c: thread in Ubuntu 22.04
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 | /** * @file helloworld.c * @author your name (geovindu@163.com) * @brief thread * @version 0.1 * @date 2023-10-24 * ide: vscode c11,c17 Ubuntu 22.04 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2023 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants 2023 * */#include<stdlib.h>#include<stdio.h>#include<ctype.h>#include<string.h>#include<malloc.h>#include<time.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<sys/wait.h>#include<threads.h>#include<math.h>#include<unistd.h> //Header file for sleep(). man 3 sleep for details. #include<pthread.h> #include "include/CheckTieck.h"#include "include/TakeNumber.h"#define threadcout 5////thrd_t threadId[threadcout];mtx_t task_mtx; struct timespec duration={.tv_sec=1,.tv_nsec=0};size_t task=0;/** * @brief 线程 * * @param agr * @return int */ int execrteTask(void *agr) { mtx_lock(&task_mtx); size_t local_task = ++task; mtx_unlock(&task_mtx); // mtx_lock(&task_mtx); // mutex lock - blocks until acquired // printf_s("Task %zd started.\n", ++task); printf("Task %zd started.\n", local_task); thrd_sleep(&duration, NULL); // Just to make things take longer... double x = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i< 1000000000 ; ++i) x = sqrt(3.1415926); printf(" Task %zd finished\n", local_task); // printf_s(" Task %zd finished\n", task); // mtx_unlock(&task_mtx); // mutex unlock - for use by other threads return 0; }// 定义一个结构体,用于存储函数的参数和返回值typedef struct { int x; // 输入参数 int y; // 返回值} data_t;// 定义一个函数,接受一个指向data_t结构体的指针,打印该结构体中的x值的平方,并将该值加一存入y中void *square_and_add_one(void *arg) { data_t *data = (data_t *)arg; printf("The square of %d is %d\n", data->x, data->x * data->x); data->y = data->x + 1; return NULL;}/** * @brief * * @param argc * @param argv * @return int */int main(void){ int argc; char *argv;//[]={'\0'}; char ddd[11]="The hello world"; argv=ddd; argc=2; // 检查命令行参数的个数,至少需要一个参数 if (argc < 2) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <number>\n", argv[0]); exit(1); } // 将第一个参数转换为整数 printf("%s",&argv[1]); int thdnum = atoi(&argv[1]); // 创建一个data_t结构体,并初始化其x值为num data_t data; data.x = thdnum; // 创建一个线程,并传入square_and_add_one函数和data结构体的地址 pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, square_and_add_one, &data); // 等待线程结束,并打印其返回值 pthread_join(tid, NULL); printf("The thread returned %d\n", data.y); if(thrd_error == mtx_init(&task_mtx, mtx_timed)) { //int ret = vfprintf(stdout, fmt, vl); fprintf(stderr, "Mutex creation failed.\n"); //stderr thrd_exit(-2); } // Create the threads to carry out the tasks concurrently for(size_t i = 0 ; i<threadcout ; ++i) if(thrd_error == thrd_create(&(threadId[i]), execrteTask, NULL)) { fprintf(stderr, "Thread creation failed.\n"); thrd_exit(-1); } // Join the additional threads to the main thread for(size_t j = 0 ; j <threadcout ; ++j) thrd_join(threadId[j], NULL); pid_t pid; int status; pid = fork(); // 创建一个新进程 if (pid < 0) { // 如果创建失败,输出错误信息 fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed"); return 1; } else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程 printf("I am the child %d\n",pid); execl("/bin/ls", "ls", NULL); // 在子进程中执行 /bin/ls 程序 printf("I am the child %d, and execl failed\n",pid); // 如果 execl 返回,那么说明出错 } else { // 父进程 wait(&status); // 等待子进程结束 printf("I am the parent %d, and my child has ended\n",pid); } printf("hello wolrd, c launguage! weblcome geovindu!涂聚文"); QueueCalling *queue1; char select='1'; //int num=1;//顾客序号 int num=0; //叫号编号 queue1=QueueInit(); //初始化队列 if(queue1==NULL) { printf("创建队列时出错!\n"); //getch(); getchar(); return 0; } do{ //这里处理,列表不会显示两次 if(select=='1' || select=='2') { printf("\n请选择具体操作:\n"); printf("1.新到顾客\n"); printf("2.下一个顾客\n"); printf("0.退出\n") ; fflush(stdin); } select=getchar();//getch(); switch(select) { case '1': add(queue1); printf("\n现在共有%d位顾客在等候!\n",QueueLen(queue1)); break; case '2': next(queue1); printf("\n现在共有%d位顾客在等候!\n",QueueLen(queue1)); break; case '0': break; } }while(select!='0'); QueueFree(queue1); //释放队列 //getch(); getchar(); return 0;} |
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 | /** * @file helloworld.c * @author your name (geovindu@163.com) * @brief thread * @version 0.1 * @date 2023-10-24 * ide: vscode c11,c17 Ubuntu 22.04 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2023 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants 2023 * */#include<stdlib.h>#include<stdio.h>#include<ctype.h>#include<sys/types.h>#include<string.h>#include<malloc.h>#include<time.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<sys/wait.h>#include<threads.h>#include<math.h>#include<unistd.h> //Header file for sleep(). man 3 sleep for details. #include<pthread.h> #include "include/CheckTieck.h"#include "include/TakeNumber.h"#include "include/twoDimensional.h"#define threadcout 5////thrd_t threadId[threadcout];mtx_t task_mtx; struct timespec duration={.tv_sec=1,.tv_nsec=0};size_t task=0;/** * @brief 线程 * * @param agr * @return int */ int execrteTask(void *agr) { mtx_lock(&task_mtx); size_t local_task = ++task; mtx_unlock(&task_mtx); // mtx_lock(&task_mtx); // mutex lock - blocks until acquired // printf_s("Task %zd started.\n", ++task); printf("Task %zd started.\n", local_task); thrd_sleep(&duration, NULL); // Just to make things take longer... double x = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i< 1000000000 ; ++i) x = sqrt(3.1415926); printf(" Task %zd finished\n", local_task); // printf_s(" Task %zd finished\n", task); // mtx_unlock(&task_mtx); // mutex unlock - for use by other threads return 0; }// 定义一个结构体,用于存储函数的参数和返回值typedef struct { int x; // 输入参数 int y; // 返回值} data_t;// 定义一个函数,接受一个指向data_t结构体的指针,打印该结构体中的x值的平方,并将该值加一存入y中void *square_and_add_one(void *arg) { data_t *data = (data_t *)arg; printf("The square of %d is %d\n", data->x, data->x * data->x); data->y = data->x + 1; return NULL;}/** * @brief * * @param argc * @param argv * @return int */int main(void){ pid_t pid; int status; pid = fork(); // 创建一个新进程 if (pid < 0) { // 如果创建失败,输出错误信息 fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed"); return 1; } else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程 printf("I am the child %d\n",pid); //execl("/bin/ls", "ls", NULL); // 在子进程中执行 /bin/ls 程序 //execl("/usr/bin/env", "env", NULL, NULL); //OK打印环境变量 //execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c","echo 'Hello!' >> test.txt",(char *) NULL); //OK 添加到文件文尾 execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c","echo 'Hello!' > test.txt",(char *) NULL); //OK 只有hello的字符 //execle("/bin/ls","ls","./",NULL); // ok显示文件夹的文件 //execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", "/bin/cat > test.txt", (char *) NULL); //ok 创建文件,并可以输入内容,关闭即保存 //execl("/bin/cat","cat","1.txt","2.txt",NULL);//显示了两个文件内容 //execl("/bin/cat", "cat", "-n", "1.js", NULL);//ok 读文件显示号 //execl("/bin/cat", "cat", "-n", "1.txt", NULL); //ok 读文件显示号 printf("I am the child %d, and execl failed\n",pid); // 如果 execl 返回,那么说明出错 } else { // 父进程 wait(&status); // 等待子进程结束 printf("I am the parent %d, and my child has ended\n",pid); } return 0;} |
如何在程序里使用这些内存。
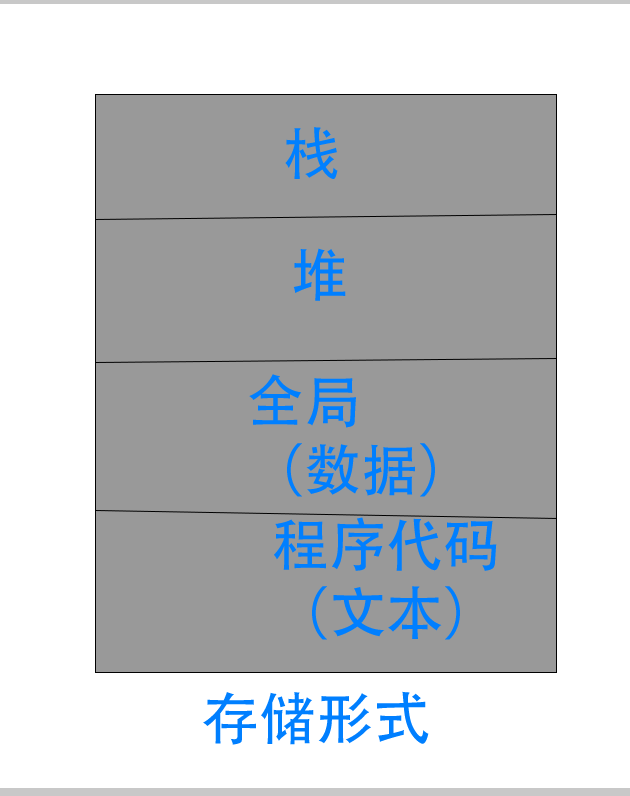
C的存储结构是非常重要的,C的存储结构主要由堆区、栈区、全局常量区、程序代码区组成。其中重要的是堆和栈,它们都属于RAM; 因此,它们是个稳定的,并且在运行时经常会改变。
函数的局部变量是在栈中创建的;同时,在堆中指针是需要你的程序手动处理的(malloc/free),堆的作用域是在程序被运行时。
栈存储变量的空间比堆的小,其原理是为了让栈存储那些只需要短暂的变量。
另一方面,堆可以处理内存需求更大的变量,堆是动态分配的。当然,堆的访问速度取决于每个段的访问对象。堆由开发人员手动处理。也就是说,有可能出现内存泄漏。堆中的变量是全局的,可以通过指针访问。
栈是一个后进先出(last-in-first-out,LIFO)的结构,这对于递归函数非常有用。每次声明一个变量,它将被在于该段的顶部(这就是一个使用pust-pop函数的后进先出结构的栈)。
输入输出格式说明符:
输出格式说明符
printf
printf_s
sprintf
sprintf_s
snprintf
snprintf_s
fprintf
fprintf_s
vfprintf
vsprintf
vprintf
vsnprintf
vfprintf_s
vprintf_s
vsnprintf_s
vsprintf_s
输入格式说明符
scanf
scanf_s
vscanf
vscanf_s
sscanf
sscanf_s
vsscanf
vsscanf_s
fscanf
fscanf_s
vfscanf
vfscanf_s
来源: Beginnin C: From Beginner to Pro, Sixth Edition
https://github.com/Apress/beginning-c-6e
https://www.demo2s.com/c/c-execl-bin-ls-ls-a-l-null.html
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg0, ... /*, (char *)0 */);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg0, ... /*,
(char *)0, char *const envp[]*/);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg0, ... /*, (char *)0 */);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execve(const char *path, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int fexecve(int fd, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
1 | execl("/bin/cat","cat","1.js",">","2.js",NULL); |




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
2022-10-24 Python: Observer Pattern
2022-10-24 Python: Mediator Pattern
2011-10-24 Csharp windowform bindingNavigator,bindingSource,DataGridView簡單分頁:首頁,上一頁,下一頁,末頁
2009-10-24 World Currency Symbols世界货币符号