TypeScript: Factory Method pattern
人与人沟通,除了信息对称之外,还有认知....
npm install -g typescript
npm install -g ts-node
index.ts
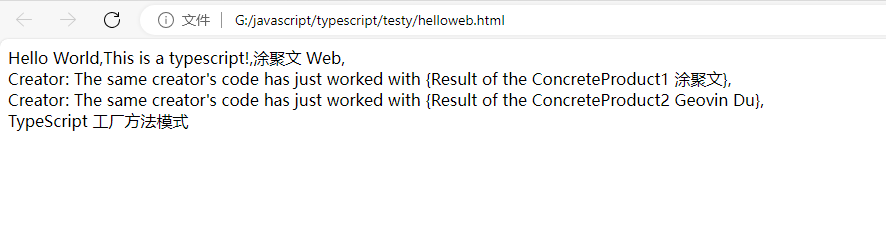
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 | //import * as fs from "fs";//TypeScript 工厂方法模式 Factory Method in TypeScript/** * The Creator class declares the factory method that is supposed to return an * object of a Product class. The Creator's subclasses usually provide the * implementation of this method. */abstract class Creator { /** * Note that the Creator may also provide some default implementation of the * factory method. */ public abstract factoryMethod(): Product; /** * Also note that, despite its name, the Creator's primary responsibility is * not creating products. Usually, it contains some core business logic that * relies on Product objects, returned by the factory method. Subclasses can * indirectly change that business logic by overriding the factory method * and returning a different type of product from it. */ public someOperation(): string { // Call the factory method to create a Product object. const product = this.factoryMethod(); // Now, use the product. return `Creator: The same creator's code has just worked with ${product.operation()}`; }}/** * Concrete Creators override the factory method in order to change the * resulting product's type. */class ConcreteCreator1 extends Creator { /** * Note that the signature of the method still uses the abstract product * type, even though the concrete product is actually returned from the * method. This way the Creator can stay independent of concrete product * classes. */ public factoryMethod(): Product { return new ConcreteProduct1(); }}class ConcreteCreator2 extends Creator { public factoryMethod(): Product { return new ConcreteProduct2(); }}/** * The Product interface declares the operations that all concrete products must * implement. */interface Product { operation(): string;}/** * Concrete Products provide various implementations of the Product interface. */class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product { public operation(): string { return '{Result of the ConcreteProduct1 涂聚文}'; }}/** * 返回字符串 */class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product { public operation(): string { return '{Result of the ConcreteProduct2 Geovin Du}'; }}/** * The client code works with an instance of a concrete creator, albeit through * its base interface. As long as the client keeps working with the creator via * the base interface, you can pass it any creator's subclass. */function clientCode(creator: Creator) { // ... console.log('Client: I\'m not aware of the creator\'s class, but it still works.'); console.log(creator.someOperation()); // ...}const hello : string = "Hello World,This is a typescript!,涂聚文,hi."console.log(hello)console.log('App: Launched with the ConcreteCreator1.');let cr1=new ConcreteCreator1();clientCode(cr1);let pu1:string =cr1.someOperation();console.log('');console.log('App: Launched with the ConcreteCreator2.');let cr2=new ConcreteCreator2();clientCode(cr2);let pu2:string=cr2.someOperation();console.log("geovindu");let message: string = 'Hello World,This is a typescript!,涂聚文 Web';document.body.innerHTML = message+","+pu1+","+pu2+",TypeScript 工厂方法模式";/*const path = "./src/message.txt";const data = "Hello World!";const encoding = "utf8";console.log(data);fs.writeFile(path, data, encoding, error => { if (error) { console.log(error); }});*///https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/typescript/typescript-debugging |
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | <!doctype html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <head><title>TypeScript Hello Web</title> <meta name="Description" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/> <meta name="Keywords" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/> <meta name="author" content="geovindu,涂聚文,Geovin Du"/> </head> <body> <script src="dist/index.js"></script> </body></html> |
哲学管理(学)人生, 文学艺术生活, 自动(计算机学)物理(学)工作, 生物(学)化学逆境, 历史(学)测绘(学)时间, 经济(学)数学金钱(理财), 心理(学)医学情绪, 诗词美容情感, 美学建筑(学)家园, 解构建构(分析)整合学习, 智商情商(IQ、EQ)运筹(学)生存.---Geovin Du(涂聚文)
分类:
Ajax&JavaScript
标签:
desgin patterns




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
2022-09-25 CSharp:Flyweight Patterns
2022-09-25 Java: Iterator/Cursor Patterns
2011-09-25 SQLHelper.cs