typescript: Iterator Pattern
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 | /** * Iterator Pattern 迭代器是一种行为设计模式, 让你能在不暴露复杂数据结构内部细节的情况下遍历其中所有的元素 * file: Iteratorts.ts npm install -g babel-cli * Intent: Lets you traverse elements of a collection without exposing its * underlying representation (list, stack, tree, etc.). */interface Iterator<T> { //,any,undefined /** * Return the current element. */ current(): T;//string; // /** * Return the current element and move forward to next element. */ next(): T;//string; //T /** * Return the key of the current element. */ key(): number; /** * Checks if current position is valid. */ valid(): boolean; /** * Rewind the Iterator to the first element. */ rewind(): void;}/** * */interface Aggregator { /** * Retrieve an external iterator. */ getIterator(): Iterator<string>; // ,any,undefined}/** * Concrete Iterators implement various traversal algorithms. These classes * store the current traversal position at all times. ,any,undefined */ class AlphabeticalOrderIterator implements Iterator<string> { //new AlphabeticalOrderIterator(this, true) Iterator<string, any, undefined> private collection: WordsCollection; //aggregates: Aggregator[] /** * Stores the current traversal position. An iterator may have a lot of * other fields for storing iteration state, especially when it is supposed * to work with a particular kind of collection. */ private position: number = 0; /** * This variable indicates the traversal direction. */ private reverse: boolean = false; /** * * @param collection * @param reverse */ constructor(collection: WordsCollection, reverse: boolean = false) { this.collection = collection; this.reverse = reverse; if (reverse) { this.position = collection.getCount() - 1; } } /** * */ public rewind() { this.position = this.reverse ? this.collection.getCount() - 1 : 0; } /** * * @returns */ public current(): string { return this.collection.getItems()[this.position]; } /** * * @returns */ public key(): number { return this.position; } /** * * @returns */ public next() { let item=""; //item = this.collection.getItems()[this.position]; //this.position += this.reverse ? -1 : 1; //return item; /* item = this.collection.getItems()[this.position].toString(); this.position += this.reverse ? -1 : 1; */ if (this.position < this.collection.getCount.length) { const aggregate = this.collection[this.position] this.position += 1 return aggregate } item = this.collection.getItems()[this.position]; this.position += this.reverse ? -1 : 1; return item; // throw new Error('At End of Iterator'); } /** * * @returns * */ public valid(): boolean { if (this.reverse) { return this.position >= 0; } return this.position < this.collection.getCount(); }}/** * Concrete Collections provide one or several methods for retrieving fresh * iterator instances, compatible with the collection class. */class WordsCollection implements Aggregator { /** * */ private items: string[] = []; /** * * @returns */ public getItems(): string[] { return this.items; } /** * * @returns */ public getCount(): number { return this.items.length; } /** * * @param item */ public addItem(item: string): void { this.items.push(item); } /** * * @returns */ public getIterator(): Iterator<string> { let str=""; //str=new AlphabeticalOrderIterator(this).next().getIterator(); let d= new AlphabeticalOrderIterator(this).next(); //return; return new AlphabeticalOrderIterator(this); } /** * * @returns */ public getReverseIterator(): Iterator<string> { let str=""; //new AlphabeticalOrderIterator(this, true).next(); //return ; return new AlphabeticalOrderIterator(this, true); }}/** * 2. */interface IIterator { next(): IAggregate // Return the object in collection hasNext(): boolean // Returns Boolean whether at end of collection or not}class IteratorConcept implements IIterator { // The concrete iterator (iterable) index: number aggregates: IAggregate[] constructor(aggregates: IAggregate[]) { this.index = 0 this.aggregates = aggregates } next() { if (this.index < this.aggregates.length) { const aggregate = this.aggregates[this.index] this.index += 1 return aggregate } throw new Error('At End of Iterator') } hasNext() { return this.index < this.aggregates.length }}interface IAggregate { // An interface that the aggregates should implement method(): string //void}class Aggregate implements IAggregate { // A concrete object method(): string { //void let str=""; console.log('This method has been invoked') str="This method has been invoked"; return str; }}// The Clientconst AGGREGATES = [ new Aggregate(), new Aggregate(), new Aggregate(), new Aggregate(),]let pubIter1="";let pubIter2="";let pubIter3="Geovin Du";let pubIter4="geovindu";// AGGREGATES is an array that is already iterable by default.// but we can create own own iterator on top anyway.const ITERABLE = new IteratorConcept(AGGREGATES)while (ITERABLE.hasNext()) { pubIter1=pubIter1+","+ ITERABLE.next().method()}/** * 1. The client code may or may not know about the Concrete Iterator or Collection * classes, depending on the level of indirection you want to keep in your * program. */const collection = new WordsCollection();collection.addItem('First');collection.addItem('Second');collection.addItem('Third');const iterator = collection.getIterator();/**/console.log('Straight traversal:');let cc=0;//while (iterator.valid())//pubIter2=pubIter2+iterator.current();for(cc=0;cc<collection.getCount();cc++) { let getstr=iterator.next(); console.log(getstr); pubIter2=pubIter2+getstr;}console.log('');console.log('Reverse traversal:');const reverseIterator = collection.getReverseIterator();//pubIter3=pubIter3+reverseIterator.current();//while (reverseIterator.valid()) { //console.log(reverseIterator.next());let dui=0;for(dui=0;dui<collection.getCount();dui++){ let getstr=reverseIterator.next(); console.log(getstr); pubIter3=pubIter3+getstr;}//}let messageIter: string = 'Hello World,This is a typescript!,涂聚文 Geovin Du.Web';document.body.innerHTML = messageIter+",<br/>one="+pubIter1+",<br/>two="+pubIter2+",<br/>three="+pubIter3+",<br/>four="+pubIter4+",<br/>TypeScript Iterator Design Pattern 迭代器模式"; |
调用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | <!doctype html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <head><title>TypeScript Hello Iterator Design Pattern 迭代器</title> <meta name="Description" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/><meta name="Keywords" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/><meta name="author" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/> </head> <body> <script src="dist/Iteratorts.js"> // //type="module" </script> </body></html> |
输出:
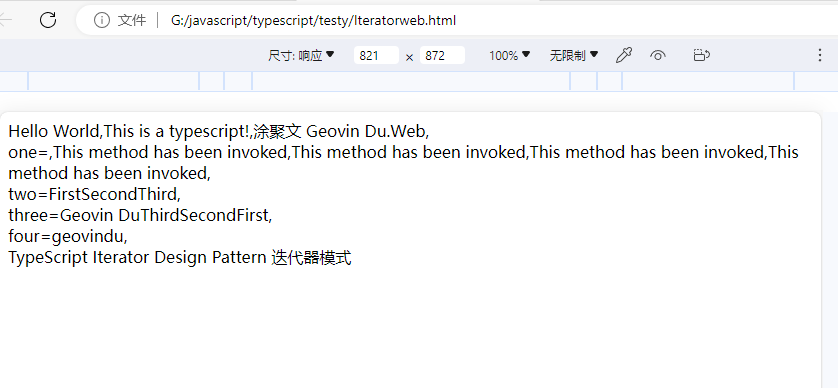
哲学管理(学)人生, 文学艺术生活, 自动(计算机学)物理(学)工作, 生物(学)化学逆境, 历史(学)测绘(学)时间, 经济(学)数学金钱(理财), 心理(学)医学情绪, 诗词美容情感, 美学建筑(学)家园, 解构建构(分析)整合学习, 智商情商(IQ、EQ)运筹(学)生存.---Geovin Du(涂聚文)
分类:
Ajax&JavaScript
标签:
desgin patterns
, 設計模式




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
2022-10-11 CSharp: Mediator Pattern in donet core 3
2018-10-11 SQL Server: Datetime,Datetime2
2016-10-11 MySQL 5.7 create VIEW or FUNCTION or PROCEDURE