Java 基础 (IO转换流)
-
转换流提供了在字节流和字符流之间的转换
-
Java API提供了两个转换流:
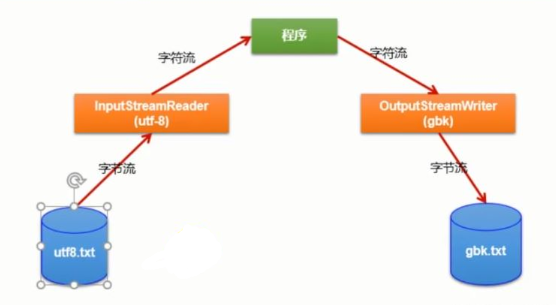
InputStreamReader : 将 InputStream 转换为 Reader
OutputStreamWriter : 将 Writer 转换为 OutputStream -
字节流中的数据都是字符时,转成字符流操作更高效。
-
很多时候我们使用转换流来处理文件乱码问题。实现编码和解码的功能。
1. 转换流: 属于字符流 InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流OutputStreamWriter:将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流 2. 作用: 提供字节流与字符流之间的转换 3. 解码: 字节、字节数组 ---> 字符数组、字符串 编码: 字符数组、字符串 ---> 字节、字节数组 4. 字符集 1) ASCII: 美国标准信息交换码。 用一个字节的7位可以表示。 2) ISO8859-1: 拉丁码表。欧洲码表 用一个字节的8位表示。 3) GB2312: 中国的中文编码表。最多两个字节编码所有字符 4) GBK: 中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号。最多两个字节编码 5) Unicode: 国际标准码,融合了目前人类使用的所有字符。为每个字符分配唯一的字符码。所有的文字都用两个字节来表示。 6) UTF-8: 变长的编码方式,可用1-4个字节来表示一个字符。 面向传输的众多 UTF (UCS Transfer Format)标准出现了,顾名思义,UTF-8就是每次8个位传输数据,而 UTF-16就是每次16个位。这是为传输而设计的编码,并使编码无国界,这样就可以显示全世界上所有文化的字符了。 Unicode 只是定义了一个庞大的、全球通用的字符集,并为每个字符规定了唯一确定的编号,具体存储成什么样的字节流,取决于字符编码方案。推荐的 Unicode 编码是 UTF-8 和 UTF-16。
InputStreamReaderTest.java
package com.klvchen.java; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.*; public class InputStreamReaderTest { @Test public void test1() throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("dbcp.txt"); //InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis); //使用系统默认的字符集 //参数2指明了字符集,具体使用哪个字符集,取决于文件dbcp.txt保存时使用的字符集 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8"); char[] cbuf = new char[20]; int len; while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) { String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len); System.out.print(str); } isr.close(); } @Test public void test2() throws IOException { //1.造文件,造流 File file1 = new File("dbcp.txt"); File file2 = new File("dbcp_gbk.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf-8"); OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk"); //2.读写过程 char[] cbuf = new char[20]; int len; while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) { osw.write(cbuf, 0 ,len); } //3.关闭资源 isr.close(); osw.close(); } }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY