typescript: Bridge Pattern
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 | /** * Bridge Pattern 桥接是一种结构型设计模式, 可将业务逻辑或一个大类拆分为不同的层次结构, 从而能独立地进行开发。 * https://dev.to/takaakit/uml-diagram-for-gof-design-pattern-examples-in-typescript-46d5#singleton * The Abstraction defines the interface for the "control" part of the two class * hierarchies. It maintains a reference to an object of the Implementation * hierarchy and delegates all of the real work to this object. */class AbstractionBridge { /** * */ protected implementation: Implementation; /** * * @param implementation */ constructor(implementation: Implementation) { this.implementation = implementation; } /** * * @returns */ public operation(): string { const result = this.implementation.operationImplementation(); return `Abstraction: Base operation with:\n${result}`; }}/** * You can extend the Abstraction without changing the Implementation classes. */class ExtendedAbstraction extends AbstractionBridge { /** * * @returns */ public operation(): string { const result = this.implementation.operationImplementation(); return `ExtendedAbstraction: Extended operation with:\n${result}`; }}/** * The Implementation defines the interface for all implementation classes. It * doesn't have to match the Abstraction's interface. In fact, the two * interfaces can be entirely different. Typically the Implementation interface * provides only primitive operations, while the Abstraction defines higher- * level operations based on those primitives. */interface Implementation { /** * */ operationImplementation(): string;}/** * Each Concrete Implementation corresponds to a specific platform and * implements the Implementation interface using that platform's API. */class ConcreteImplementationA implements Implementation { /** * * @returns */ public operationImplementation(): string { return 'ConcreteImplementationA: Here\'s the result on the platform A.'; }}class ConcreteImplementationB implements Implementation { /** * * @returns */ public operationImplementation(): string { return 'ConcreteImplementationB: Here\'s the result on the platform B.'; }}/** * Except for the initialization phase, where an Abstraction object gets linked * with a specific Implementation object, the client code should only depend on * the Abstraction class. This way the client code can support any abstraction- * implementation combination. */function clientCodeBridge(abstraction: AbstractionBridge) { // .. console.log(abstraction.operation()); return abstraction.operation(); // ..}/** * The client code should be able to work with any pre-configured abstraction- * implementation combination. */let implementation = new ConcreteImplementationA();let abstraction = new AbstractionBridge(implementation);clientCodeBridge(abstraction);let sbridge1=clientCodeBridge(abstraction);console.log('');implementation = new ConcreteImplementationB();abstraction = new ExtendedAbstraction(implementation);clientCodeBridge(abstraction);let sbridge="gevindu";let sbridge2=clientCodeBridge(abstraction);let messagebridge: string = 'Hello World,This is a typescript!,涂聚文 Geovin Du Web';document.body.innerHTML = messagebridge+","+sbridge1+","+sbridge2+",TypeScript Bridge Pattern 桥接模式" |
调用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | <!doctype html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <head><title>TypeScript:桥接模式</title> <meta name="Description" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/><meta name="Keywords" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/><meta name="author" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/> </head> <body> <script src="dist/Bridgets.js"></script> </body></html> |
输出:
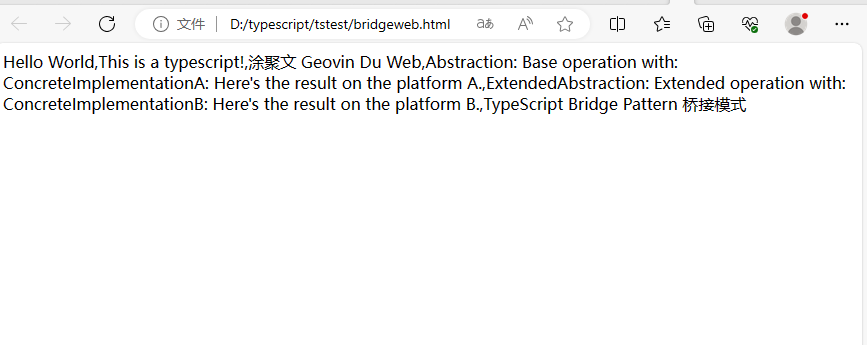
哲学管理(学)人生, 文学艺术生活, 自动(计算机学)物理(学)工作, 生物(学)化学逆境, 历史(学)测绘(学)时间, 经济(学)数学金钱(理财), 心理(学)医学情绪, 诗词美容情感, 美学建筑(学)家园, 解构建构(分析)整合学习, 智商情商(IQ、EQ)运筹(学)生存.---Geovin Du(涂聚文)
分类:
Ajax&JavaScript
标签:
desgin patterns
, 設計模式




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
2022-10-07 CSharp: Visitor Pattern in donet core 3
2022-10-07 CSharp: Singleton Pattern in donet core 3