事务_数据库连接池_DBUtils_MVC
事务:
1、事务(Transaction):指的是一组操作逻辑,里面包含了很多个单一的操作逻辑。如果有一个逻辑失败,那么无论其它逻辑是否成功,都算失败。
2、为什么需要事务:
为了保证一组关联逻辑的全部正确执行。举例:银行转账
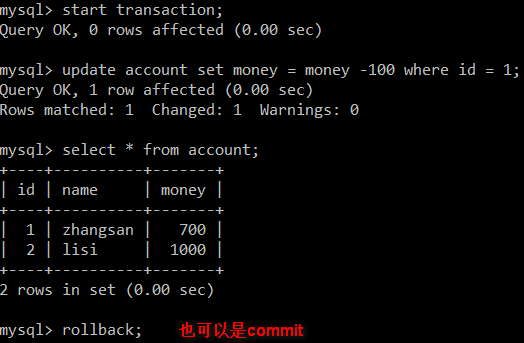
3、如何开启事务,以及事务的两种结果处理:
开启事务:start transaction;
两种结果处理:commit / rollback
4、示例:
关闭自动提交
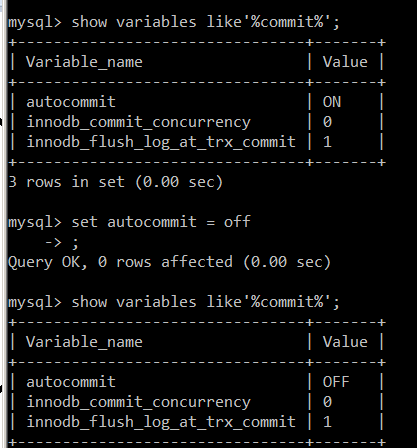
演示事务:
@Test public void testTransaction(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { conn = JDBCUtil.getConn(); //连接,事务默认就是自动提交的。 关闭自动提交。 conn.setAutoCommit(false); String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where id = ?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //扣钱, 扣ID为1 的100块钱 ps.setInt(1, 100); ps.setInt(2, 1); ps.executeUpdate(); int a = 10 /0 ; //加钱, 给ID为2 加100块钱 ps.setInt(1, -100); ps.setInt(2, 2); ps.executeUpdate(); //成功: 提交事务。 conn.commit(); } catch (SQLException e) { try { //事变: 回滚事务 conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtil.release(conn, ps, rs); } }
5、事务特性:(ACID)
原子性:事务中包含的逻辑,不可分割。
一致性:事务执行前后。数据完整性
隔离性:事务在执行期间不应该受到其他事务的影响
持久性:事务执行成功,那么数据应该持久保存到磁盘上。
6、事务隔离级别以及对应的安全隐患:
读未提交(read uncommitted):脏读
读已提交(read committed):解决脏读,引发不可重复的
可重复度(repeatable read):解决脏读,不可重复的,引发幻读
可串行化(serializable):解决脏读,不可重复读,幻读
安全隐患:
读:
脏读
一个事务读到了另一个事务未提交的数据
不可重复读
一个事务读到了另一个事务已提交的数据,造成前后两次查询结果不一致
幻读
一个事务读到了另一个事务insert的数据 ,造成前后查询结果不一致 。
写:
丢失更新。
7、事务隔离级别排序:
按效率(高->低):读未提交 > 读已提交 > 可重复读 > 可串行化
按拦截程度(高->低):可串行化 > 可重复读 > 读已提交 > 读未提交
8、事务只是针对连接连接对象,如果再开一个连接对象,那么那是默认的提交。
9、mySql 默认的隔离级别是 可重复读
Oracle 默认的隔离级别是 读已提交
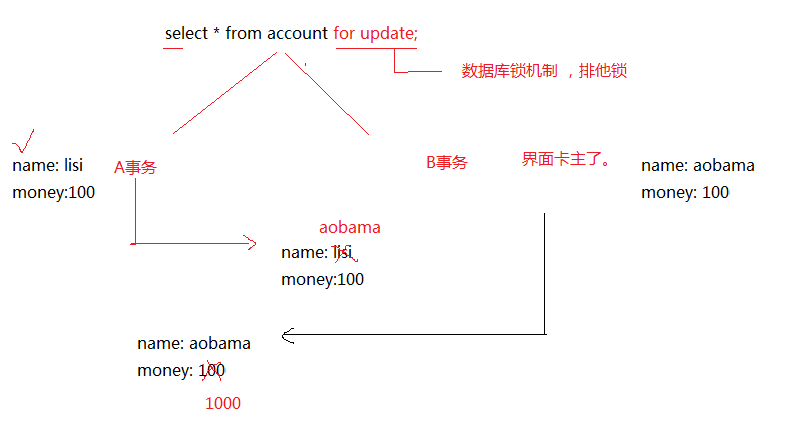
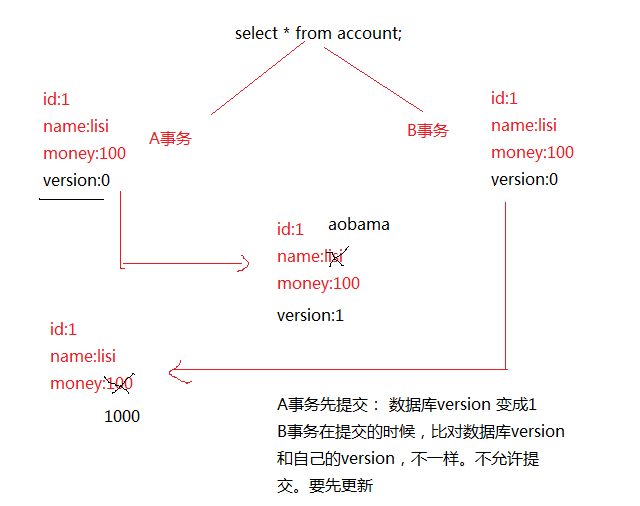
10、解决丢失更新的方式:
悲观锁:
乐观锁:
数据库连接池:
DBCP:
1、不使用配置文件的方式:
Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //1. 构建数据源对象 BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource(); //连的是什么类型的数据库, 访问的是哪个数据库 , 用户名, 密码。。 dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost/bank"); dataSource.setUsername("root"); dataSource.setPassword("root"); //2. 得到连接对象 conn = dataSource.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into account values(null , ? , ?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "admin"); ps.setInt(2, 1000); ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtil.release(conn, ps); }
2、使用配置文件方式:
Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { BasicDataSourceFactory factory = new BasicDataSourceFactory(); Properties properties = new Properties(); InputStream is = new FileInputStream("src//dbcpconfig.properties"); properties.load(is); DataSource dataSource = factory.createDataSource(properties); //2. 得到连接对象 conn = dataSource.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into account values(null , ? , ?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "liangchaowei"); ps.setInt(2, 100); ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtil.release(conn, ps); }
CP30:
1、不适用配置文件
Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //1. 创建datasource ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); //2. 设置连接数据的信息 dataSource.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost/bank"); dataSource.setUser("root"); dataSource.setPassword("root"); //2. 得到连接对象 conn = dataSource.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into account values(null , ? , ?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "admi234n"); ps.setInt(2, 103200); ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtil.release(conn, ps); }
2、使用配置文件(注意:CP30的配置文件可以用properties或者xml,常用xml)
Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //就new了一个对象。 ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); //2. 得到连接对象 conn = dataSource.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into account values(null , ? , ?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "wangwu2"); ps.setInt(2, 2600); ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtil.release(conn, ps); }
DBUtils:
1、增删改
//dbutils 只是帮我们简化了CRUD 的代码, 但是连接的创建以及获取工作。 不在他的考虑范围 QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(new ComboPooledDataSource()); //增加 //queryRunner.update("insert into account values (null , ? , ? )", "aa" ,1000); //删除 //queryRunner.update("delete from account where id = ?", 5); //更新 //queryRunner.update("update account set money = ? where id = ?", 10000000 , 6);
2、查询
1)匿名内部类方式,自定义返回值的接收配置
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(new ComboPooledDataSource()); Account account = queryRunner.query("select * from account where id = ?", new ResultSetHandler<Account>(){ @Override public Account handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { Account account = new Account(); while(rs.next()){ String name = rs.getString("name"); int money = rs.getInt("money"); account.setName(name); account.setMoney(money); } return account; } }, 6); System.out.println(account.toString());
2)使用框架写好的实现类
查询单个对象 QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(new ComboPooledDataSource()); //查询单个对象 Account account = queryRunner.query("select * from account where id = ?", new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class), 8); 查询多个对象 QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(new ComboPooledDataSource()); List<Account> list = queryRunner.query("select * from account ", new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
3、ResultSetHandler 常用的实现类
BeanHandler, 查询到的单个数据封装成一个对象
BeanListHandler, 查询到的多个数据封装 成一个List<对象>
ArrayHandler, 查询到的单个数据封装成一个数组
ArrayListHandler, 查询到的多个数据封装成一个集合 ,集合里面的元素是数组。
MapHandler, 查询到的单个数据封装成一个map
MapListHandler,查询到的多个数据封装成一个集合 ,集合里面的元素是map。
需要对应的jar包请留言


