolution和标准卷积不同,标准卷积的卷积核作用在所有输入通道上(input channels),而depthwise convolution针对每个输入通道采用不同的卷积核,也就是说一个卷积核对应一个输入通道。而pointwise convolution其实就是普通的卷积,只不过采用的是1x1的卷积核。
图2中更清晰地展示了两种操作,对于depthwise separable convolution,其首先是采用depthwise convolution对不同的输入通道分别进行卷积,然后采用pointwise convolution将上面的输出再进行结合。整体效果和标准卷积差不多,但是会大大减少计算量和模型参数量
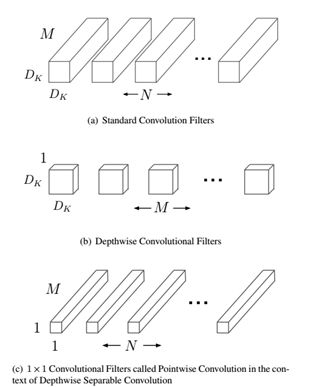
图1 Depthwise separable convolution
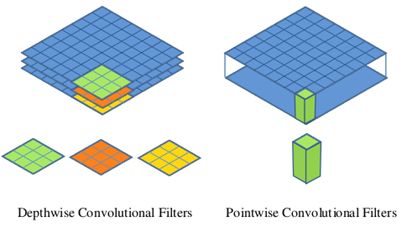
图2 Depthwise convolution和 pointwise convolution
这里简单分析一下depthwise separable convolution在计算量上与标准卷积的差别。假定输入特征图大小是,而输出特征图大小是
,其中
是特征图的width和height,这里假定两者是相同的,M指的是通道数(channels),卷积核为
对于标准卷积,其计算量为:
对于depthwise convolution。其输入为,输出为
,卷积核为
。但是一个卷积核只对应一个通道。因此一个输出通道的计算量为
![]() ,而输出有M个通道。故计算量为
,而输出有M个通道。故计算量为
对于pointwise convolution。其输入为,输出为
,卷积核为1x1。
其计算量为:
所以depthwise separable convolution总计算量为:
可以比较depthwise separable convolution和标准卷积的计算量:
一般情况下比较大,
![]() 就很接近0,那么如果采用3x3卷积核的话,depthwise separable convolution相较标准卷积可以降低大约9倍的计算量。其实后面会有对比,参数量会减少很多。
就很接近0,那么如果采用3x3卷积核的话,depthwise separable convolution相较标准卷积可以降低大约9倍的计算量。其实后面会有对比,参数量会减少很多。
MobileNet网络结构
前面讲述了depthwise separable convolution,这是MobileNet的基本组件,但是在真正应用中会加入batchnorm,并使用ReLU激活函数,所以
depthwise separable convolution的基本结构如图3所示。
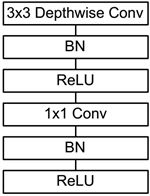
图3 加入BN和ReLU的depthwise separable convolution
MobileNet的网络结构如表1所示。首先是一个3x3的标准卷积,然后后面就是堆积depthwise separable convolution,并且可以看到其中的部分depthwise convolution会通过strides=2进行下采样(down sampling)。然后采用average pooling将feature变成1x1,根据预测类别大小加上全连接层,最后一个是softmax层。
如果单独计算depthwise convolution和pointwise convolution,整个网络的有28层(这里Avg Pool和Softmax不计算在内。13+10+4+1=28)。我们还可以分析整个网络的参数和计算量分布,如表2所示。可以看到整个计算量基本集中在1x1卷积上,如果你熟悉卷积底层实现的话,你应该知道卷积一般通过im2col方式实现,其需要内存重组,但是当卷积核为1x1时,其实就不需要这种操作了,底层可以有更快的实现。对于参数也主要集中在1x1卷积,除此之外还有就是全连接层占了一部分参数。
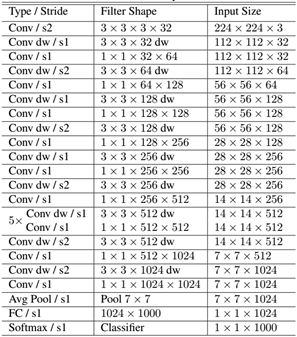
表1 MobileNet的网络结构
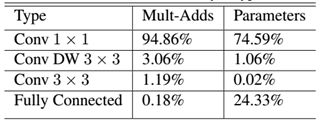
表2 MobileNet网络的计算与参数分布
MobileNet到底效果如何,这里与GoogleNet和VGG16做了对比,如表3所示。相比VGG16,MobileNet的准确度稍微下降,但是优于GoogleNet。然而,从计算量和参数量上MobileNet具有绝对的优势
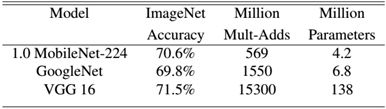
表3 MobileNet与GoogleNet和VGG16性能对比
MobileNet瘦身
前面说的是MobileNet的基准模型,但是有时候需要更小的模型,那么就需要对MobileNet进行瘦身。这里引入了两个超参数:width multiplier和resolution multiplier。第一个参数width multiplier主要是按比例减少通道数,该参数记为 α,其取值范围为(0,1],那么输入与输出通道数将变成 和
,对于depthwise separable convolution,其计算量变为:
因为主要计算量在后一项,所以width multiplier可以按照比例降低计算量,其实参数量也会下降。第二个参数resolution multiplier主要是按比例降低特征图的大小,记为 ,比如原来输入特征图是224x224,可以减少为192x192,加上resolution multiplier,depthwise separable
convolution的计算量为:
要说明的是,resolution multiplier仅仅影响计算量,但是不改变参数量。引入两个参数肯定会降低MobileNet的性能。总结来看是在accuracy和computation,以及accuracy和model size之间做折中。
MobileNet的Tensorflow实现
tensorflow的nn库有depthwise convolution算子tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d,所以MobileNet很容易在tensorflow上实现:
class MobileNet(object): def __init__(self, inputs, num_classes=1000, is_training=True, width_multiplier=1, scope="MobileNet"): """ The implement of MobileNet(ref:https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861) :param inputs: 4-D Tensor of [batch_size, height, width, channels] :param num_classes: number of classes :param is_training: Boolean, whether or not the model is training :param width_multiplier: float, controls the size of model :param scope: Optional scope for variables """ self.inputs = inputs self.num_classes = num_classes self.is_training = is_training self.width_multiplier = width_multiplier # construct model with tf.variable_scope(scope): # conv1 net = conv2d(inputs, "conv_1", round(32 * width_multiplier), filter_size=3, strides=2) # ->[N, 112, 112, 32] net = tf.nn.relu(bacthnorm(net, "conv_1/bn", is_training=self.is_training)) net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 64, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_2") # ->[N, 112, 112, 64] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 128, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_3", downsample=True) # ->[N, 56, 56, 128] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 128, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_4") # ->[N, 56, 56, 128] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 256, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_5", downsample=True) # ->[N, 28, 28, 256] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 256, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_6") # ->[N, 28, 28, 256] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_7", downsample=True) # ->[N, 14, 14, 512] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_8") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_9") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_10") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_11") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_12") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 1024, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_13", downsample=True) # ->[N, 7, 7, 1024] net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 1024, self.width_multiplier, "ds_conv_14") # ->[N, 7, 7, 1024] net = avg_pool(net, 7, "avg_pool_15") net = tf.squeeze(net, [1, 2], name="SpatialSqueeze") self.logits = fc(net, self.num_classes, "fc_16") self.predictions = tf.nn.softmax(self.logits) def _depthwise_separable_conv2d(self, inputs, num_filters, width_multiplier, scope, downsample=False): """depthwise separable convolution 2D function""" num_filters = round(num_filters * width_multiplier) strides = 2 if downsample else 1 with tf.variable_scope(scope): # depthwise conv2d dw_conv = depthwise_conv2d(inputs, "depthwise_conv", strides=strides) # batchnorm bn = bacthnorm(dw_conv, "dw_bn", is_training=self.is_training) # relu relu = tf.nn.relu(bn) # pointwise conv2d (1x1) pw_conv = conv2d(relu, "pointwise_conv", num_filters) # bn bn = bacthnorm(pw_conv, "pw_bn", is_training=self.is_training) return tf.nn.relu(bn)
完整实现可以参见GitHub
总结
本文介绍了Google提出的移动端模型MobileNet,其核心是采用了可分解的depthwise separable convolution,其不仅可以降低模型计算复杂度,而且大大地降低了模型大小。当然MobileNet还有其他版本,后面再介绍
参考:
MobileNet:Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications



