GPU Tips
<1> Basic

#include <stdio.h> #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <device_launch_parameters.h> #define NUM 15 __global__ void square(float *dout,float *din) { int idx = threadIdx.x; float f = din[idx]; dout[idx] = f*f; } int main(int argc,char **argv) { const int bytes = sizeof(float) * NUM; float host_in[NUM]; // save some value for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++) { host_in[i] = float(i); } float host_out[NUM]; cudaError_t cudaStatus; // GPU SETTINGS // Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system. cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?"); return; } // define gpu memory, GPU memory allocation float *device_in = 0; float *device_out = 0; cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&device_in, bytes); cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&device_out,bytes); cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(device_in,host_in,bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // GPU kernel // 1 block,Num threads square<<<1,NUM>>>(device_out,device_in); cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize(); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus); } cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(host_out, device_out, bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!"); } // Free GPU memory cudaFree(device_in); cudaFree(device_out); for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++) { fprintf(stdout,"%f \n",host_out[i]); } getchar(); return 0; }
<2> N blocks and block's threads one dim

#include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <device_launch_parameters.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define ARRAYSize 50000000 #define THREADS_PER_BLOCK 1024 #define fnvalue(a,size)\ {\ for(int i=0;i<size;i++) \ {\ a[i] = float(i);\ }\ }\ #define CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(STATUS)\ {\ if (STATUS != cudaSuccess)\ {\ fprintf(stdout,"Error in line %d\n ",__LINE__);\ }\ }\ __global__ void add(float *d_out,float *d_x, float *d_y) { int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; if (index<ARRAYSize) { d_out[index] = d_x[index] + d_y[index]; } } int main(int argc,char **argv) { const int bytes = sizeof(float)*ARRAYSize; // host memory float *h_x = (float*)malloc(bytes); float *h_y = (float*)malloc(bytes); float *h_out = (float*)malloc(bytes); // give host value fnvalue(h_x,ARRAYSize); fnvalue(h_y,ARRAYSize); // device memory float *d_x,*d_y,*d_out; // cuda setttings cudaError_t dstat; dstat = cudaSetDevice(0); CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); dstat = cudaMalloc((void**)&d_x, bytes); CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); dstat = cudaMalloc((void**)&d_y, bytes); CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); dstat = cudaMalloc((void**)&d_out, bytes); CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); fprintf(stdout,"Copy data go GPU\n"); cudaMemcpy(d_x,h_x,bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); cudaMemcpy(d_y,h_y,bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); add<<<ARRAYSize/THREADS_PER_BLOCK,THREADS_PER_BLOCK>>>(d_out,d_x,d_y); fprintf(stdout,"Copy GPU data to cpu\n"); dstat = cudaMemcpy(h_out,d_out,bytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // DEBUG SOME VALUE for(int i=100600;i<100900;i++) { if ((i+1)%4==0) { fprintf(stdout,"%f\n", h_out[i]); } else { fprintf(stdout,"%f ", h_out[i]); } } getchar(); // FREE CPU MEMORY free(h_x); free(h_y); free(h_out); // FREE GPU MEMORY dstat = cudaFree(d_x); CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); dstat = cudaFree(d_y); CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); dstat = cudaFree(d_out); CHECK_CUDA_STATUS(dstat); return 0; }
<3> Unified memory:

#include <iostream> #include <math.h> // Kernel function to add the elements of two arrays __global__ void add(int n, float *x, float *y) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) y[i] = x[i] + y[i]; } int main(void) { int N = 1<<20; float *x, *y; // Allocate Unified Memory – accessible from CPU or GPU cudaMallocManaged(&x, N*sizeof(float)); cudaMallocManaged(&y, N*sizeof(float)); // initialize x and y arrays on the host for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { x[i] = 1.0f; y[i] = 2.0f; } // Run kernel on 1M elements on the GPU add<<<1, 1>>>(N, x, y); // Wait for GPU to finish before accessing on host cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // Check for errors (all values should be 3.0f) float maxError = 0.0f; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) maxError = fmax(maxError, fabs(y[i]-3.0f)); std::cout << "Max error: " << maxError << std::endl; // Free memory cudaFree(x); cudaFree(y); return 0; }
<4>Some tips
(1)
下图表示一维的block是由grid生成的。
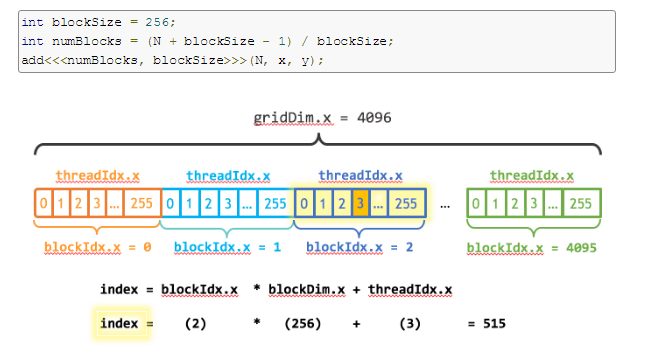
__global__ void add(int n, float *x, float *y) { int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; int stride = blockDim.x * gridDim.x; for (int i = index; i < n; i += stride) y[i] = x[i] + y[i]; }
(2) 关于SharedMemory ,其实是在一个block上的共享memory
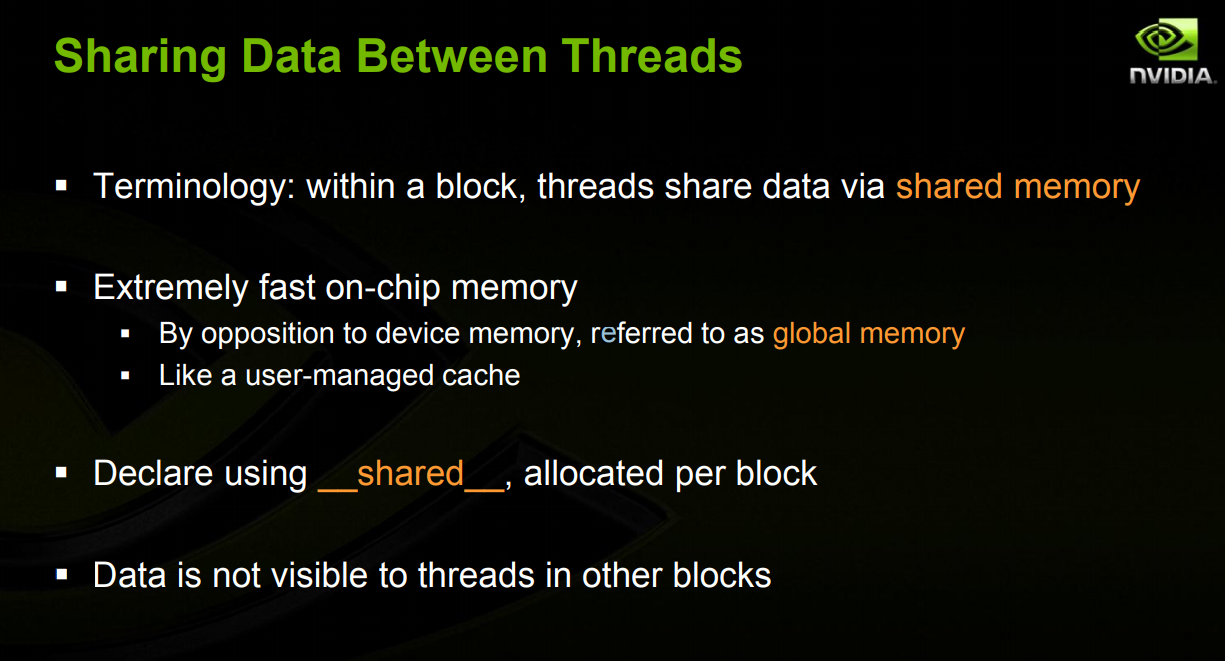
code:

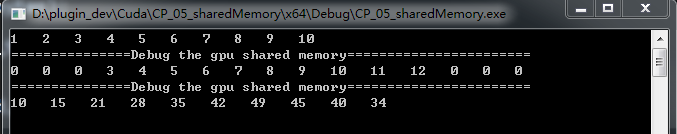
#include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <device_launch_parameters.h> #include <device_functions.h> #define RADIUS 3 #define BLOCKSIZE 10 __global__ void process(int *d_out,int *d_in,int *shared_mem) { __shared__ int temp[BLOCKSIZE + 2* RADIUS ]; int gindex = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x; int lindex = threadIdx.x + RADIUS; //printf("%d ",lindex); // Read input elements into shared memory temp[lindex] = d_in[gindex]; if (threadIdx.x < RADIUS) { temp[lindex - RADIUS] = d_in[gindex - RADIUS]; temp[lindex + BLOCKSIZE] = d_in[gindex + BLOCKSIZE]; } shared_mem[lindex] = lindex; // this code for debug __syncthreads(); // Apply the stencil int result = 0; for (int offset = -RADIUS ; offset <= RADIUS ; offset++) { result += temp[lindex + offset]; } // Store the result d_out[gindex] = result; } int main(int argc,char**argv) { // allocation of memory int host_rawSize = 10; int host_bytes = sizeof(int) * host_rawSize; int shared_bytes = (host_rawSize+2*RADIUS) * sizeof(int); int *host_data = (int*)malloc(host_bytes); int *host_outData = (int*)malloc(host_bytes); int *host_sharedMemData = (int*)malloc(shared_bytes); for(int i=0;i<host_rawSize;i++) { host_data[i] = int(i)+1; } for(int i=0;i<host_rawSize;i++) { fprintf(stdout,"%d ",host_data[i]); } fprintf(stdout,"\n"); int *dev_in; cudaMallocManaged((void**)&dev_in , host_bytes); //cudaMallocManaged(&dev_in , host_bytes); //cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_rawdata,bytes); cudaMemcpy(dev_in,host_data,host_bytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); int dev_out_bytes = host_rawSize *sizeof(int); // 4*sizeof(float) int *dev_out; int *dev_shared; cudaMallocManaged(&dev_out , dev_out_bytes); cudaMallocManaged(&dev_shared , shared_bytes); process<<<1,host_rawSize>>>(dev_out,dev_in,dev_shared); cudaMemcpy(host_outData, dev_out, dev_out_bytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaMemcpy(host_sharedMemData,dev_shared,shared_bytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); printf("===============Debug the gpu shared memory=======================\n"); for(int i=0;i<host_rawSize + 2*RADIUS;i++) { fprintf(stdout,"%d ",host_sharedMemData[i]); } printf("\n===============Debug the gpu shared memory=======================\n"); for(int i=0;i<host_rawSize;i++) { fprintf(stdout,"%d ",host_outData[i]); } fprintf(stdout,"\n"); getchar(); return 0; }
<1>simple caculation:
I = (R+G+B)/3
I = R*0.299f + G*0.587f + 0.114f*B
CPU:
// Serial implementation for running on CPU using a single thread. void rgbaToGreyscaleCpu(const uchar4* const rgbaImage, unsigned char *const greyImage, const size_t numRows, const size_t numCols) { for (size_t r = 0; r < numRows; ++r) { for (size_t c = 0; c < numCols; ++c) { const uchar4 rgba = rgbaImage[r * numCols + c]; const float channelSum = .299f * rgba.x + .587f * rgba.y + .114f * rgba.z; greyImage[r * numCols + c] = channelSum; } } }
GPU:
// CUDA kernel which is run in parallel by many GPU threads. __global__ void rgbaToGreyscaleCudaKernel(const uchar4* const rgbaImage, unsigned char* const greyImage, const int numRows, const int numCols) { //First create a mapping from the 2D block and grid locations //to an absolute 2D location in the image, then use that to //calculate a 1D offset const long pointIndex = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x*blockIdx.x; if(pointIndex<numRows*numCols) { // this is necessary only if too many threads are started uchar4 const imagePoint = rgbaImage[pointIndex]; greyImage[pointIndex] = .299f*imagePoint.x + .587f*imagePoint.y + .114f*imagePoint.z; } } // Parallel implementation for running on GPU using multiple threads. void rgbaToGreyscaleCuda(const uchar4 * const h_rgbaImage, uchar4 * const d_rgbaImage, unsigned char* const d_greyImage, const size_t numRows, const size_t numCols) { const int blockThreadSize = 256; const int numberOfBlocks = 1 + ((numRows*numCols - 1) / blockThreadSize); // a/b rounded up const dim3 blockSize(blockThreadSize, 1, 1); const dim3 gridSize(numberOfBlocks , 1, 1); rgbaToGreyscaleCudaKernel<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(d_rgbaImage, d_greyImage, numRows, numCols); }




