VDB R&D
VDB Data value visualize: 结论从houdini得知.
API常用文字:
interior:内部
Narrow-band:窄带
background:窄带外
SDF: XY plane Data visualize:
{
(1)用法:vdb sdf levelset球,采样其体素值到对应的点位置的颜色观察。houdini节点vdb from polygons(参数上Exterior band voxels:3,Interior band voxels:3)没有开启Fill interior
则形成体素值:
interior是-0.3 (这个值是由Interior band voxels:3 得到)
Narrow-band: 从interior到narrow-band方向:-0.3 到 0
background:从narrow-band到background方向:0.3 (Exterior band voxels:3)
(2)用法:
假如要让interior成为一个梯度值,而不是恒定值,houdini做了一个牛逼的按钮,Fill interior.
interior里的体素值立马成为梯度的,大概是从-3.73过渡到narrow-band
}
FOG Volume: XY plane Data visualize:
{
(1) 普通不勾选fill interior:
interior是1
Narrow-band: 从interior到narrow-band方向:1 到 0
background:从narrow-band到background方向:0
(2) 勾选fill interior:
interior到narrow-band方向从1->0.3有个过渡
Narrow-band: 从interior到narrow-band方向:0.3 到 0
background:从narrow-band到background方向:0
}
==================================================================START======================================================
<1> ,make vdb sphere,and convert to volume
#include <openvdb/openvdb.h> #include <openvdb/tools/LevelSetSphere.h> using namespace std; // Populate the given grid with a narrow-band level set representation of a sphere. // The width of the narrow band is determined by the grid's background value. // (Example code only; use tools::createSphereSDF() in production.) template<class GridType> void static makeSphere(GridType& grid, float radius, const openvdb::Vec3f& c) { typedef typename GridType::ValueType ValueT; // Distance value for the constant region exterior to the narrow band const ValueT outside = grid.background(); // Distance value for the constant region interior to the narrow band // (by convention, the signed distance is negative in the interior of // a level set) const ValueT inside = -outside; // Use the background value as the width in voxels of the narrow band. // (The narrow band is centered on the surface of the sphere, which // has distance 0.) int padding = int(openvdb::math::RoundUp(openvdb::math::Abs(outside))); // The bounding box of the narrow band is 2*dim voxels on a side. int dim = int(radius + padding); // Get a voxel accessor. typename GridType::Accessor accessor = grid.getAccessor(); // Compute the signed distance from the surface of the sphere of each // voxel within the bounding box and insert the value into the grid // if it is smaller in magnitude than the background value. openvdb::Coord ijk; int &i = ijk[0]; int &j = ijk[1]; int &k = ijk[2]; for (i = c[0] - dim; i < c[0] + dim; ++i) { const float x2 = openvdb::math::Pow2(i - c[0]); for (j = c[1] - dim; j < c[1] + dim; ++j) { const float x2y2 = openvdb::math::Pow2(j - c[1]) + x2; for (k = c[2] - dim; k < c[2] + dim; ++k) { // The distance from the sphere surface in voxels const float dist = openvdb::math::Sqrt(x2y2 + openvdb::math::Pow2(k - c[2])) - radius; // Convert the floating-point distance to the grid's value type. ValueT val = ValueT(dist); // Only insert distances that are smaller in magnitude than // the background value. if (val < inside || outside < val) continue; // Set the distance for voxel (i,j,k). accessor.setValue(ijk, val); } } } // Propagate the outside/inside sign information from the narrow band // throughout the grid. openvdb::tools::signedFloodFill(grid.tree()); } template <class T> static void convertToVolume(T &grid) { // Convert the level set sphere to a narrow-band fog volume, in which // interior voxels have value 1, exterior voxels have value 0, and // narrow-band voxels have values varying linearly from 0 to 1. const float outside = grid->background(); const float width = 2.0 * outside; // Visit and update all of the grid's active values, which correspond to // voxels on the narrow band. for (openvdb::FloatGrid::ValueOnIter iter = grid->beginValueOn(); iter; ++iter) { float dist = iter.getValue(); iter.setValue((outside - dist) / width); } // Visit all of the grid's inactive tile and voxel values and update the values // that correspond to the interior region. for (openvdb::FloatGrid::ValueOffIter iter = grid->beginValueOff(); iter; ++iter) { if (iter.getValue() < 0.0) { iter.setValue(1.0); iter.setValueOff(); } else{ iter.setValue(0); iter.setValueOff(); } } } int main() { openvdb::initialize(); // Create a shared pointer to a newly-allocated grid of a built-in type: // in this case, a FloatGrid, which stores one single-precision floating point // value per voxel. Other built-in grid types include BoolGrid, DoubleGrid, // Int32Grid and Vec3SGrid (see openvdb.h for the complete list). // The grid comprises a sparse tree representation of voxel data, // user-supplied metadata and a voxel space to world space transform, // which defaults to the identity transform. openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr grid = openvdb::FloatGrid::create(/*background value=*/2.0); // Populate the grid with a sparse, narrow-band level set representation // of a sphere with radius 50 voxels, located at (1.5, 2, 3) in index space. makeSphere(*grid, /*radius=*/50.0, /*center=*/openvdb::Vec3f(1.5, 2, 3)); // Associate some metadata with the grid. grid->insertMeta("radius", openvdb::FloatMetadata(50.0)); // Associate a scaling transform with the grid that sets the voxel size // to 0.5 units in world space. grid->setTransform( openvdb::math::Transform::createLinearTransform(/*voxel size=*/0.5)); // Identify the grid as a level set. grid->setGridClass(openvdb::GRID_LEVEL_SET); //grid->setGridClass(openvdb::GRID_FOG_VOLUME); // Name the grid "LevelSetSphere". grid->setName("LevelSetSphere"); // Create a VDB file object. openvdb::io::File file("mygrids.vdb"); // Add the grid pointer to a container. openvdb::GridPtrVec grids; // Write out the contents of the container. grids.push_back(grid); file.write(grids); file.close(); // ============================================================= convert level set sphere to a fog volume sphere ===================================================== std::cout << "read a new sdf volume and change it to fog\n"; openvdb::io::File readFile("mygrids.vdb"); readFile.open(); openvdb::GridBase::Ptr readGrid; for(openvdb::io::File::NameIterator nameIter = readFile.beginName();nameIter!=readFile.endName();++nameIter) { if(nameIter.gridName() == "LevelSetSphere") { readGrid = readFile.readGrid(nameIter.gridName()); } else { std::cout << "skip other grid modifile " << nameIter.gridName() <<std::endl; } } openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr cast_grid = openvdb::gridPtrCast<openvdb::FloatGrid>(readGrid); cast_grid->setGridClass(openvdb::GRID_FOG_VOLUME); readFile.close(); convertToVolume(cast_grid); openvdb::GridPtrVec WM_grids; WM_grids.push_back(cast_grid); openvdb::io::File WM_file("mygrids_convertToVolume.vdb"); WM_file.write(WM_grids); WM_file.close(); return 0; }
<2> vdb from particles
主要观察粒子的density,velocity
#include <openvdb/openvdb.h>
#include <openvdb/tools/ParticlesToLevelSet.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>

struct MyParticle { openvdb::Vec3R p, v; openvdb::Real r; }; class MyParticleList { // change protected to the public,direct find the mRadiusScale,mVelocityScale public: openvdb::Real mRadiusScale; openvdb::Real mVelocityScale; std::vector<MyParticle> mParticleList; public: std::vector<MyParticle> &get_mPartcileList() { return mParticleList; } public: typedef openvdb::Vec3R PosType; MyParticleList(openvdb::Real rScale=1, openvdb::Real vScale=1) : mRadiusScale(rScale), mVelocityScale(vScale) {} void add(const openvdb::Vec3R &p, const openvdb::Real &r, const openvdb::Vec3R &v=openvdb::Vec3R(0,0,0)) { MyParticle pa; pa.p = p; pa.r = r; pa.v = v; mParticleList.push_back(pa); } /// @return coordinate bbox in the space of the specified transfrom openvdb::CoordBBox getBBox(const openvdb::GridBase& grid) { openvdb::CoordBBox bbox; openvdb::Coord &min= bbox.min(), &max = bbox.max(); openvdb::Vec3R pos; openvdb::Real rad, invDx = 1/grid.voxelSize()[0]; for (size_t n=0, e=this->size(); n<e; ++n) { this->getPosRad(n, pos, rad); const openvdb::Vec3d xyz = grid.worldToIndex(pos); const openvdb::Real r = rad * invDx; for (int i=0; i<3; ++i) { min[i] = openvdb::math::Min(min[i], openvdb::math::Floor(xyz[i] - r)); max[i] = openvdb::math::Max(max[i], openvdb::math::Ceil( xyz[i] + r)); } } return bbox; } //typedef int AttributeType; // The methods below are only required for the unit-tests openvdb::Vec3R pos(int n) const {return mParticleList[n].p;} openvdb::Vec3R vel(int n) const {return mVelocityScale*mParticleList[n].v;} openvdb::Real radius(int n) const {return mRadiusScale*mParticleList[n].r;} ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /// The methods below are the only ones required by tools::ParticleToLevelSet /// @note We return by value since the radius and velocities are modified /// by the scaling factors! Also these methods are all assumed to /// be thread-safe. /// Return the total number of particles in list. /// Always required! size_t size() const { return mParticleList.size(); } /// Get the world space position of n'th particle. /// Required by ParticledToLevelSet::rasterizeSphere(*this,radius). void getPos(size_t n, openvdb::Vec3R&pos) const { pos = mParticleList[n].p; } void getPosRad(size_t n, openvdb::Vec3R& pos, openvdb::Real& rad) const { pos = mParticleList[n].p; rad = mRadiusScale*mParticleList[n].r; } void getPosRadVel(size_t n, openvdb::Vec3R& pos, openvdb::Real& rad, openvdb::Vec3R& vel) const { pos = mParticleList[n].p; rad = mRadiusScale*mParticleList[n].r; vel = mVelocityScale*mParticleList[n].v; } // The method below is only required for attribute transfer void getAtt(size_t n, openvdb::Index32& att) const { att = openvdb::Index32(n); } };
Buiding the density,and write it out.

int main() { const float voxelSize = 0.2f, halfWidth = 2.0f; openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr density_grid = openvdb::createLevelSet<openvdb::FloatGrid>(voxelSize, halfWidth); MyParticleList pa(1,1); // this multiply is radius scale , velocity scale // This particle radius = 1 < 1.5 i.e. it's below the Nyquist frequency and hence ignored pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 1)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 5, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 2)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 10, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 3)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 15, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 4)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 20, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 5)); openvdb::tools::ParticlesToLevelSet<openvdb::FloatGrid> raster(*density_grid); raster.rasterizeTrails(pa, 0.75);//scale offset between two instances // always prune to produce a valid narrow-band level set. raster.finalize(true); density_grid->setGridClass(openvdb::GRID_LEVEL_SET); density_grid->setName("density"); convertToVolume(density_grid); // Create a VDB file object. openvdb::io::File file("mygrids.vdb"); // Add the grid pointer to a container. openvdb::GridPtrVec grids; grids.push_back(density_grid); // Write out the contents of the container. file.write(grids); file.close(); }
一个更好的方法Buiding the density.and write it out

// Note densityGrid allocation memory in this function and transform same as densityGrid void buildingDensityGrid(openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr &densityGrid, openvdb::math::Transform::Ptr &transform,MyParticleList &pa,bool isRasterToSphere = true) { float backGround = 0.1f; float voxelSize = 0.1; transform = openvdb::math::Transform::createLinearTransform(voxelSize); densityGrid = openvdb::FloatGrid::create(backGround); std::cout << "set density grid class type\n"; densityGrid->setGridClass(openvdb::GRID_LEVEL_SET); densityGrid->setTransform(transform); openvdb::tools::ParticlesToLevelSet<openvdb::FloatGrid> raster(*densityGrid); if(isRasterToSphere) { raster.rasterizeSpheres(pa,pa.mRadiusScale); } else{ raster.rasterizeTrails(pa,0.75); } raster.finalize(true); std::cout << "raster to end\n"; } int main() { MyParticleList pa(1,1); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 1)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 5, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 2)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 10, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 3)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 15, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 4)); pa.add(openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 20, 0), 1, openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 5)); openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr densityGrid; openvdb::math::Transform::Ptr transform; buildingDensityGrid(densityGrid,transform,pa); densityGrid->setName("density"); convertToVolume(densityGrid); // Create a VDB file object. std::cout << "write vdb \n"; openvdb::io::File file("mygrids.vdb"); // Add the grid pointer to a container. openvdb::GridPtrVec grids; grids.push_back(densityGrid); // Write out the contents of the container. file.write(grids); file.close(); }
接下来VelocityBuilding,直接写了个包裹库,并且在houdini测试了下openvdb::Vec3sGrid的运动模糊。
GLY_OpenVdbWrapper.h
// // Created by gearslogy on 4/13/17. // #ifndef ARNOLDVDBPOINTS_GLY_OPENVDBWAPPER_H #define ARNOLDVDBPOINTS_GLY_OPENVDBWAPPER_H #include <memory> #include <openvdb/openvdb.h> #include <openvdb/tools/ParticlesToLevelSet.h> #include <openvdb/tools/LevelSetUtil.h> #include <openvdb/tools/TopologyToLevelSet.h> // DEFINE OUR PARTICLES STRUCT namespace TopVertex { struct MyParticle { openvdb::Vec3R p, v; openvdb::Real r; // per particle has own radius }; class MyParticleList { // change protected to the public,direct find the mRadiusScale,mVelocityScale public: openvdb::Real mRadiusScale; openvdb::Real mVelocityScale; std::vector<MyParticle> mParticleList; typedef openvdb::Vec3R PosType; MyParticleList(openvdb::Real rScale=1, openvdb::Real vScale=1) : mRadiusScale(rScale), mVelocityScale(vScale) {} void add(const openvdb::Vec3R &p, const openvdb::Real &r, const openvdb::Vec3R &v=openvdb::Vec3R(0,0,0)) { MyParticle pa; pa.p = p; pa.r = r; pa.v = v; mParticleList.push_back(pa); } /// @return coordinate bbox in the space of the specified transfrom openvdb::CoordBBox getBBox(const openvdb::GridBase& grid) { openvdb::CoordBBox bbox; openvdb::Coord &min= bbox.min(), &max = bbox.max(); openvdb::Vec3R pos; openvdb::Real rad, invDx = 1/grid.voxelSize()[0]; for (size_t n=0, e=this->size(); n<e; ++n) { this->getPosRad(n, pos, rad); const openvdb::Vec3d xyz = grid.worldToIndex(pos); const openvdb::Real r = rad * invDx; for (int i=0; i<3; ++i) { min[i] = openvdb::math::Min(min[i], openvdb::math::Floor(xyz[i] - r)); max[i] = openvdb::math::Max(max[i], openvdb::math::Ceil( xyz[i] + r)); } } return bbox; } //typedef int AttributeType; // The methods below are only required for the unit-tests openvdb::Vec3R pos(int n) const {return mParticleList[n].p;} openvdb::Vec3R vel(int n) const {return mVelocityScale*mParticleList[n].v;} openvdb::Real radius(int n) const {return mRadiusScale*mParticleList[n].r;} ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /// The methods below are the only ones required by tools::ParticleToLevelSet /// @note We return by value since the radius and velocities are modified /// by the scaling factors! Also these methods are all assumed to /// be thread-safe. /// Return the total number of particles in list. /// Always required! size_t size() const { return mParticleList.size(); } /// Get the world space position of n'th particle. /// Required by ParticledToLevelSet::rasterizeSphere(*this,radius). void getPos(size_t n, openvdb::Vec3R&pos) const { pos = mParticleList[n].p; } void getPosRad(size_t n, openvdb::Vec3R& pos, openvdb::Real& rad) const { pos = mParticleList[n].p; rad = mRadiusScale*mParticleList[n].r; } void getPosRadVel(size_t n, openvdb::Vec3R& pos, openvdb::Real& rad, openvdb::Vec3R& vel) const { pos = mParticleList[n].p; rad = mRadiusScale*mParticleList[n].r; vel = mVelocityScale*mParticleList[n].v; } // The method below is only required for attribute transfer void getAtt(size_t n, openvdb::Index32& att) const { att = openvdb::Index32(n); } }; } // namespace TopVertex { class GLY_OpenVdbWrapper { public: // Rater point parm struct RasterParms { float backGround; float voxelSize; float halfWidth; }; // define some variable type using Ptr = std::shared_ptr<GLY_OpenVdbWrapper>; using RasterT = openvdb::tools::ParticlesToLevelSet<openvdb::FloatGrid, openvdb::Index32>; enum POINT_RASTER_TYPE{RS_Sphere=0x0,RS_trailer=0x1}; // define a static pointer to our class static GLY_OpenVdbWrapper* creator(); // GLY_OpenVdbWrapper(); ~GLY_OpenVdbWrapper(); // SAMPLE POINTS API void samplePointsSetPoints(const std::vector<openvdb::Vec3R> &posList); void samplePointsSetPoints(double *array,int rawSize); void samplePointsSetRadius(double *array,int rawSize); void samplePointsSetRadius(const std::vector<openvdb::Real> &radiusList); void samplePointsSetVelocity(const std::vector<openvdb::Vec3R> &vel); void samplePointsSetVelocity(double *array,int rawsize); void samplePointsSetRadiusScale(double radius); void samplePointsSetVelocityScale(double v); void samplePointsAppendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R p,openvdb::Vec3R v,openvdb::Real radius); void samplePointsRasterDensityGrid(POINT_RASTER_TYPE type,openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr &gridPtr,RasterParms &rasterParm); void samplePointsRasterVelocityGrid(openvdb::math::Transform::Ptr &density_transform,openvdb::Vec3SGrid::Ptr &velocityGrid); private: class SamplePoints; std::unique_ptr<SamplePoints> mPimplSamplePoints; }; } #endif //ARNOLDVDBPOINTS_GLY_OPENVDBWAPPER_H
GLY_OpenVdbWrapper.cpp
// // Created by gearslogy on 4/13/17. // #include "GLY_OpenVdbWrapper.h" #include <assert.h> #include <algorithm> using namespace TopVertex; //=======================================SamplePoints details================================= // class GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::SamplePoints { public: SamplePoints():mParticleListPtr(new MyParticleList(1,1)) { } ~SamplePoints() { std::cout << "Release SamplePoints memory\n"; } void setRadiusScale(double radius) { mParticleListPtr->mRadiusScale = radius; } void setVelocityScale(double v) { mParticleListPtr->mVelocityScale = v; } void setPoints(const std::vector<openvdb::Vec3R> &posList) { auto &pa = mParticleListPtr->mParticleList; pa.resize(posList.size()); for(int i=0;i<posList.size();i++) { pa[i].p = posList[i]; } } void setPoints(double *array,int rawsize) { assert(rawsize%3==0); auto &pa = mParticleListPtr->mParticleList; pa.resize(rawsize/3); for(int i=0;i<rawsize/3;i++) { double x = array[i]; double y = array[i+1]; double z = array[i+2]; auto t = openvdb::Vec3R(x,y,z); pa[i].p = t; } } void setRadius(const std::vector<openvdb::Real> &radiusList) { assert(radiusList.size()==mParticleListPtr->mParticleList.size()); auto &pa = mParticleListPtr->mParticleList; for(int i=0;i<pa.size();i++) { pa[i].r = radiusList[i]; } } void setRadius(double *array,int pointsNum) { assert(pointsNum==mParticleListPtr->mParticleList.size()); auto &pa = mParticleListPtr->mParticleList; for(int i=0;i<pa.size();i++) { pa[i].r = array[i]; } } void setVelocity(const std::vector<openvdb::Vec3R> &vel) { assert(vel.size() == mParticleListPtr->mParticleList.size()); auto &pa = mParticleListPtr->mParticleList; for(int i=0;i<vel.size();i++) { pa[i].v = vel[i]; } } void setVelocity(double *array,int rawsize) { assert(rawsize%3==0); auto &pa = mParticleListPtr->mParticleList; for(int i=0;i<rawsize/3;i++) { double x = array[i]; double y = array[i+1]; double z = array[i+2]; auto t = openvdb::Vec3R(x,y,z); pa[i].v = t; } } void appendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R p,openvdb::Vec3R v,openvdb::Real radius) { mParticleListPtr->add(p,radius,v); } void clearPoints(){mParticleListPtr->mParticleList.clear();} void rasterDensity(POINT_RASTER_TYPE type,openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr &gridPtr,RasterParms &rasterParm) { std::cout << "Start process samplePoints Raster Density\n"; float backGround = rasterParm.backGround; float voxelSize = rasterParm.voxelSize; float halfWidth = rasterParm.halfWidth; openvdb::math::Transform::Ptr transform = openvdb::math::Transform::createLinearTransform(voxelSize); //gridPtr = openvdb::FloatGrid::create(backGround); //this is simple and can work gridPtr = openvdb::createLevelSet<openvdb::FloatGrid>(voxelSize, halfWidth); gridPtr->setGridClass(openvdb::GRID_LEVEL_SET); gridPtr->setTransform(transform); openvdb::tools::ParticlesToLevelSet<openvdb::FloatGrid,openvdb::Index> raster(*gridPtr); if(type==0x0) // RS_Sphere { raster.rasterizeSpheres(*mParticleListPtr); } else { raster.rasterizeTrails(*mParticleListPtr,0.75); } raster.finalize(true); openvdb::tools::sdfToFogVolume(*gridPtr); gridPtr->setName("density"); mId=raster.attributeGrid(); } void rasterVelocityGrid(openvdb::math::Transform::Ptr &density_transform,openvdb::Vec3SGrid::Ptr &gridPtr) { typedef typename openvdb::Int32Grid::TreeType::ValueConverter<openvdb::Vec3s >::Type TreeTypeWarpVec; typedef typename openvdb::Grid<TreeTypeWarpVec> GridType; typename TreeTypeWarpVec::Ptr tree( new TreeTypeWarpVec(mId->tree(), openvdb::Vec3s(0,0,0) , openvdb::TopologyCopy())); //typename GridType::Ptr velocity_grid(GridType::create(tree)); //为grid开辟内存*/ gridPtr = openvdb::Vec3SGrid::create(tree); gridPtr->setVectorType(openvdb::VecType(0)); // MY Method openvdb::Coord ijk; openvdb::Vec3SGrid::Accessor vel_accessor = gridPtr->getAccessor(); for(auto iter = mId->beginValueOn();iter.test();++iter) { auto d = *iter; //std::cout << " D:..." <<d <<std::endl; ijk = iter.getCoord(); openvdb::math::Vec3s vel = mParticleListPtr->vel(d); vel*=140; vel_accessor.setValue(ijk,vel); } gridPtr->setName("vel"); gridPtr->setTransform(density_transform); } private: std::unique_ptr<MyParticleList > mParticleListPtr; RasterT::AttGridType::Ptr mId; //remeber the id of point in voxel }; // //============================================GLY_OpenVdbWrapper================================================== // GLY_OpenVdbWrapper Details GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::GLY_OpenVdbWrapper():mPimplSamplePoints(new GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::SamplePoints()) { } GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::~GLY_OpenVdbWrapper() { std::cout << "Release Wrapper memory\n"; } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetPoints(const std::vector<openvdb::Vec3R> &posList) { mPimplSamplePoints->setPoints(posList); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetPoints(double *array,int rawSize) { mPimplSamplePoints->setPoints(array,rawSize); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetRadius(double *array, int rawSize) { mPimplSamplePoints->setRadius(array,rawSize); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetRadius(const std::vector<openvdb::Real> &radiusList) { mPimplSamplePoints->setRadius(radiusList); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetVelocity(const std::vector<openvdb::Vec3R> &vel) { mPimplSamplePoints->setVelocity(vel); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetVelocity(double *array, int rawsize) { mPimplSamplePoints->setVelocity(array,rawsize); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetRadiusScale(double radius) { mPimplSamplePoints->setRadiusScale(radius); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsSetVelocityScale(double v) { mPimplSamplePoints->setVelocityScale(v); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsAppendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R p, openvdb::Vec3R v, openvdb::Real radius) { mPimplSamplePoints->appendPoint(p,v,radius); } GLY_OpenVdbWrapper* GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::creator() { return new GLY_OpenVdbWrapper; } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsRasterDensityGrid(POINT_RASTER_TYPE type, openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr &gridPtr, RasterParms &rasterParm) { mPimplSamplePoints->rasterDensity(type,gridPtr,rasterParm); } void GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::samplePointsRasterVelocityGrid(openvdb::math::Transform::Ptr &density_transform, openvdb::Vec3SGrid::Ptr &velocityGrid) { mPimplSamplePoints->rasterVelocityGrid(density_transform,velocityGrid); }
main.cpp:
// // Created by gearslogy on 4/14/17. // #include "GLY_OpenVdbWrapper.h" using namespace std; using namespace TopVertex; int main() { GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::Ptr wrapper(GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::creator()); wrapper->samplePointsAppendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R(0, 0, 0), openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 1) ,1); wrapper->samplePointsAppendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R(0, 5, 0), openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 2) ,1.5); wrapper->samplePointsAppendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R(0, 10, 0), openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 3) ,2.0); wrapper->samplePointsAppendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R(0, 15, 0), openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 4) ,2.5); wrapper->samplePointsAppendPoint(openvdb::Vec3R(0, 20, 0), openvdb::Vec3R( 0, 0, 5) ,3.0); // create grid named "density" openvdb::FloatGrid::Ptr densityGrid; GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::RasterParms parms; parms.backGround = 0.1; parms.voxelSize = 0.1; parms.halfWidth = 0.5; wrapper->samplePointsRasterDensityGrid(GLY_OpenVdbWrapper::RS_Sphere,densityGrid,parms); // Create velocity Grid "velocity" openvdb::Vec3SGrid::Ptr velocityGrid; auto densityTransform = densityGrid->transformPtr(); wrapper->samplePointsRasterVelocityGrid(densityTransform,velocityGrid); // IO Operator openvdb::io::File file("mygrids.vdb"); openvdb::GridPtrVec grids; grids.push_back(densityGrid); grids.push_back(velocityGrid); file.write(grids); file.close(); }
Test plugin for katana:
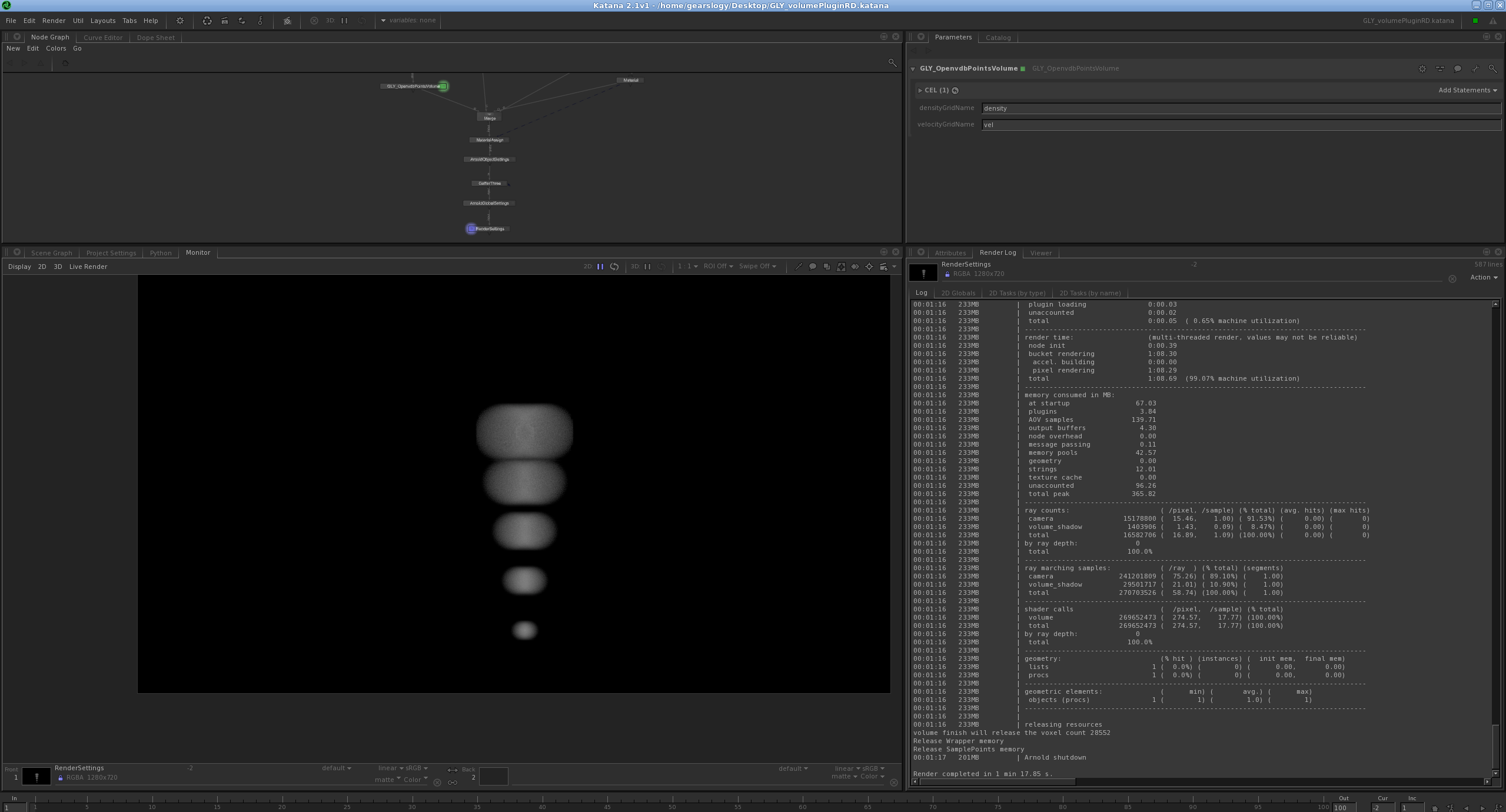
Update katana plugin:
升级了光线求交,直接快的飞起来
Arnold粒子体积渲染(Arnold particles volume rendering):
插件loading模式:AlembicAPI->OpenvdbAPI->ArnoldAPI
然后KatanaAPI再写个插件 读取这个ArnoldAPI写出来的proc,

update volume:
重要的事情不说两遍,static 关键字在一个so上被一个进程,2个instance调用,全局的static object内存地址是他妈一样的,也就是说是共享的地址。会导致你假如创建两个instance,你却希望有两份不一样的全局变量内容,结果,太感人了,确实是错的,是一样的。
如果独立进程,独立instance调用so上的全局变量,ok没问题。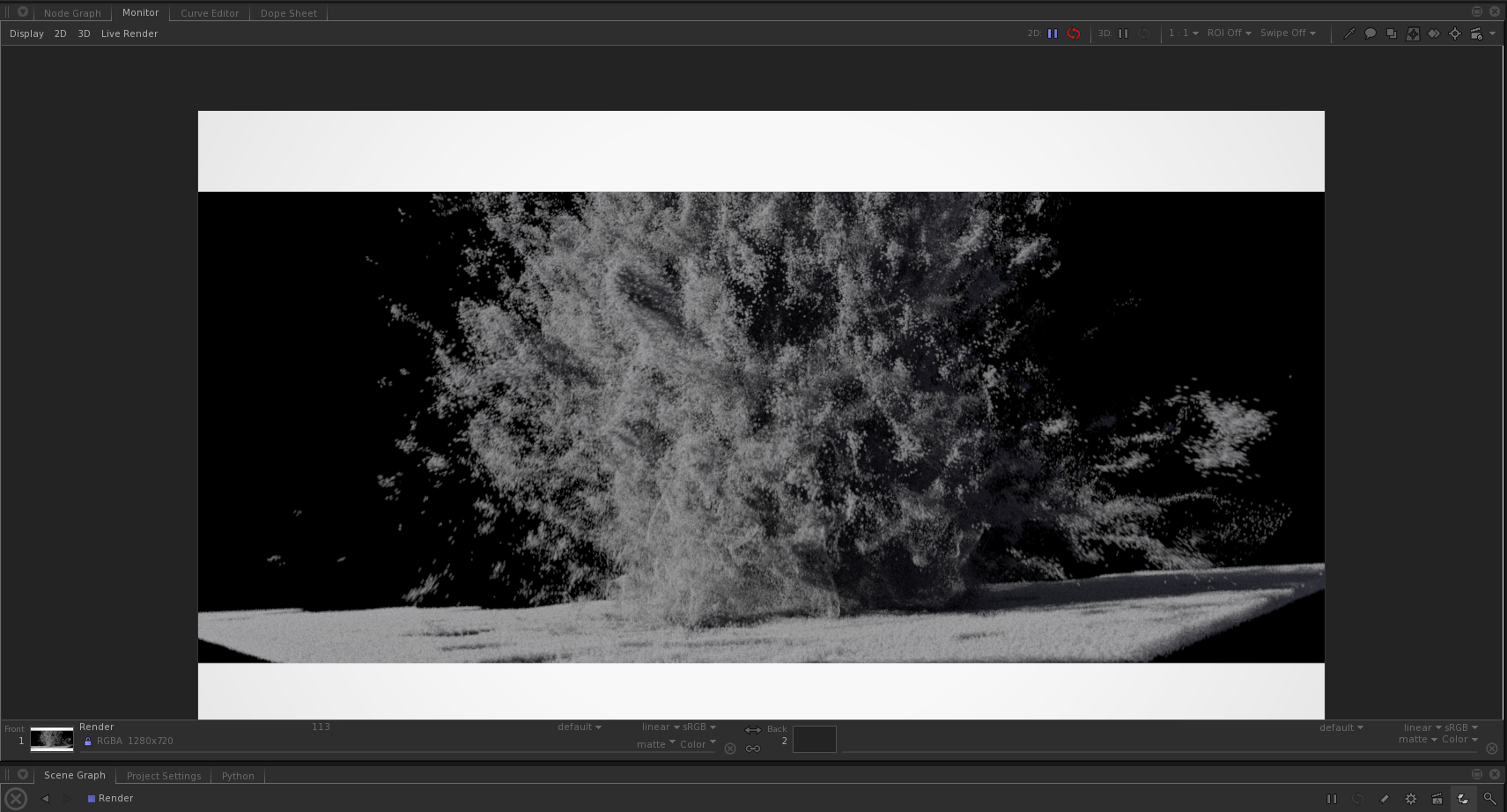
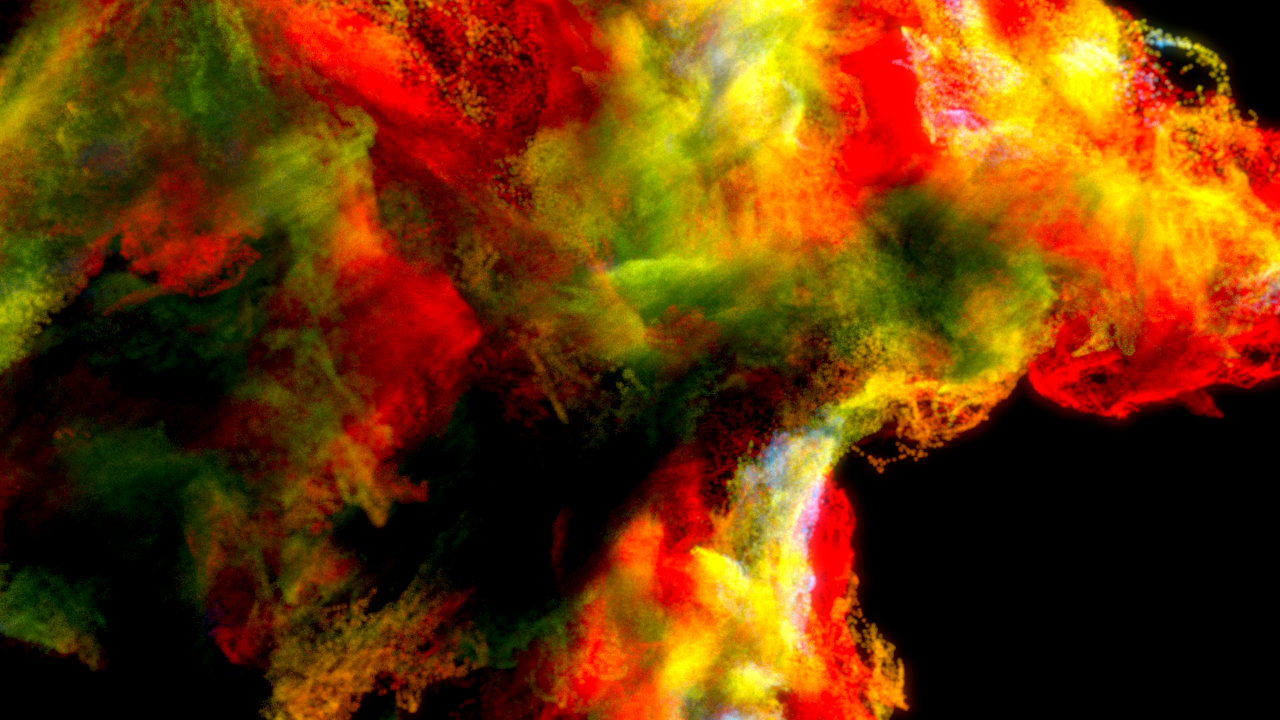
Rendering the cd field:
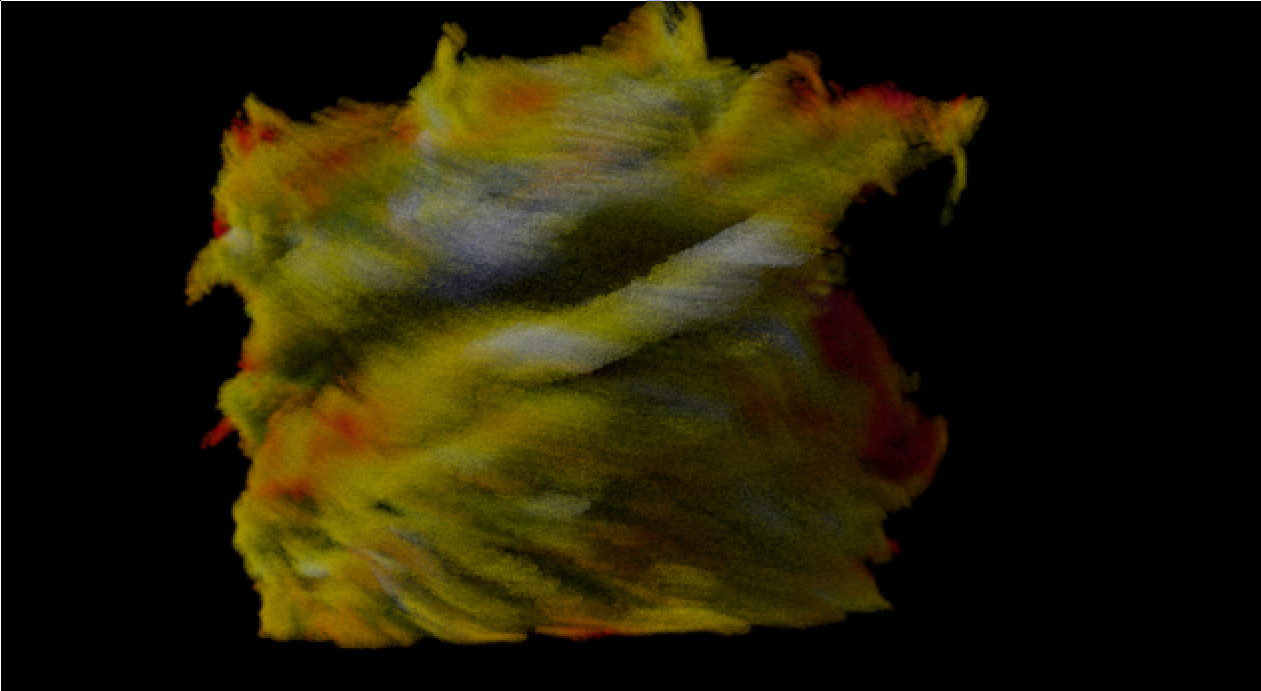

posted on 2017-03-13 17:26 gearslogy 阅读(2490) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报




