Python: OpenWeatherMap json Deserialization of Python Objects
openweathermap.json
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | { "coord": { "lon": 114.0683, "lat":22.5455 } , "weather":[ { "id": 803, "main":"Clouds", "description":"多云", "icon":"04d" } ], "base":"stations", "main": { "temp": 299.1, "feels_like":299.1, "temp_min":296.39, "temp_max":300.29, "pressure":1018, "humidity":79, "sea_level":1018, "grnd_level":1017 } , "visibility":10000, "wind": { "speed": 2.73, "deg":137, "gust":3.32 } , "clouds": { "all": 82 } , "dt":1702530001, "sys": { "type": 2, "id":2031340, "country":"CN", "sunrise":1702508106, "sunset":1702546869 } , "timezone":28800, "id":1795565, "name":"Shenzhen", "cod":200} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 | # encoding: utf-8# 版权所有 2023 涂聚文有限公司# 许可信息查看:# 描述:# Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂聚文.# IDE : PyCharm 2023.1 python 3.11# Datetime : 2023/12/14 22:14# User : geovindu# Product : PyCharm# Project : pyBaiduAi# File : Clouds.py# explain : 学习import jsonimport picklefrom typing import Listfrom typing import Anyfrom dataclasses import dataclass@dataclassclass Clouds: all: int @staticmethod def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Clouds': _all = int(obj.get("all")) return Clouds(_all)@dataclassclass Coord: lon: float """ 经度 """ lat: float """ 纬度 """ @staticmethod def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Coord': _lon = float(obj.get("lon")) _lat = float(obj.get("lat")) return Coord(_lon, _lat)@dataclassclass Main: """ """ temp: float """ 温度 """ feels_like: float temp_min: float """ 最低温 """ temp_max: float """ 最高温 """ pressure: int humidity: int """ 湿魔 """ sea_level: int grnd_level: int @staticmethod def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Main': _temp = float(obj.get("temp")) _feels_like = float(obj.get("feels_like")) _temp_min = float(obj.get("temp_min")) _temp_max = float(obj.get("temp_max")) _pressure = int(obj.get("pressure")) _humidity = int(obj.get("humidity")) _sea_level = int(obj.get("sea_level")) _grnd_level = int(obj.get("grnd_level")) return Main(_temp, _feels_like, _temp_min, _temp_max, _pressure, _humidity, _sea_level, _grnd_level)@dataclassclass Sys: """ 系统信息 """ type: int id: int country: str """ 所属国家 """ sunrise: int """ 日出时间戳 """ sunset: int """ 日落时间戳 """ @staticmethod def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Sys': _type = int(obj.get("type")) _id = int(obj.get("id")) _country = str(obj.get("country")) _sunrise = int(obj.get("sunrise")) _sunset = int(obj.get("sunset")) return Sys(_type, _id, _country, _sunrise, _sunset)@dataclassclass Weather: """ 天气情况 """ id: int main: str description: str """ 天气 """ icon: str """ 图标ID """ @staticmethod def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Weather': _id = int(obj.get("id")) _main = str(obj.get("main")) _description = str(obj.get("description")) _icon = str(obj.get("icon")) return Weather(_id, _main, _description, _icon)@dataclassclass Wind: """ 风况 """ speed: float """ 风速 """ deg: int gust: float @staticmethod def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Wind': _speed = float(obj.get("speed")) _deg = int(obj.get("deg")) _gust = float(obj.get("gust")) return Wind(_speed, _deg, _gust)@dataclassclass OpenWeather: """" 天气类 """ coord: Coord weather: List[Weather] base: str main: Main visibility: int wind: Wind clouds: Clouds dt: int sys: Sys timezone: int id: int name: str cod: int @staticmethod def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'OpenWeather': _coord = Coord.from_dict(obj.get("coord")) _weather = [Weather.from_dict(y) for y in obj.get("weather")] _base = str(obj.get("base")) _main = Main.from_dict(obj.get("main")) _visibility = int(obj.get("visibility")) _wind = Wind.from_dict(obj.get("wind")) _clouds = Clouds.from_dict(obj.get("clouds")) _dt = int(obj.get("dt")) _sys = Sys.from_dict(obj.get("sys")) _timezone = int(obj.get("timezone")) _id = int(obj.get("id")) _name = str(obj.get("name")) _cod = int(obj.get("cod")) return OpenWeather(_coord, _weather, _base, _main, _visibility, _wind, _clouds, _dt, _sys, _timezone, _id, _name, _cod) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 | # encoding: utf-8# 版权所有 2023 ©涂聚文有限公司# 许可信息查看:# 描述:# Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂聚文.# IDE : PyCharm 2023.1 python 311# Datetime : 2023/12/15 8:13# User : geovindu# Product : PyCharm# Project : EssentialAlgorithms# File : DateTimeHelper.py# explain : 学习import timeimport datetimeclass TimeHelper(object): """ 时间转换 """ @staticmethod def gettime(timeStamp:int): """ 时间戳转成日期时间 :param timeStamp: :return: """ timeArray = time.localtime(timeStamp) #timeArray = datetime.datetime.utcfromtimestamp(timeStamp) #beikingStyleTime =datetime.datetime.utcfromtimestamp(timeStamp)# time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timeArray) #beijing_timezone = datetime.timezone(datetime.timedelta(hours=8)) #beikingStyleTime = utc_time.astimezone(beijing_timezone) beikingStyleTime=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timeArray) return beikingStyleTime @staticmethod def getTimeStamp(nowdatetime:datetime.datetime): """ 由 datetime对象 转换为 时间戳 :param nowdatetime :return: """ year=nowdatetime.year month=nowdatetime.month day=nowdatetime.day hour=nowdatetime.hour minute=nowdatetime.minute seconde=nowdatetime.second timeArray = nowdatetime.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") #'2023-12-31 09:30:18' timeStamp = time.mktime(timeArray) return timeStamp @staticmethod def getDateTime(timeStamp:int): """ 时间戳转成日期时间 :param timeStamp: :return: """ #无效 #dateArray = datetime.datetime.utcfromtimestamp(timeStamp) #beikingStyleTime = dateArray.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") beikingStyleTime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime(timeStamp)) return beikingStyleTime @staticmethod def getDateTimeStamp(nowdatetime: datetime.datetime): """ 由 datetime对象 转换为 时间戳 :param nowdatetime :return: """ year = nowdatetime.year month = nowdatetime.month day = nowdatetime.day hour = nowdatetime.hour minute = nowdatetime.minute seconde = nowdatetime.second dateArray = datetime.datetime(year=year, month=month, day=day, hour=hour, minute=minute, second=seconde) timeStamp = dateArray.timestamp() return timeStamp @staticmethod def getFTC(ff: float): """ 华氏度转摄氏度 摄氏度(℃)、华氏度(℉)、开氏度(K)、列氏度(°Re)、兰氏度(°R)温度单位数据 :param ff: :return: """ temperature = str(round(((ff - 32) / 1.8000), 2))+'℃' return temperature @staticmethod def getKTC(kk: float): """ 开尔文转摄氏度 :param kk: :return: """ temperature = str(round((kk - 273.15), 2))+'℃' return temperature |
调用:
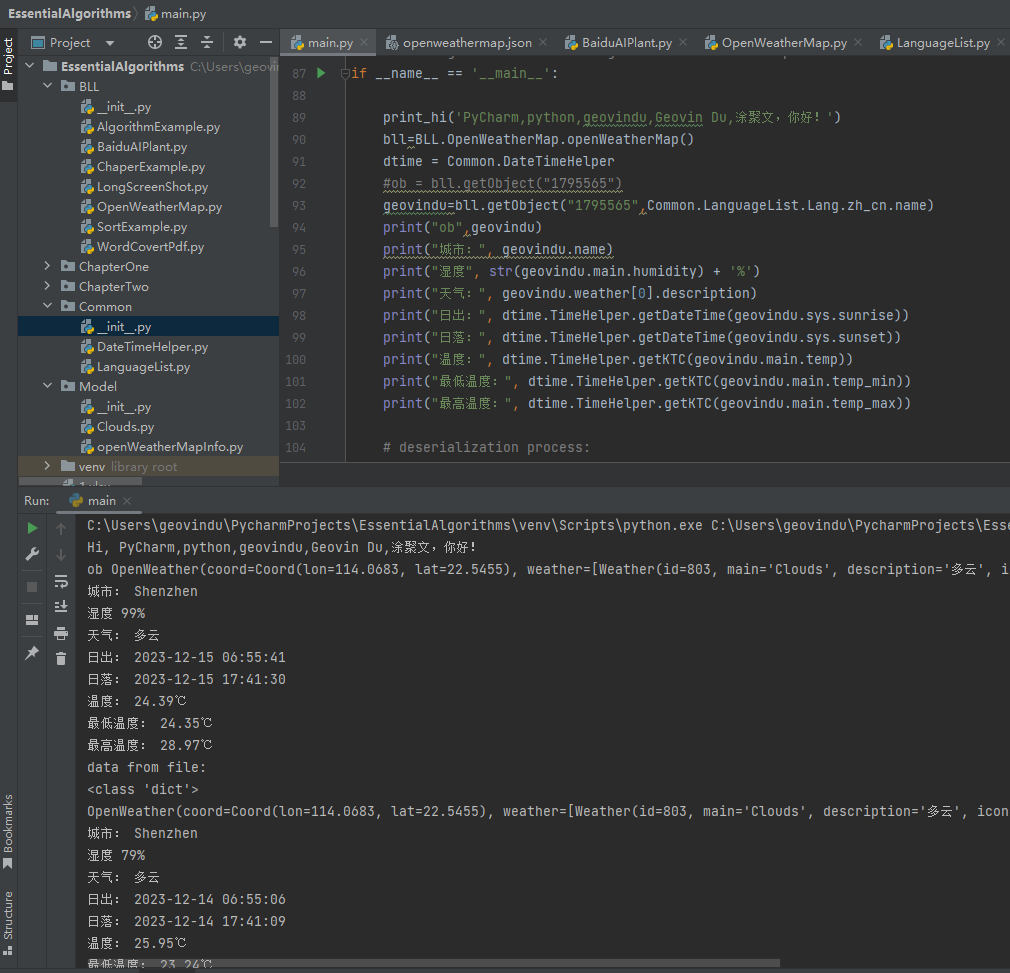
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | import Common.DateTimeHelperimport Model.Cloudsimport Model.openWeatherMapInfoimport Common.LanguageListimport BLL.OpenWeatherMapimport requestsdef print_hi(name): # Use a breakpoint in the code line below to debug your script. print(f'Hi, {name}') # Press Ctrl+F8 to toggle the breakpoint.# Press the green button in the gutter to run the script.if __name__ == '__main__': print_hi('PyCharm,python,geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文,你好!') bll=BLL.OpenWeatherMap.openWeatherMap() dtime = Common.DateTimeHelper #ob = bll.getObject("1795565") geovindu=bll.getObject("1795565",Common.LanguageList.Lang.zh_cn.name) print("ob",geovindu) print("城市:", geovindu.name) print("湿度", str(geovindu.main.humidity) + '%') print("天气:", geovindu.weather[0].description) print("日出:", dtime.TimeHelper.getDateTime(geovindu.sys.sunrise)) print("日落:", dtime.TimeHelper.getDateTime(geovindu.sys.sunset)) print("温度:", dtime.TimeHelper.getKTC(geovindu.main.temp)) print("最低温度:", dtime.TimeHelper.getKTC(geovindu.main.temp_min)) print("最高温度:", dtime.TimeHelper.getKTC(geovindu.main.temp_max)) # deserialization process: with open('openweathermap.json', encoding='utf-8') as json_file: data = json.load(json_file) print("data from file:") print(type(data)) root = Model.Clouds.OpenWeather.from_dict(data) print(root) print("城市:", root.name) print("湿度", str(root.main.humidity)+'%') print("天气:", root.weather[0].description) #1. #print("日出:", dtime.TimeHelper.gettime(root.sys.sunrise)) #print("日落:", dtime.TimeHelper.gettime(root.sys.sunset)) #2. print("日出:", dtime.TimeHelper.getDateTime(root.sys.sunrise)) print("日落:", dtime.TimeHelper.getDateTime(root.sys.sunset)) print("温度:",dtime.TimeHelper.getKTC(root.main.temp)) print("最低温度:", dtime.TimeHelper.getKTC(root.main.temp_min)) print("最高温度:", dtime.TimeHelper.getKTC(root.main.temp_max)) |
输出
哲学管理(学)人生, 文学艺术生活, 自动(计算机学)物理(学)工作, 生物(学)化学逆境, 历史(学)测绘(学)时间, 经济(学)数学金钱(理财), 心理(学)医学情绪, 诗词美容情感, 美学建筑(学)家园, 解构建构(分析)整合学习, 智商情商(IQ、EQ)运筹(学)生存.---Geovin Du(涂聚文)




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
2021-12-14 java:create package