数据结构与算法分析C++语言描述(第四版)图论学习记录
我对 9.3.1节中无权最短路径算法,进行了一点修改,对书中例子也进行了测试,发现居然也适用于有权最短路径求解。
对 赋权图最短路径求解,我仍然使用和 9.3.1节中求解无权图最短路径同样的方式,参见 函数 dijkstra 。
邻接表的定义,额外增加了一个 int 表示变的长度。另外当我发现达到某一个点具有更小的路径时,只要这个点有和其他点邻接。那么我就再次把这个点加入队列,对其重新计算。
这个点之后邻接到的点的距离,都需要再求一次。原本时间复杂度为 O(E+V),现在计算的边E个数会增加,就算的点V个数也会增加,我推测增加的量不会超过原本图中存在的E,V个数。那么时间复杂度上界最多为O(2E+2V)?
我又对书中9.3.2节的Dijkstra算法文字描述,进行了实现参见函数 dijkstra_2
原先 dijkstra_2,是线性查找最小距离的未知点,现在我使用了一个最小二叉堆(基础数据结构是数组)BinaryHeap<dist_vertex_info>& vertex_heap
图的定义
下面是我自己对图的一些定义,为了简洁我省略了部分代码。完整内容可以看源码。
//无权图的点的定义
struct Vertex
{
string name = ""; //点的名称
unordered_set<string> adjacent; //记录点 邻接的其他点,只包含 点的名字信息
//以下信息,可以定义在其他地方。我为了一时的方便,就笼统的放在一起了
int indegree = 0; //点的入度
int topNum = 0; //拓扑排序编号
int dfsNum = 0; //深度优先搜索编号
int low = 0; //编号最低的顶点
Vertex* parent = nullptr; //记录自己的父亲节点
bool visited = false; //便于深度搜索
unordered_map<string, pathInfo> t_path; //记录点 到其他点的路径信息
unordered_map<string, int> t_tree; //记录点 到其他点的 生成树 信息
};
//图中边的定义 计算最小生成树时用到
struct Edge
{
string start_name = ""; //一个点的名称
string end_name = ""; //另一个点的名称
int weight = 1; //权值
bool operator<(Edge& e)
{
return weight < e.weight;
}
};
//有权图,点的定义
struct weight_vertex : public Vertex
{
unordered_map<string, int> adjacent; //邻接表
weight_vertex(string name, unordered_map<string, int> adj) //额外增加了 int 记录邻接到另外一个点的距离信息
{
//Vertex();
this->name = name;
adjacent = adj;
}
};
//图的定义
using WeightGraph = unordered_map<string, weight_vertex*>; //用映射 <点名,有权点> 定义一个图
using Graph = unordered_map<string, Vertex*>; //用映射 <点名,无权点> 定义一个图
网络流最大流问题
代码是书中,算法文字描述的正规实现。
//最大流问题
void max_flow(string start_name, string end_name, WeightGraph& Graph);
void s_to_t(string start_name, string end_name, WeightGraph& graph, vector<string>& path);
最小生成树
//最小生成树 Prim 算法
void mintree_prim(WeightGraph& Graph);
void dijkstra_for_mintree(string name, WeightGraph& graph);
//最小生成树 Kruskal 算法
void mintree_kruskal(WeightGraph& Graph);prim算法基本与 dijkstra 算法相同,只不过路径不再取累加的最短路径。而是往旧的生成树中并入一条边时,取最短的一条边 构成的路径。
Kruskal 算法使用最小二叉堆存储图的边,每次从中取最短的一条边。使用存储点名(string)的不相交集类判断生成树是否加入新的边,不相交集存满图中所有的点。
深度优先搜索,割点,连通性
void assignNum(string name, Graph&, int& );
void assignLow(string name, Graph&);
void dfs(string start, Graph&, int& dfsNum); //深度搜索 树的 先序遍历
void find_art(string start, Graph&, int& dfsNum); //找 割点欧拉回路
void EulerPath(Graph& graph);
string find_valid_name(list<string>&name, Graph& graph);
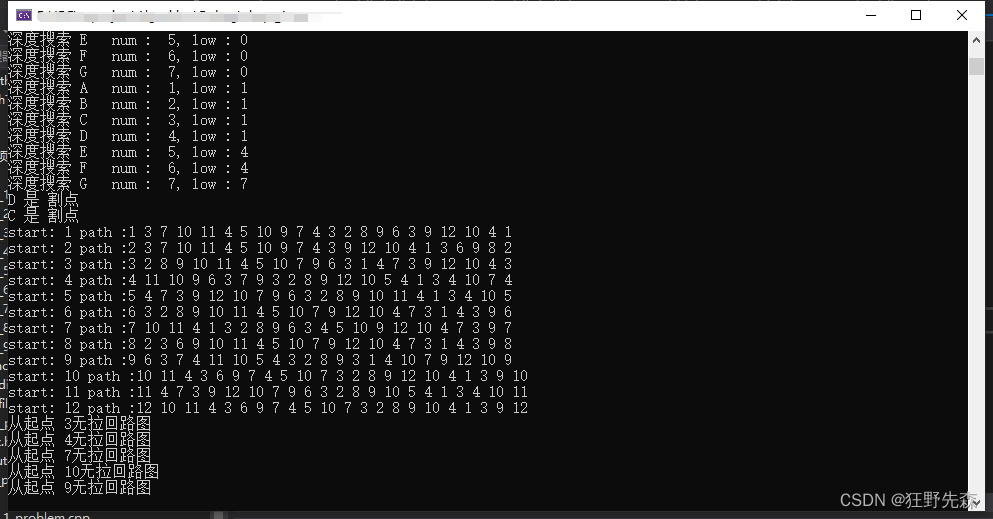
void EulerPath(Graph& ograph)
{
for (auto& kv : ograph)
{
auto start = kv.first;
auto graph = ograph;
list<string> path;//路径,存 点的名字
dfs_print_2(start, graph, path); //找一条回路 共计 O(E)
//要想找到欧拉回路,要求每次找到的路径包含 3 个点,并且 “成圈”
if (path.size() <= 3)
{
cout << "从起点 "<<start<< "无拉回路图" << endl;
continue;;
}
else if (path.size() > 3 && path.front() != path.back())
{
cout << "从起点 " << start << "无拉回路图" << endl;
continue;
}
auto valid_name = find_valid_name(path, graph); // 共计 O(E) 一个圈最少3条边最多 E 条边
bool isSucc = true;
while (valid_name != "") //每次至少削减 3条边,while次数 最多 E/3 次
{
list<string> tmpPath;
dfs_print_2(valid_name, graph, tmpPath);
//将 path 和 tmpPath 拼接 //拼接路径共计花费线性 O(E) 时间
if (tmpPath.size() >= 3 && tmpPath.front() == tmpPath.back())
{
auto first_name = tmpPath.front();
auto iter_tmp = tmpPath.begin();
auto iter = path.begin(); //路径最长为 O(V+1)
for (; iter != path.end(); ++iter)
{
if (first_name == *iter)
{
break;
}
}
iter++;
iter_tmp++;
for (; iter_tmp != tmpPath.end(); iter_tmp++)
{
path.insert(iter, *iter_tmp);
}
//再找一个点继续
//直至所有 邻接边都被用完
valid_name = find_valid_name(tmpPath, graph);
int abcd = 123;
}
else
{
isSucc = false;
}
if(isSucc == false)
break;
}
//要想找到欧拉回路,要求每次找到的路径包含 3 个点,并且 “成圈”
if (path.size() >= 3 && path.front() != path.back() || isSucc == false)
{
cout << "从起点 " << start << "无拉回路图" << endl;
continue;
}
int abc = 111;
cout << "start: "<<start<<" path :";
for (auto iter = path.begin(); iter != path.end(); ++iter)
{
cout << *iter << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//时间复杂度为 O(E)
//
}
string find_valid_name(list<string>& path, Graph& graph)
{
for (auto& name : path)
if (graph[name].adjacent.size() > 0)
return name;
return "";
}如果有同样在看这本书的小伙伴,欢迎跟我讨论讨论!
1.首先是 chapt_9_graph.h
#ifndef _chapt_9_graph
#define _chapt_9_graph
#include<unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::unordered_map;
using std::unordered_set;
using std::string;
using std::vector;
//图的抽象定义
//点的定义
//点名,点的信息
//路径信息 用以记录一个点到另外一个点的路径信息
struct pathInfo
{
vector<string> path;
int dis = 0;
bool know = false; //是否已被处理标识
void print(string startVertex)
{
cout << startVertex << ": ";
cout << startVertex << "→";
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); ++i)
{
cout << path[i];
if (i < path.size() - 1)
cout << "→";
}
cout << " dist : " << dis << endl;
}
};
struct Vertex
{
string name = ""; //点的名称
int indegree = 0; //点的入度
int topNum = 0; //拓扑排序编号
int dfsNum = 0; //深度优先搜索编号
int low = 0; //编号最低的顶点
Vertex* parent = nullptr; //记录自己的父亲节点
bool visited = false; //便于深度搜索
unordered_set<string> adjacent; //邻接表
unordered_map<string, pathInfo> t_path;
void print()
{
std::cout << name;
}
Vertex()
{
}
Vertex(string name, std::vector<string> names)
{
this->name = name;
for (auto& name : names)
this->adjacent.insert(name);
indegree = 0;
topNum = 0;
}
void print_path_table()
{
if (t_path.empty())
{
cout << "没有最短路径信息" << endl;
return;
}
//输出到到各个点的最短路径,距离信息
cout << endl;
for (auto& kv : t_path)
{
kv.second.print(name);
}
}
vector<string> getPath(string name)
{
vector<string> path;
if (name == this->name)
return path;
path = t_path[name].path;
return path;
}
void updatePathInfo(string prevNmae, string name)//上一个点,当前点
{
t_path[name].path.clear();
auto oldPath = getPath(prevNmae);
for (int i = 0; i < oldPath.size(); ++i)
t_path[name].path.push_back(oldPath[i]);
t_path[name].path.push_back(name);
}
};
//图中边的定义
struct Edge
{
string start_name = "";
string end_name = "";
bool isDirect = true;
int weight = 1;
};
//图的定义
struct Graph
{
unordered_map<string, Vertex*> V; //点的集合
unordered_map<string, Edge*> E; //边的集合
};
void topSort(Graph& graph); //拓扑排序
void initAdjacent(Graph& graph); //初始化各个点的 入度 O(V^2) //O(V^2)
void initAdjacent_2(Graph& graph); //初始化各个点的 入度 //O(E)
//无权最短路径算法(无权图,每边长度为1 任意一点 到其他所有点的最短路径
void unweighted(string name, Graph& graph); //O(V^2)
void unweighted_2(string name, Graph& graph); //O(E+V)
//有权图,点的定义
struct weight_vertex : public Vertex
{
unordered_map<string, int> adjacent; //邻接表
weight_vertex(string name, unordered_map<string, int> adj)
{
Vertex();
this->name = name;
adjacent = adj;
}
};
//图的定义
using WeightGraph = unordered_map<string, weight_vertex*>;
//有权最短路径算法(……
void dijkstra(string name, WeightGraph& graph);
int _unknow_vertex_count(string name, WeightGraph& graph); //dijkstra_2 的内部函数
string _smallest_unknow_dist_vertex(string name, WeightGraph& graph); //dijkstra_2 的内部函数
struct dist_vertex_info //一个结构,用来存放在 二叉堆
{
string name;
int dis;
bool operator<(dist_vertex_info a)
{
return dis < a.dis;
}
};
string _smallest_unknow_dist_vertex_2(BinaryHeap<dist_vertex_info>& vertex_heap);/从一个最小二叉堆,获取最小未知点存储距离信息
void dijkstra_2(string name, WeightGraph& graph); //对书中dijkstra 算法的正规实现时间复杂度为 O(V^2+E)
//最大流问题
void max_flow(string start_name, string end_name, WeightGraph& Graph);
void s_to_t(string start_name, string end_name, WeightGraph& graph, vector<string>& path);
#endif
2.chapt_9_graph.cpp 定义部分
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "chapt_9_graph.h"
void initAdjacent(Graph& graph)
{
//计算入度,
//只要任意一点,被其他任何一个点所邻接,那么入度+1
int count = 0;
for (auto& kv : graph)//O(V)
{
for (auto& kv2 : graph) //O(V)
{
count++;
if (kv2.first != kv.first)
{
//若 v2 邻接 v
//v的入度 +1
auto iter = kv2.second->adjacent.find(kv.first);
if (iter != kv2.second->adjacent.end())
kv.second->indegree++;
}
}
}
//共计 O(V^2)
int abcd = 111;
}
void initAdjacent_2(Graph& graph)
{
//计算入度,
//只要任意一点,有邻接点,那么被邻接的点 入度+1
int count = 0;
for (auto& kv : graph)//O(E)
{
for (auto name : kv.second->adjacent)
{
graph[name]->indegree++;
count++;
}
}
int abcd = 111;
}
void topSort(Graph& graph)
{
//initAdjacent(graph); //O(V^2)
initAdjacent_2(graph); //O(E)
queue<Vertex*> q;
int counter = 0;
//将入度为0 的 点 ,加入队列
for (auto& kv : graph) //O(V)
if (0 == kv.second->indegree)
q.push(kv.second);
cout << "\ntopsort result: [ ";
int whileCount = 0;
while (q.empty() == false) //O(E)
{
auto v = q.front();
q.pop();
counter++;
v->topNum = counter;
cout << v->name << ", ";
//移除该点,减少邻接点的入度,将入度为0 的点再次加入队列
for (auto& name : v->adjacent)
{
whileCount++;
graph[name]->indegree--;
if (graph[name]->indegree == 0)
q.push(graph[name]);
}
}
cout << " ] " << endl;
//时间复杂度 共计 O(2E+V)
}
void unweighted(string name, Graph& graph)
{
auto& startVertex = graph[name];
for (auto& kv : graph) //O(V) //路径表初始化
{
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].dis = -1;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know = false;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].path.clear();
}
//自己到自己的距离设置为0
startVertex->t_path[name].dis = 0;
startVertex->t_path[name].path.push_back(name);
//startVertex->print_path_table();
//从距离 0 开始,一次+1
for (int dist = 0; dist < graph.size(); ++dist) //O(V)
{
for(auto& kv : graph) //O(V)
if (startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know == false && startVertex->t_path[kv.first].dis == dist)
{
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know = true;
for (auto& name_adj : kv.second->adjacent)
{
if (startVertex->t_path[name_adj].dis == -1)
{
startVertex->t_path[name_adj].dis = dist + 1;
startVertex->updatePathInfo(kv.first, name_adj);
}
}
}
}
//时间复杂度 O(V^2)
//最后输出整个最短路径表
startVertex->print_path_table();
}
//使用队列从 距离 的遍历 O(V)次,降低到图中实际的次数
void unweighted_2(string name, Graph& graph)
{
auto& startVertex = graph[name];
for (auto& kv : graph) //O(V) //路径表初始化
{
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].dis = -1;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know = false;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].path.clear();
}
//自己到自己的距离设置为0
startVertex->t_path[name].dis = 0;
startVertex->t_path[name].path.push_back(name);
queue<Vertex*> q;
q.push(startVertex);
while (q.empty() == false)//O(V)
{
auto v = q.front();
q.pop();
startVertex->t_path[v->name].know = true;
for (auto& name : v->adjacent) //每条边处理 1 次,共计 O(E)
if (startVertex->t_path[name].dis == -1)
{
startVertex->t_path[name].dis = startVertex->t_path[v->name].dis + 1;
startVertex->updatePathInfo(v->name, name);
q.push(graph[name]);
}
}
//时间复杂度 O(V+E)
//最后输出整个最短路径表
startVertex->print_path_table();
}
void dijkstra(string name, WeightGraph& graph)
{
auto& startVertex = graph[name];
for (auto& kv : graph) //O(V) //路径表初始化
{
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].dis = -1;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know = false;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].path.clear();
}
//自己到自己的距离设置为0
startVertex->t_path[name].dis = 0;
startVertex->t_path[name].path.push_back(name);
queue<weight_vertex*> q;
q.push(startVertex);
int count = 0; //35 13
int frontCount = 0; //11 10
while (q.empty() == false)//O(E)
{
auto v = q.front();
frontCount++;
q.pop();
startVertex->t_path[v->name].know = true;
for (auto& kv : v->adjacent)
{
auto name = kv.first;
auto dis = kv.second;
count++;
if (startVertex->t_path[name].dis == -1)
{
startVertex->t_path[name].dis = startVertex->t_path[v->name].dis + dis;
startVertex->updatePathInfo(v->name, name);
q.push(graph[name]);
}
else
{
auto newDis = startVertex->t_path[v->name].dis + dis;
if (newDis < startVertex->t_path[name].dis)
{
startVertex->t_path[name].dis = newDis; //当 临接点的距离被修改时,再次加入该点重新计算
startVertex->updatePathInfo(v->name, name);
if(graph[name]->adjacent.empty() == false)
q.push(graph[name]);
}
}
}
}
//时间复杂度 O(E+V)
//最后输出整个最短路径表
startVertex->print_path_table();
int asaa = 111;
}
int _unknow_vertex_count(string name, WeightGraph& graph)
{
int count = 0;
auto& startVertex = graph[name];
for (auto& kv : graph) //O(V) //路径表初始化
{
if (startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know == false)
count++;
}
return count;
}
string _smallest_unknow_dist_vertex(string name, WeightGraph& graph)
{
auto& startVertex = graph[name];
int minDist = INT_MAX;
string ret_name = "";
for (auto& kv : graph) //O(V)
{
if (startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know == false)
{
if (startVertex->t_path[kv.first].dis < minDist)
{
minDist = startVertex->t_path[kv.first].dis;
ret_name = kv.first;
}
}
}
return ret_name;
}
string _smallest_unknow_dist_vertex_2(BinaryHeap<dist_vertex_info>& vertex_heap)
{
string ret = "";
if(vertex_heap.size() > 0)
{
ret = vertex_heap.findMin().name; //每次 O(logE)
vertex_heap.deleteMin(); //共计 E 次 delete
}
return ret;
}
void dijkstra_2(string name, WeightGraph& graph)
{
auto& startVertex = graph[name];
for (auto& kv : graph) //O(V) //路径表初始化
{
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].dis = INT_MAX;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].know = false;
startVertex->t_path[kv.first].path.clear();
}
//自己到自己的距离设置为0
startVertex->t_path[name].dis = 0;
startVertex->t_path[name].path.push_back(name);
dist_vertex_info dvi;
dvi.name = name;
dvi.dis = 0;
vector<dist_vertex_info> v_dis_v;
v_dis_v.push_back(dvi);
BinaryHeap< dist_vertex_info> heap{ v_dis_v }; //使用一个小二叉堆,存储距离信息
while (_unknow_vertex_count(name, graph) > 0) //O(V)
{
//这里是在从 已设置预设距离,但是 know 为false 的点集合中找出一个最短距离的点。这个集合就是 某一点与它邻接的所有点构成的边
//一个点最多可以和 V-1 个点邻接,线性查找的话,需要 O(V-1)约等于 O(V)啦
//string min_unknow_dis_name = _smallest_unknow_dist_vertex(name, graph); //O(V)
string min_unknow_dis_name = _smallest_unknow_dist_vertex_2(heap); //共计O(logE)
if(min_unknow_dis_name == "")
break;; //有点不可达 直接跳出,避免死循环
startVertex->t_path[min_unknow_dis_name].know = true;
for (auto& kv : graph[min_unknow_dis_name]->adjacent)
{
auto adj_name = kv.first;
if (startVertex->t_path[adj_name].know == false) //邻接点构成的边 共计 O(E)
{
if (startVertex->t_path[adj_name].dis == INT_MAX)
{
startVertex->t_path[adj_name].dis = startVertex->t_path[min_unknow_dis_name].dis + kv.second;
startVertex->updatePathInfo(name, adj_name);
}
else
{
auto newDis = startVertex->t_path[min_unknow_dis_name].dis + kv.second;
if (newDis < startVertex->t_path[adj_name].dis)
{
startVertex->t_path[adj_name].dis = newDis;
startVertex->updatePathInfo(name, adj_name);
}
}
dist_vertex_info dvi;
dvi.name = adj_name;
dvi.dis = kv.second; //这里要加入线段的距离,而不是累加的距离startVertex.t_path[adj_name].dis;
//将距离信息,装入堆中
heap.insert(dvi); //共进行 E次 插入 共计花费 O(ElogE)
}
}
}
startVertex->print_path_table();
//线性查找最小未知距离点的时间复杂度为 O(V^2 + E)
//使用二叉堆时间复杂度变为 O(VlogE + E + ElogE) 还有 E <= V^2 → logE <= 2log(V)
//可化为2VlogV+E+2ElogV → O(ElogV)
}
void max_flow(string start_name, string end_name, WeightGraph& graph)
{
//构造三个图,
//1.原本的图; 2.流图; 3.残余图
WeightGraph ori_Graph = graph;
WeightGraph flow_Graph = graph; //流图一开始是无权,即 各个点的邻接情况距离 都为 0
for (auto& kv : flow_Graph)
for (auto& adj_dis : kv.second.adjacent)
adj_dis.second = 0;
WeightGraph left_Graph = graph;
//一开始 残余图 就是 原本的图
//每次从残余图中找出一条从 s 到 t 的路径,残余图需要对路径上的个点的 邻接情况,进行修改
//去路径的最小流量,加在流图上,同样的点,同样的浏览
//重复从残余图中s到t的路径,直至找不到
//此时 残余图中就含有 s 到 t 的最大流量 就是 t 的邻接表 流量的总和
vector<string> path;
s_to_t(start_name, end_name, left_Graph, path); //路径没有包含 起始点
while (path.empty() == false)
{
vector<string> tmpPath;
tmpPath.push_back(start_name);
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); ++i)
tmpPath.push_back(path[i]);
path = std::move(tmpPath);
//找出这条路径上的最小流量
int min_flow = left_Graph[path[0]].getadjdis(path[1]);
for (int i=1; i<path.size()-1;++i)
{
int tmp_flow = left_Graph[path[i]].getadjdis(path[i+1]);
if (tmp_flow < min_flow)
min_flow = tmp_flow;
}
//修改 残余图
for (int i = 0; i < path.size()-1; ++i)
{
auto cur_node_name = path[i];
auto adj_node_name = path[i + 1];
left_Graph[cur_node_name].adjacent[adj_node_name] -= min_flow;
if (left_Graph[cur_node_name].adjacent[adj_node_name] == 0)
{
left_Graph[cur_node_name].adjacent.erase(adj_node_name); //移除原来那条边
}
//反向边不存在就 增加
if (left_Graph[adj_node_name].adjacent.find(cur_node_name) == left_Graph[adj_node_name].adjacent.end())
{
left_Graph[adj_node_name].adjacent[cur_node_name] = min_flow; //添加一条反向边
}
else
left_Graph[adj_node_name].adjacent[cur_node_name] += min_flow; //存在就修改原来的值
}
//添加 流图
for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; ++i)
{
auto cur_node_name = path[i];
auto adj_node_name = path[i + 1];
flow_Graph[cur_node_name].adjacent[adj_node_name] += min_flow;
}
path.clear();
s_to_t(start_name, end_name, left_Graph, path);
}
int abc = 1111;
int max_f = 0;
for (auto& x : left_Graph[end_name].adjacent)
max_f += x.second;
cout << "最大流量为 : " << max_f << endl;
}
void s_to_t(string start_name, string end_name, WeightGraph& graph, vector<string>& path)
{
auto tmpGraph = graph;
dijkstra_2(start_name, tmpGraph);
path = tmpGraph[start_name].t_path[end_name].path;
}
void mintree_prim(WeightGraph& Graph)
{
int v_count = 0;
for (auto& kv : Graph)
v_count++;
//随便从一个点开始
for (auto& kv : Graph)
{
auto tmpGraph = Graph;
dijkstra_for_mintree(kv.first, tmpGraph); //O(ElogV)
break;
}
}
void mintree_kruskal(WeightGraph& Graph)
{
//从图中找到所有的边
//将所有的边放入最小堆
//每次从最小堆中取一个最短的一条边,也就是两个点,尝试进行合并,直至包含所有点
unordered_map<string, Edge> um_edges;
int v_count = 0;
for (auto& kv : Graph) //两个for 循环 共计 O(E+V)
{
v_count++; //统计点的个数
auto v_name = kv.first;
for (auto& adj : kv.second.adjacent)
{
Edge e;
e.start_name = v_name;
e.end_name = adj.first;
e.weight = adj.second;
if (um_edges.find(e.start_name + e.end_name) == um_edges.end() && um_edges.find(e.end_name + e.start_name) == um_edges.end())
um_edges[e.start_name + e.end_name] = e;
}
}
vector<Edge> v_edges;
for (auto& kv : um_edges) //O(E)
{
/*Edge e;
e.start_name = kv.second.start_name;
e.end_name = kv.second.end_name;
e.weight = kv.second.weight;*/
v_edges.push_back(kv.second);
}
BinaryHeap<Edge> bh_edges{ v_edges }; //O(E)
DisjSets_string disjs_v;
int tree_len = 0;
while (disjs_v.size() < v_count) //O(V)
{
auto edge = bh_edges.findMin();
bh_edges.deleteMin();
auto one_set = disjs_v.find(edge.start_name);// O(logV)
auto two_set = disjs_v.find(edge.end_name);
if (one_set != two_set || (one_set == two_set && one_set == ""))
{
tree_len += edge.weight;
disjs_v.unionSets(edge.start_name, edge.end_name);
}
}
cout << "kruskal min tree path len : " << tree_len << endl;
int a = 1234;
}
3. 部分测试 main.cpp
WeightGraph weightedGraph; //书中 图9.20 的定义
auto wv1 = weight_vertex("v1", { { "v2", 2},{"v4", 1 } });
weightedGraph["v1"] = wv1;
auto wv2 = weight_vertex("v2", { {"v4",3}, {"v5",10} });
weightedGraph["v2"] = wv2;
auto wv3 = weight_vertex("v3", { {"v1",4}, {"v6", 5} });
weightedGraph["v3"] = wv3;
auto wv4 = weight_vertex("v4", { {"v3",2}, {"v5",2},{"v6",8} , {"v7",4} });
weightedGraph["v4"] = wv4;
auto wv5 = weight_vertex("v5", { {"v6",7} });
weightedGraph["v5"] = wv5;
auto wv6 = weight_vertex("v6", { });
weightedGraph["v6"] = wv6;
auto wv7 = weight_vertex("v7", { {"v6",1} });
weightedGraph["v7"] = wv7;
//dijkstra("v1", weightedGraph);
dijkstra_2("v1", weightedGraph);
//最大流测试 //书中 图9.41 的定义
WeightGraph wg_9_41;
wg_9_41["s"] = weight_vertex("s", { {"a",4}, {"b",2} });
wg_9_41["a"] = weight_vertex("a", { {"b",1}, {"d",4}, {"c",2} });
wg_9_41["b"] = weight_vertex("b", { {"d",2} });
wg_9_41["c"] = weight_vertex("c", { {"t",3} });
wg_9_41["d"] = weight_vertex("d", { {"t",3} });
wg_9_41["t"] = weight_vertex("t", { });
max_flow("s", "t", wg_9_41);
//欧拉回路问题测试
Graph eulerGraph;
auto egv1 = Vertex("1", { "3", "4" });
eulerGraph["1"] = egv1;
auto egv2 = Vertex("2", { "3" ,"8" });
eulerGraph["2"] = egv2;
auto egv3 = Vertex("3", { "1", "2", "6", "9", "7", "4"});
eulerGraph["3"] = egv3;
auto egv4 = Vertex("4", { "1", "3", "7", "11", "10", "5"});
eulerGraph["4"] = egv4;
auto egv5 = Vertex("5", { "4", "10", });
eulerGraph["5"] = egv5;
auto egv6 = Vertex("6", { "3", "9", });
eulerGraph["6"] = egv6;
auto egv7 = Vertex("7", { "3", "9", "4", "10"});
eulerGraph["7"] = egv7;
auto egv8 = Vertex("8", { "2", "9"});
eulerGraph["8"] = egv8;
auto egv9 = Vertex("9", { "3", "6", "8", "12", "10", "7"});
eulerGraph["9"] = egv9;
auto egv10 = Vertex("10", {"4", "7", "9", "12", "11", "5"});
eulerGraph["10"] = egv10;
auto egv11 = Vertex("11", { "4", "10"});
eulerGraph["11"] = egv11;
auto egv12 = Vertex("12", { "9", "10"});
eulerGraph["12"] = egv12;
EulerPath(eulerGraph);
Graph eulerGraph_9_71;
eulerGraph_9_71["3"] = Vertex("3", { "9", "7", "4" });
eulerGraph_9_71["4"] = Vertex("4", { "3", "7", "10" });
eulerGraph_9_71["7"] = Vertex("7", { "3", "9", "4", "10" });
eulerGraph_9_71["9"] = Vertex("9", { "3", "7", "10" });
eulerGraph_9_71["10"] = Vertex("10", { "4", "7", "9" });
EulerPath(eulerGraph_9_71);
本文来自博客园,作者:狂野先森,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/geeon/p/17759624.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号