移动端事件
1、移动端事件包括:Touch(触摸事件)、Pointer(指针事件)
2、Touch事件的类型
- touchstart(手指按到屏幕,PC端无效)
- touchmove(手指在屏幕上移动,移出div后同样生效)
- touchend(手指抬起,离开屏幕)
- touchcancel(手指在屏幕上的时候,发生了一些意外,比如电话打进来或者有弹出层)
touchend和touchcancel往往只触发一个
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: olive;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
div.addEventListener("touchstart",function(){
console.log('touchstart');
})
div.addEventListener('touchmove',function(){
console.log('touchmove')
})
div.addEventListener('touchend',function(){
console.log('touchend')
})
div.addEventListener('touchcancel',function(){
console.log('touchcancel')
})
</script>
</html>
3、Touch事件的注意事项
- Touch事件在PC端不能触发,鼠标事件在PC端和移动端都能触发、
- 即使触摸点移出目标元素,touchmove依然会触发,但是onmousemove不会触发
- Touch事件的特征判断(判断浏览器是否支持Touch事件,类似于onload的判断)
console.log("onload" in window) (true)
console.log("ontouchstart" in window)
- DOM2级和DOM0级都支持
4、event对象的常用属性
- 事件类型type
- 目标元素target
- 触摸点
- touches:屏幕上的所有触摸点(返回的是touchList数组)
- targetTouches:仅包含事件目标的触摸点
- changedTouches:事件触发时,状态发生了改变的所有触摸点

5、触摸点的常用属性
- 触摸点,即touches数组里面的元素
- identifier,触摸点id(唯一标志符),一般多指触摸有用
- target,目标元素,获取的是目标触摸点的DOM元素
- screenX / screenY:触摸点相对于屏幕左边缘的X、Y坐标(较少使用)
- clientX / clientY:触摸点相对于可视区左边缘的X、Y坐标,不包括任何滚动偏移
- pageX / pageY:触摸点相对于HTML文档左边缘的X、Y坐标,包括滚动偏移(pageX = clientX + 滚动条横向滚动的距离)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: olive;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
div.addEventListener("touchstart",function(e){
//单指触摸
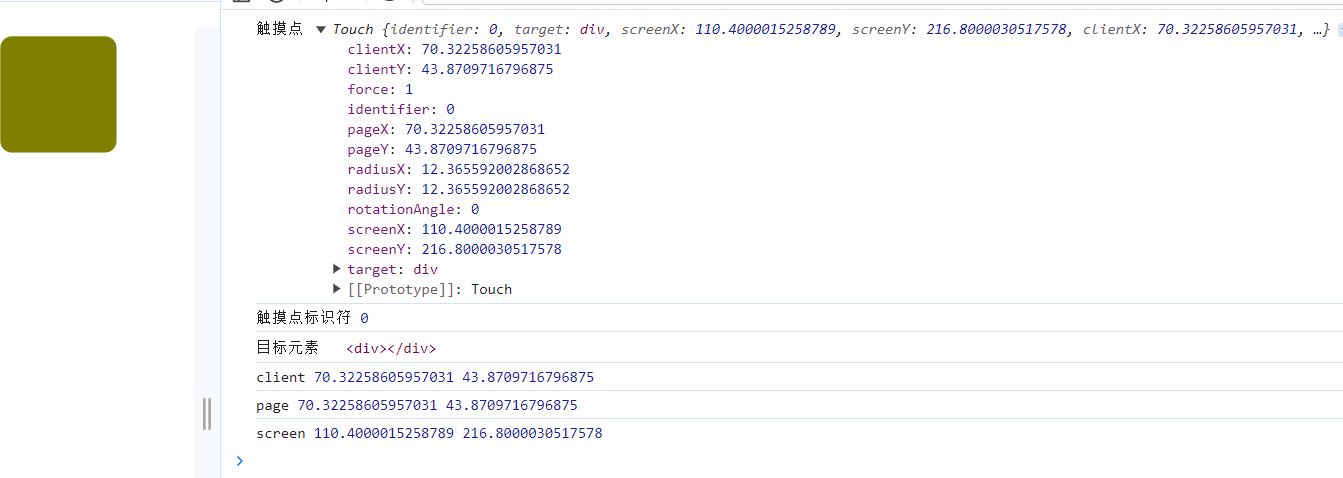
console.log('触摸点',e.touches[0]);
//获取第一个触摸点的唯一标识符
console.log('触摸点标识符',e.touches[0].identifier);
//获取第一个触摸点的DOM元素
console.log('目标元素',e.touches[0].target);
console.log('client',e.touches[0].clientX,e.touches[0].clientY);
console.log('page',e.touches[0].pageX,e.touches[0].pageY);
console.log('screen',e.touches[0].screenX,e.touches[0].screenY);
})
</script>
</html>
6、阻止浏览器的默认行为
阻止scrolling(滚动)、pinch/zoom(手指缩放)、鼠标事件等默认行文
- 使用meta标签:使用viewport meta标签并设置user-scalable=no可以阻止用户缩放页面(将禁止所有的缩放功能,包括双指缩放)
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no">
- 使用CSS:可以将CSS的touch-action属性设置为manipulation来阻止双击放大行为。这不会影响页面的其他缩放功能
touch-action的用法详见:touch-action - CSS:层叠样式表 | MDN (mozilla.org)
html, body {
touch-action: manipulation;
}
- 使用JS:通过监听;连续的两次点击事件并阻止默认行为来禁止双击放大
let lastTouchTime = 0;
document.addEventListener('touchstart', function (event) {
const currentTime = Date.now();
if (currentTime - lastTouchTime < 300) { // 300ms内的连续点击视为双击
event.preventDefault();
}
lastTouchTime = currentTime;
}, { passive: false }); // 这里添加了 { passive: false },因为一些浏览器(如Google)缩放视为被动事件,不能阻止,需要关掉
7、单指拖拽(Touch)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: olive;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body style="height: 2000px;">
<div>hello world</div>
</body>
<script>
const drag = $el => {
//定义开始位置对象
const startPos = {};
//定义移动位置对象
const movePos = {};
//定义结束位置对象
const curPos = {
x: 0,
y: 0
};
//添加事件函数
$el.addEventListener("touchstart", startHandler,false);
$el.addEventListener("touchmove", moveHandler,false);
$el.addEventListener("touchend", endHandler,false);
$el.addEventListener("touchcancel", endHandler,false);
function startHandler(e) {
//清除浏览器默认行为
e.preventDefault();
//定义当前的接触点(单指)
const touch = e.changedTouches[0];
//将当前接触点的位置信息存入startPos
startPos.x = touch.pageX;
startPos.y = touch.pageY;
}
function moveHandler(e) {
//定义移动后接触点(单指)
const touch = e.changedTouches[0];
//计算移动的距离
movePos.x = curPos.x + touch.pageX - startPos.x;
movePos.y = curPos.y + touch.pageY - startPos.y;
//将移动的距离通过translate3d表现出来(!important:使用``,而不是'')
$el.style.transform = `translate3d(${movePos.x}px,${movePos.y}px,0)`;
}
function endHandler() {
curPos.x = movePos.x;
curPos.y = movePos.y;
}
};
var div = document.querySelector("div");
drag(div);
</script>
</html>
8、Pointer事件的类型
既有鼠标事件的影子,又有touch触摸事件的影子
在PC端触发,相当于mouse事件,在移动端触发,相当于touch事件
pointerover==> mouseoverpointerenter==> mouseenterpointerout==> mouseoutpointerleave==> mouseleavepointerdown==> mousedown/touchstartpointermove==> mousemove/touchmovepointerup==> mouseup/touchendpointercancel==> touchcancel

9、注意事项
Pointer事件直接继承了鼠标事件,在此基础上又添加了其他一些内容,处理Pointer事件和处理鼠标事件几乎一致
Pointer事件在PC端和移动端都会触发
触摸点移出目标元素,touchmove事件会持续触发,pointermove和mousemove事件不会再被触发
Pointer事件的特征检测(判断浏览器是否支持Pointer事件),方法与load和touch相同
// Pointer 事件的特征检测.html
console.log("onpointermove" in window);
10、event对象的常用属性
所有属性都在event对象上,没有触摸点属性(一般只会有一个指针)
- pointerId,指针id(唯一标识符)
- type,事件类型
- pointerType,指针类型(鼠标、笔、触摸等)
- target,目标元素
- screenX / screenY,指针相对于屏幕左边缘的X、Y坐标
- clientX / clientY(也称 x/y),指针相对于可视区域左边缘的X、Y坐标,不包括任何滚动
- pageX / pageY,指针相对于HTML文档左边缘的X、Y坐标,包括页面的滚动(pageX = clientX + 页面横向滚动的距离)
11、阻止浏览器默认行为
阻止scrolling,pinch/zoom,鼠标事件等默认行为
Pointer的事件处理函数中,e.preventDefault() 阻止的是PC端的默认行为(不能阻止scrolling,pinch/zoom,鼠标事件等默认行为,可以阻止图片拖动的默认行为)
可以在touch的事件处理函数中使用e.preventDefault()阻止移动端的默认行为
// 在 touch 的事件处理函数中使用 evt.preventDefault().html
const div = document.querySelector("div");
div.addEventListener("pointerdown", (ev) => {
// 指针id(唯一标识符)
console.log(ev.pointerId);
// type 事件类型
console.log(ev.type);
});
div.addEventListener("touchstart", (ev) => {
ev.preventDefault();
});
也可以使用touch-action设置触摸操作时浏览器的默认行为(与touch一致)
12、单指拖拽(Pointer)
在移动端和PC端都可以进行拖拽
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: red;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box" id="box"></div>
</body>
<script>
//定义函数
const drag = $el => {
//定义开始位置对象
const startPoint = {};
//定义移动距离对象
const movePoint = {};
//定义当前位置对象
const curPos = {
x:0,
y:0
}
//定义点击事件函数
$el.addEventListener('pointerdown',startHandler,false);
//清除浏览器默认事件
$el.addEventListener('touchstart',function(e){
e.preventDefault();
},false)
//定义开始函数
function startHandler(e){
//添加鼠标移动,松开,取消事件函数(因为PC端移出目标元素,pointermove不再生效,所以将这些事件定义在document上)
document.addEventListener('pointermove',moveHandler,false);
document.addEventListener('pointerup',endHandler,false);
document.addEventListener('pointercancel',endHandler,false);
startPoint.x = e.pageX;
startPoint.y = e.pageY;
}
//定义移动函数
function moveHandler(e){
e.preventDefault();
movePoint.x = curPos.x + e.pageX - startPoint.x;
movePoint.y = curPos.y + e.pageY - startPoint.y;
$el.style.transform = `translate3d(${movePoint.x}px,${movePoint.y}px,0)`
}
//定义结束函数
function endHandler(e){
curPos.x = movePoint.x;
curPos.y = movePoint.y
//释放事件
document.removeEventListener('pointermove',moveHandler,false);
document.removeEventListener('pointerup',endHandler,false);
document.removeEventListener('pointercancel',endHandler,false);
}
};
//调用drag函数
const box = document.getElementById('box');
drag(box);
</script>
</html>
13、手势模拟(可调用库)
使用Pointer模拟上下左右滑动
设置条件:滑动距离 > 100px && 滑动时间 < 500ms 够快够长
- 上滑y轴距离的绝对值 > x轴距离的绝对值 && y轴移动为负
- 下滑y轴距离的绝对值 > X轴距离的绝对值 && y轴移动为正
- 左滑x轴距离的绝对值 > y轴距离的绝对值 && x轴移动为负
- 右滑x轴距离的绝对值 > y轴距离的绝对值 && x轴移动为正
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
img{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="./blackhole.png" alt="" id="gesture">
</body>
<script>
//定义函数
function swipe($el,cb){
//定义开始的触摸点
const startPoint = {};
//定义时间和距离阈值
const thrshold = {
time:500,
distance:100
}
//绑定按下事件函数
$el.addEventListener('pointerdown',startHandler,false);
//清除移动端默认事件
$el.addEventListener('touchstart',function(e){
e.preventDefault();
})
function startHandler(e){
//清除PC端默认事件
e.preventDefault();
//记录开始的时间
startPoint.time = new Date().getTime();
//记录开始时的位置
startPoint.x = e.pageX;
startPoint.y = e.pageY;
//绑定point抬起和取消事件
document.addEventListener('pointerup',endHandler,false);
document.addEventListener('pointercancel',endHandler,false);
}
function endHandler(e){
const process = {};
let direction = '';
//计算过程耗费的时间
process.time = new Date().getTime() - startPoint.time;
//计算移动的距离
process.x = e.pageX - startPoint.x;
process.y = e.pageY - startPoint.y;
//判断是否是扫动手势
if(process.time > thrshold.time || Math.abs(process.x) < thrshold.distance && Math.abs(process.y) < thrshold.distance) return;
else{
if(Math.abs(process.x) < Math.abs(process.y)){
if(process.y > 0) direction = "down";
else direction = 'up';
}
else{
if(process.x > 0) direction = 'right';
else direction = 'left';
}
cb.call($el,direction);
}
document.removeEventListener('pointup',endHandler,false);
document.removeEventListener('pointcancel',endHandler,false);
}
}
const img = document.getElementById('gesture');
swipe(img,function(direction){
console.log(direction)
})
</script>
</html>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号