python: Sorting Algorithms
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 | # encoding: utf-8# 版权所有 2023 涂聚文有限公司# 许可信息查看:Python Sorting Algorithms# 描述: * https://www.programiz.com/dsa/counting-sort# * https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sorting-algorithms/# Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂聚文.# IDE : PyCharm 2023.1 python 311# Datetime : 2023/9/21 21:55# User : geovindu# Product : PyCharm# Project : EssentialAlgorithms# File : SortingAlgorithms.py# explain : 学习import tkinter as tkfrom tkinter import ttkimport itertoolsimport mathimport sysimport osfrom typing import Listclass SortingAlgorithms(object): """ 排序算法 """ def BubbleSort(array:list): """ 1。Bubble Sort冒泡排序法 :param array int数组 :return: """ # loop to access each array element for i in range(len(array)): # loop to compare array elements for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1): # compare two adjacent elements # change > to < to sort in descending order if array[j] > array[j + 1]: # swapping elements if elements # are not in the intended order temp = array[j] array[j] = array[j + 1] array[j + 1] = temp def BubbleSort2(array:list): """ 1。Bubble Sort冒泡排序法 :param array int数组 :return: """ # loop through each element of array for i in range(len(array)): # keep track of swapping swapped = False # loop to compare array elements for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1): # compare two adjacent elements # change > to < to sort in descending order if array[j] > array[j + 1]: # swapping occurs if elements # are not in the intended order temp = array[j] array[j] = array[j + 1] array[j + 1] = temp swapped = True # no swapping means the array is already sorted # so no need for further comparison if not swapped: break def SelectionSort(array:list): """ 2 python Program for Selection Sort 选择排序 :param array int数组 :return: """ for i in range(len(array)): # Find the minimum element in remaining # unsorted array min_idx = i for j in range(i+1, len(array)): if array[min_idx] > array[j]: min_idx = j # Swap the found minimum element with # the first element array[i], array[min_idx] = array[min_idx], array[i] def InsertionSort(array:list): """ 3 Insertion Sort插入排序 :param array int数组 :return: """ # Traverse through 1 to len(arr) for i in range(1, len(array)): key = array[i] # Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are # greater than key, to one position ahead # of their current position j = i - 1 while j >= 0 and key < array[j]: array[j + 1] = array[j] j -= 1 array[j + 1] = key def Partition(array, low, high): """ :param array int数组 :param low: :param high: :return: """ # Choose the rightmost element as pivot pivot = array[high] # Pointer for greater element i = low - 1 # Traverse through all elements # compare each element with pivot for j in range(low, high): if array[j] <= pivot: # If element smaller than pivot is found # swap it with the greater element pointed by i i = i + 1 # Swapping element at i with element at j (array[i], array[j]) = (array[j], array[i]) # Swap the pivot element with # the greater element specified by i (array[i + 1], array[high]) = (array[high], array[i + 1]) # Return the position from where partition is done return i + 1 def QuickSort(array, low, high): """ 4 Quick Sort 快速排序 :param array int数组 :param low: :param high: :return: """ if low < high: # Find pivot element such that # element smaller than pivot are on the left # element greater than pivot are on the right pi = SortingAlgorithms.Partition(array, low, high) # Recursive call on the left of pivot SortingAlgorithms.QuickSort(array, low, pi - 1) # Recursive call on the right of pivot SortingAlgorithms.QuickSort(array, pi + 1, high) def MergeSort(array:list): """ 5 Merge Sort 合并/归并排序 :param array int数组 :return: """ if len(array) > 1: # Finding the mid of the array mid = len(array) // 2 # Dividing the array elements L = array[:mid] # Into 2 halves R = array[mid:] # Sorting the first half SortingAlgorithms.MergeSort(L) # Sorting the second half SortingAlgorithms.MergeSort(R) i = j = k = 0 # Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] while i < len(L) and j < len(R): if L[i] <= R[j]: array[k] = L[i] i += 1 else: array[k] = R[j] j += 1 k += 1 # Checking if any element was left while i < len(L): array[k] = L[i] i += 1 k += 1 while j < len(R): array[k] = R[j] j += 1 k += 1 def CountingSort(array:list,hight:int): """ 6 Counting Sort 计数排序 :param array int数组 :param hight 最大的整数 如100,数组中必须小数此数的整数 :return: """ size = len(array) output = [0] * size # Initialize count array dcount = [0] * hight # Store the count of each elements in count array print(size) for i in range(0, size): dcount[array[i]] += 1 # Store the cummulative count 最大的数 for i in range(1, hight): dcount[i] += dcount[i - 1] # Find the index of each element of the original array in count array # place the elements in output array i = size - 1 while i >= 0: output[dcount[array[i]] - 1] = array[i] dcount[array[i]] -= 1 i -= 1 # Copy the sorted elements into original array for i in range(0, size): array[i] = output[i] def CountingSortTo(array: List[int]): """ 6 Counting Sort 计数排序 :param :return: """ max = min = 0 for i in array: if i < min: min = i if i > max: max = i count = [0] * (max - min + 1) for j in range(max - min + 1): count[j] = 0 for index in array: count[index - min] += 1 index = 0 for a in range(max - min + 1): for c in range(count[a]): array[index] = a + min index += 1 def countingSort(array, exp1): """ :param array :param exp1: :return: """ n = len(array) # The output array elements that will have sorted arr output = [0] * (n) # initialize count array as 0 count = [0] * (10) # Store count of occurrences in count[] for i in range(0, n): index = array[i] // exp1 count[index % 10] += 1 # Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual # position of this digit in output array for i in range(1, 10): count[i] += count[i - 1] # Build the output array i = n - 1 while i >= 0: index = array[i] // exp1 output[count[index % 10] - 1] = array[i] count[index % 10] -= 1 i -= 1 # Copying the output array to arr[], # so that arr now contains sorted numbers i = 0 for i in range(0, len(array)): array[i] = output[i] def RadixSort(array:list): """ 7 Radix Sort 基数排序 :param array :return: """ # Find the maximum number to know number of digits max1 = max(array) # Do counting sort for every digit. Note that instead # of passing digit number, exp is passed. exp is 10^i # where i is current digit number exp = 1 while max1 / exp >= 1: SortingAlgorithms.countingSort(array, exp) exp *= 10 def insertionSort(array:list): """ :return: """ for i in range(1, len(array)): up = array[i] j = i - 1 while j >= 0 and array[j] > up: array[j + 1] = array[j] j -= 1 array[j + 1] = up return array def BucketSort(array): """ 8 Bucket Sort 桶排序 :param array :return: """ arr = [] slot_num = 10 # 10 means 10 slots, each # slot's size is 0.1 for i in range(slot_num): arr.append([]) # Put array elements in different buckets for j in array: index_b = int(slot_num * j) arr[index_b].append(j) # Sort individual buckets for i in range(slot_num): arr[i] = SortingAlgorithms.insertionSort(arr[i]) # concatenate the result k = 0 for i in range(slot_num): for j in range(len(arr[i])): array[k] = arr[i][j] k += 1 return array # Bucket Sort in Python def BucketSortTo(array:list): """ 8 Bucket Sort 桶排序 :param array :return: """ bucket = [] # Create empty buckets for i in range(len(array)): bucket.append([]) # Insert elements into their respective buckets for j in array: index_b = int(10 * j) bucket[index_b].append(j) # Sort the elements of each bucket for i in range(len(array)): bucket[i] = sorted(bucket[i]) # Get the sorted elements k = 0 for i in range(len(array)): for j in range(len(bucket[i])): array[k] = bucket[i][j] k += 1 return array def heapify(array:list, Nsize:int, index:int): """ :param array 数组 :param Nsize: 数组长度 :param index: 索引号 :return: """ largest = index # Initialize largest as root l = 2 * index + 1 # left = 2*i + 1 r = 2 * index + 2 # right = 2*i + 2 # See if left child of root exists and is # greater than root if l < Nsize and array[largest] < array[l]: largest = l # See if right child of root exists and is # greater than root if r < Nsize and array[largest] < array[r]: largest = r # Change root, if needed if largest != index: array[index], array[largest] = array[largest], array[index] # swap # Heapify the root. SortingAlgorithms.heapify(array, Nsize, largest) # The main function to sort an array of given size def HeapSort(array:list): """ 9 Heap Sort 堆排序 :param array :return: """ Nsize = len(array) # Build a maxheap. for i in range(Nsize // 2 - 1, -1, -1): SortingAlgorithms.heapify(array, Nsize, i) # One by one extract elements for i in range(Nsize - 1, 0, -1): array[i], array[0] = array[0], array[i] # swap SortingAlgorithms.heapify(array, i, 0) def ShellSort(array:list): """ 10 Shell Sort 希尔排序 :param array 数组 :return: """ # code here nszie=len(array) gap = nszie // 2 while gap > 0: j = gap # Check the array in from left to right # Till the last possible index of j while j < nszie: i = j - gap # This will keep help in maintain gap value while i >= 0: # If value on right side is already greater than left side value # We don't do swap else we swap if array[i + gap] > array[i]: break else: array[i + gap], array[i] = array[i], array[i + gap] i = i - gap # To check left side also # If the element present is greater than current element j += 1 gap = gap // 2 def LinearSearch(array:list,fint:int): """ 11 Linear Search线性搜索 :param array 整数数组 :param fint 要查找的数字 :return: """ nsize=len(array) # Going through array sequencially for i in range(0, nsize): if (array[i] == fint): return i #找到了 return -1 #未找到 def BinarySearch(array:list, x, low, high): """ 12 Binary Search 二分查找 :param x: :param low: :param high: :return: """ if high >= low: mid = low + (high - low) // 2 # If found at mid, then return it if array[mid] == x: return mid # Search the left half elif array[mid] > x: return SortingAlgorithms.BinarySearch(array, x, low, mid - 1) # Search the right half else: return SortingAlgorithms.BinarySearch(array, x, mid + 1, high) else: return -1 def BingoSort(array, size): """ :param array :param size: :return: """ # Finding the smallest element From the Array bingo = min(array) # Finding the largest element from the Array largest = max(array) nextBingo = largest nextPos = 0 while bingo < nextBingo: # Will keep the track of the element position to # shifted to their correct position startPos = nextPos for i in range(startPos, size): if array[i] == bingo: array[i], array[nextPos] = array[nextPos], array[i] nextPos += 1 # Here we are finding the next Bingo Element # for the next pass elif array[i] < nextBingo: nextBingo = array[i] bingo = nextBingo nextBingo = largest |
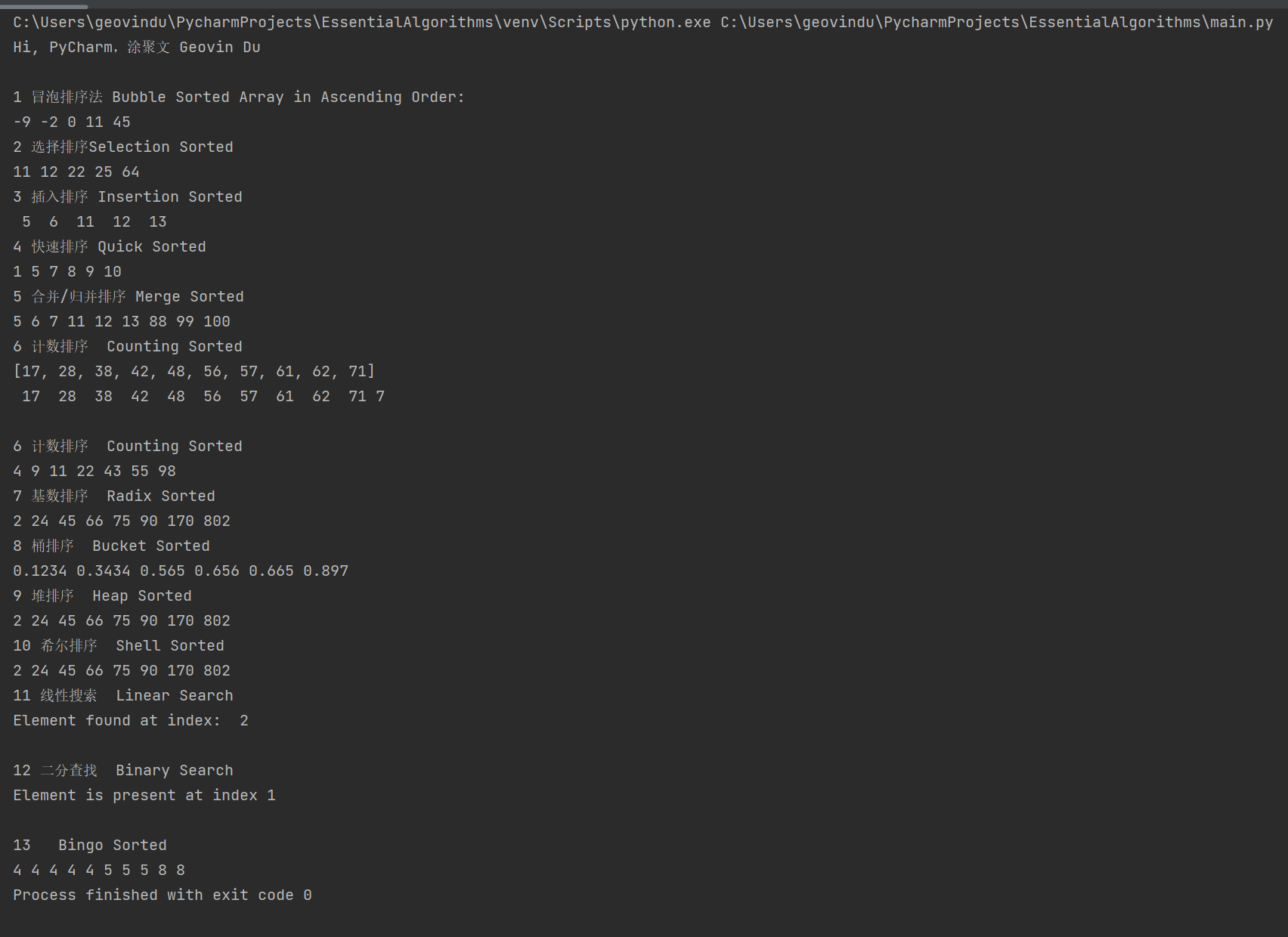
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 | # encoding: utf-8# 版权所有 2023 涂聚文有限公司# 许可信息查看:# 描述:# Author : geovindu,Geovin Du 涂聚文.# IDE : PyCharm 2023.1 python 311# Datetime : 2023/9/21 22:00# User : geovindu# Product : PyCharm# Project : EssentialAlgorithms# File : SortingExample.py# explain : 学习import ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithmsclass Example(object): """" 实例 """ def Bubble(self): """ 1。Bubble Sort冒泡排序法 :return: """ data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9] ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BubbleSort(data) print('\n1 冒泡排序法 Bubble Sorted Array in Ascending Order:') for i in range(len(data)): print("%d" % data[i], end=" ") def Select(self): """ 2 Selection Sort 选择排序 :return: """ geovindu = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11] ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.SelectionSort(geovindu) print("\n2 选择排序Selection Sorted ") for i in range(len(geovindu)): print("%d" % geovindu[i], end=" ") def Insert(self): """ 3 Insertion Sort插入排序 :return: """ arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6] ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.InsertionSort(arr) print("\n3 插入排序 Insertion Sorted ") for i in range(len(arr)): print("% d" % arr[i], end=" ") def Quick(self): """ 4 Quick Sort 快速排序 :return: """ array = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5] N = len(array) # Function call ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.QuickSort(array, 0, N - 1) print("\n4 快速排序 Quick Sorted ") for x in array: print(x, end=" ") def Merge(self): """ 5 Merge Sort 合并/归并排序 :return: """ geovindu = [12, 11, 99, 13, 5, 6, 7,88,100] ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.MergeSort(geovindu) print("\n5 合并/归并排序 Merge Sorted ") for x in geovindu: print(x, end=" ") def Counting(self): """ 6 Counting Sort 计数排序 :return: """ geovindu = [17, 56, 71, 38, 61, 62, 48, 28, 57, 42] ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.CountingSortTo(geovindu) print("\n6 计数排序 Counting Sorted ") print(geovindu) for i in range(0,len(geovindu)): print("% d" % geovindu[i], end=" ") geovindu = [4, 55, 22, 98, 9, 43, 11] ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.CountingSort(geovindu, 100) print("\n6 计数排序 Counting Sorted ") for x in geovindu: print(x, end=" ") def Radix(self): """ 7 Radix Sort 基数排序 :return: """ geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66] print("\n7 基数排序 Radix Sorted ") # Function Call ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.RadixSort(geovindu) for i in range(len(geovindu)): print(geovindu[i], end=" ") def Bucket(self): """ 8 Bucket Sort 桶排序 :return: """ #geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66] geovindu = [0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434] print("\n8 桶排序 Bucket Sorted ") # Function Call du=ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BucketSort(geovindu) for i in range(len(du)): print(du[i], end=" ") def Heap(self): """ 9 Heap Sort 堆排序 :return: """ geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66] print("\n9 堆排序 Heap Sorted ") # Function Call ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.HeapSort(geovindu) for i in range(len(geovindu)): print(geovindu[i], end=" ") def Shell(self): """ 10 Shell Sort 希尔排序 :return: """ geovindu = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66] print("\n10 希尔排序 Shell Sorted ") # Function Call ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.ShellSort(geovindu) for i in range(len(geovindu)): print(geovindu[i], end=" ") def Linear(self): """ 11 Linear Search 线性搜索 :return: """ array = [2, 4, 8,0, 1, 9] x = 8 n = len(array) result = ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.LinearSearch(array,x) print("\n11 线性搜索 Linear Search ") if (result == -1): print("Element not found") else: print("Element found at index: ", result) def Binary(self): """ 12 Binary Search 二分查找 :return: """ array = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] x = 4 result = ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BinarySearch(array, x, 0, len(array) - 1) print("\n12 二分查找 Binary Search ") if result != -1: print("Element is present at index " + str(result)) else: print("Not found") def Bingo(self): """ 13 Bingo Sort :return: """ arr = [5, 4, 8, 5, 4, 8, 5, 4, 4, 4] ChapterOne.SortingAlgorithms.SortingAlgorithms.BingoSort(arr, size=len(arr)) print("\n13 Bingo Sorted ") for i in range(len(arr)): print(arr[i], end=" ") |
调用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | exm=BLL.SortingExample.Example()exm.Bubble()exm.Select()exm.Insert()exm.Quick()exm.Merge()exm.Counting()exm.Radix()exm.Bucket()exm.Heap()exm.Shell()exm.Linear()exm.Binary()exm.Bingo() |
哲学管理(学)人生, 文学艺术生活, 自动(计算机学)物理(学)工作, 生物(学)化学逆境, 历史(学)测绘(学)时间, 经济(学)数学金钱(理财), 心理(学)医学情绪, 诗词美容情感, 美学建筑(学)家园, 解构建构(分析)整合学习, 智商情商(IQ、EQ)运筹(学)生存.---Geovin Du(涂聚文)




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!
2022-09-23 CSharp: Decorator Pattern
2022-09-23 Java: Template Method Pattern