OpenCV-Python入门教程3-图像基本操作(访问像素点/ROI/通道分离)
一、获取和修改像素点的值
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg')
# 100, 90表示行列坐标 px = img[100, 90] print(px) # 获取一个坐标单通道的值 # 0:蓝色(B) # 1:绿色(G) # 2:红色(R) px_blue = img[100, 90, 0] px_green = img[100, 90, 1] px_red = img[100, 90, 2] print(px_blue) print(px_green) print(px_red)
[103 98 197] 103 98 197
通过行、列坐标获取某个像素点的值,对于彩色图。B、G、R对应0, 1, 2
修改像素也是同样的方式:
# 修改像素的值 img[100, 90] = [255, 255, 255] print(img[100, 90])
[255 255 255]
注意:该操作只是内存中的img像素点变了,因为没有保存,所以原图并没有修改
更好的像素访问和编辑方法:
img.item(100, 90, 0)
103
# 修改蓝色通道的值 img.itemset((100, 90, 0), 50) img.item(100, 90, 0)
50
二、图片属性
1、图像形状
print(img.shape) # 形状中包括行数,列数和通道数 height, width, channels = img.shape # img是灰度图,height, width = img.shape
(263, 247, 3)
2、数据类型
print(img.dtype)
uint8
3、图像总像素数
print(img.size) # 263 * 247 * 3 = 194883
194883
二、感兴趣区域(ROI)
# 截取脸部ROI face = img[100:200, 115:188] cv2.imshow('face', face) cv2.waitKey(0)
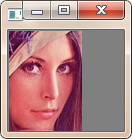
行对应y,列对应x,所以其实是img[y, x],所以要注意,不要弄混淆
三、通道分割与合并
b, g, r = cv2.split(img)
img = cv2.merge((b, g, r))
分割:cv2.split() 合并:cv.merge()
split()函数比较耗时,更高效的方式是用numpy中的索引,提取B通道:
b = img[:, :, 0] cv2.imshow('blue', b) cv2.waitKey(0)

由于是单通道图,所以呈现出来的是一种灰度图。
参考网址:https://tianchi.aliyun.com/course/courseConsole?courseId=40992&chapterIndex=1§ionIndex=4


