P5022 旅行
题目描述
小 Y 是一个爱好旅行的 OIer。她来到 X 国,打算将各个城市都玩一遍。
小Y了解到, X国的 \(n\) 个城市之间有 \(m\) 条双向道路。每条双向道路连接两个城市。 不存在两条连接同一对城市的道路,也不存在一条连接一个城市和它本身的道路。并且, 从任意一个城市出发,通过这些道路都可以到达任意一个其他城市。小 Y 只能通过这些 道路从一个城市前往另一个城市。
小 Y 的旅行方案是这样的:任意选定一个城市作为起点,然后从起点开始,每次可 以选择一条与当前城市相连的道路,走向一个没有去过的城市,或者沿着第一次访问该 城市时经过的道路后退到上一个城市。当小 Y 回到起点时,她可以选择结束这次旅行或 继续旅行。需要注意的是,小 Y 要求在旅行方案中,每个城市都被访问到。
为了让自己的旅行更有意义,小 Y 决定在每到达一个新的城市(包括起点)时,将 它的编号记录下来。她知道这样会形成一个长度为 \(n\) 的序列。她希望这个序列的字典序 最小,你能帮帮她吗? 对于两个长度均为 \(n\) 的序列 \(A\) 和 \(B\),当且仅当存在一个正整数 \(x\),满足以下条件时, 我们说序列 \(A\) 的字典序小于 \(B\)。
- 对于任意正整数 \(1≤i<x1 ≤ i < x1≤i<x\),序列 \(A\) 的第 \(i\) 个元素 \(A_i\) 和序列 \(B\) 的第 \(i\) 个元素 \(B_i\) 相同。
- 序列 \(A\) 的第 \(x\) 个元素的值小于序列 \(B\) 的第 \(x\) 个元素的值。
输入格式
输入文件共 \(m+1\) 行。第一行包含两个整数 \(n,m(m≤n)\),中间用一个空格分隔。
接下来 \(m\) 行,每行包含两个整数 \(u,v(1≤u,v≤n)\) ,表示编号为 \(u\) 和 \(v\) 的城市之 间有一条道路,两个整数之间用一个空格分隔
输出格式
输出文件包含一行,\(n\) 个整数,表示字典序最小的序列。相邻两个整数之间用一个 空格分隔。
输入输出样例
输入 #1
6 5
1 3
2 3
2 5
3 4
4 6
输出 #1
1 3 2 5 4 6
输入 #2
6 6
1 3
2 3
2 5
3 4
4 5
4 6
输出 #2
1 3 2 4 5 6
说明/提示
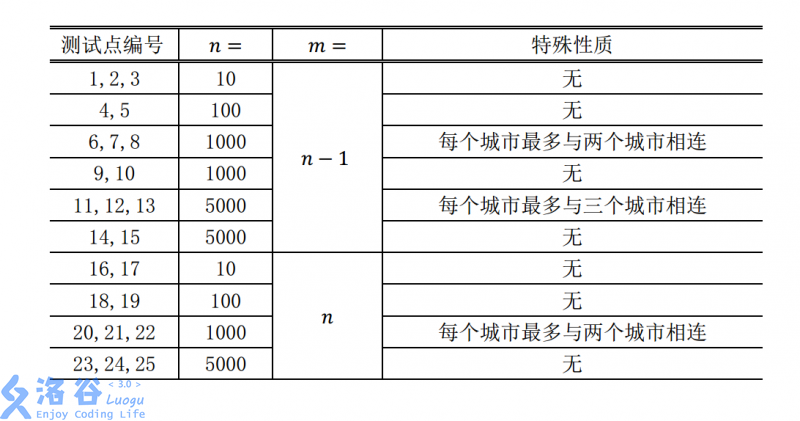
【数据规模与约定】
对于 100% 的数据和所有样例, 1≤n≤5000 且 m=n−1 或 m=n
对于不同的测试点, 我们约定数据的规模如下:
刷(水~)一波历年真题
题解
一句话题意:
给你一棵树或基环树,让你找一个遍历顺序,使这个顺序的字典序最小。
60pts
先看是一颗树的情况,这样我们只要贪心的选字典序较小的来遍历。用个堆来维护。
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5010;
int n,m,u,v,tot,cnt,head[N],ans[N];
bool vis[N];
struct node
{
int to,net;
}e[N<<1];
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s =s * 10+ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
void add(int x,int y)
{
e[++tot].to = y;
e[tot].net = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
}
void dfs(int x)
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > q;
vis[x] = 1; ans[++cnt] = x;//把这个节点加入答案中
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(vis[to]) continue;
q.push(to);//先把他的儿子放进一个堆中
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int t = q.top(); q.pop();//选字典序小的先遍历
if(vis[t]) continue;
dfs(t);
}
}
int main()
{
n = read(); m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
u = read(); v = read();
add(u,v); add(v,u);
}
dfs(1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]);
return 0;
}
100pts
后面的 \(40\) 分是基环树的分。
按照处理基环树的套路,我们先找到环,然后枚举环上的每一条边。
再把这条边断掉,来更新答案。
找环的话,直接暴力 DFS 就可以了
void find(int x,int fa)
{
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == fa) continue;
if(vis[to])//找到了环
{
sta[++top] = i;
st = to; en = x;
return;
}
pre[to] = i;//记录一下他的前驱是谁
find(to,x);
}
}
然鹅,这题卡常,我卡了一波,发现只能卡到 \(88\) pts.
最后三个点怎么也卡不过去(可能是我卡常技术太菜了)
附上我被卡常的代码
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5010;
int n,m,u,v,cnt,st,en,flag,top, tot = 1;
int head[N],ans[N],pre[N],sta[N],a[N];
bool vis[N],used[N<<1];
struct node
{
int to,net;
}e[N<<1];
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s =s * 10+ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
void add(int x,int y)
{
e[++tot].to = y;
e[tot].net = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
}
bool comp(int len)//比较两个字典序的大小
{
int i = 1;
while(i <= len && a[i] == ans[i]) i++;
return a[i] < ans[i];
}
void find(int x,int fa)//暴力找环
{
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == fa) continue;
if(vis[to])
{
sta[++top] = i;
st = to; en = x;
return;
}
pre[to] = i;
find(to,x);
}
}
void dfs(int x)
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > q;
vis[x] = 1; a[++cnt] = x;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].net)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(vis[to] || used[i]) continue;
q.push(to);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int t = q.top(); q.pop();
if(vis[t]) continue;
dfs(t);
}
}
int main()
{
n = read(); m = read(); flag = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
u = read(); v = read();
add(u,v); add(v,u);
}
if(m == n-1)//分情况讨论
{
dfs(1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ",a[i]);
return 0;
}
else
{
find(1,1);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
while(st != en)
{
sta[++top] = pre[st];//把的边存入一个栈中
st = e[pre[st]^1].to;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans[i] = n;//初始化答案
for(int i = 1; i <= top; i++)
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); cnt = 0;
used[sta[i]] = 1;//成对变化,把正向边和反向边都标记一下
used[sta[i] ^ 1] = 1;
dfs(1);
// for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) cout<<a[j]<<" ";
if(comp(n))
{
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)//更新答案
{
ans[j] = a[j];
}
}
used[sta[i]] = 0;//回溯
used[sta[i]^1] = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]);
return 0;
}
卡常无果后,看了一波 Chen_zhe 大佬的题解,发现可以先对边排一下序,这样就省去了堆的度杂度。
Vector 中有个自带的排序函数,所以图方便(主要是懒)就拿Vector 水了一发。
另外不用开栈,只需要在回溯的时候断边,在统计一下答案就能够卡过去了。
附上优化后的代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5010;
int n,m,u,v,cnt,st,en,flag,top,L,R,tot = 1;
int ans[N],pre[N],sta[N],a[N];
bool vis[N];
vector<int> e[N];
inline int read()
{
int s = 0,w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){s =s * 10+ch - '0'; ch = getchar();}
return s * w;
}
bool comp(int len)//比较字符串的大小
{
int i = 1;
while(i <= len && a[i] == ans[i]) i++;
return a[i] < ans[i];
}
bool check(int x,int y)//判断这两个节点是否是要删除的边的两个顶点
{
if((x == L && y == R) || (x == R && y == L)) return 1;
else return 0;
}
void find(int x,int fa)//暴力找环
{
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < e[x].size(); i++)
{
int to = e[x][i];
if(to == fa) continue;
if(vis[to])
{
st = to; en = x;
L = st, R = en;
return;
}
pre[to] = x;//记录一下他的前驱
find(to,x);
}
}
void dfs(int x)
{
a[++cnt] = x; vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < e[x].size(); i++)
{
int to = e[x][i];
if(vis[to] || check(x,to)) continue;
dfs(to);
}
}
int main()
{
n = read(); m = read(); flag = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
u = read(); v = read();
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sort(e[i].begin(),e[i].end());//vector 自带的排序功能
}
if(m == n-1)//树的情况
{
dfs(1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ",a[i]);
return 0;
}
else if(m == n)
{
find(1,1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans[i] = n;
while(st != en)
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));//每次都要清空一下
cnt = 0; dfs(1);
if(comp(n))//比答案要优就可以更新答案
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans[i] = a[i];
}
L = st, R = pre[st]; //L 和 R 是当前要删除的边的两个节点
st = pre[st];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]);
return 0;
}
总算把这个题水过去了,距离上次要写·鸽了半个月
老鸽子实锤了。



