C++ 11 snippets , 2
<1>auto ,initializer_list<T>,auto指向函数指针的简易,和typdef 定义的类型执行函数指针有多复杂。

#include <iostream> #include <initializer_list> #include <string> using namespace std; template <typename T> T sum(initializer_list<T> rh) { T val; for(auto p= rh.begin();p!=rh.end();p++) { val+= *p; } return val; } int main() { // use init list cout << sum({1,2,3,4,5}) <<endl; cout << sum({1.0,2.0,3.1,4.0,5.0}) <<endl; // cout << "use auto to point the function sum" <<endl; auto dadd_func = sum<double>; auto iadd_func = sum<int>; auto tadd_func = sum<string>; cout << dadd_func({1,23,4,5}) <<endl; cout << iadd_func({1,1,3,4,5}) <<endl; cout << tadd_func({"houdini","maya","json"}) <<endl; cout << "\nuse the typedef to pointer\n"; typedef int (*td_int_sum)(initializer_list<int> rh); typedef string (*td_str_sum)(initializer_list<string> rh); td_int_sum int_add = sum<int>; td_str_sum str_add = sum<string>; cout << int_add({1,2,3,4,5,6}) <<endl; cout << str_add({"s1","s2","s5"}) << endl; return 0; }
<2>funcional,std::generate,std::count_if

#include <iostream> #include <math.h> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> using namespace std; double square(double x){return x*x;} int main() { vector <int> vars(10); generate(vars.begin(),vars.end(),std::rand); for_each(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[](int v){cout << v <<endl;}); // lambda can transfer local variable int sum = 0; for_each(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[&sum](int v){sum+=v;}); cout << "the sum is " << sum <<endl; // <100 num cout << "get <100 numbers" <<endl; cout << count_if(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[](int v){ return v<100;}) <<endl; // functional function<double(double)> ef1 = square; cout << ef1(2) <<endl; // 4 function<void(int var)> ef2 = [](int val){cout << val <<endl;}; ef2(100); // 100 return 0; }
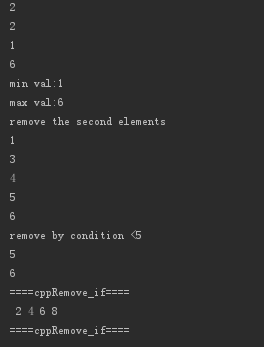
<3> remove_if,vector,min_element,max_element

include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <string> using namespace std; void cppRemove_if() { cout << "====cppRemove_if====\n"; int myInts[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int *pbegin = myInts; int *pend = myInts + sizeof(myInts)/ sizeof(int); pend = remove_if(pbegin,pend, [](const int &val)->bool{return val%2 == 1;});//2 4 5 8 ? ? ? ? for (int* p=pbegin; p!=pend; ++p) cout << ' ' << *p; cout << "\n"; cout << "====cppRemove_if====\n"; } int main() { vector<int> va{1,2,3,4,5,6}; // find, if not find elements,will return last *iter; auto va_find2 = find(va.begin(),va.end(),2); auto va_find2e = find_if(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){return x==2;}); cout << *va_find2 <<endl; cout << *va_find2e <<endl; cout << *min_element(va.begin(),va.end()) <<endl; cout << *max_element(va.begin(),va.end()) <<endl; auto min_max = minmax_element(va.begin(),va.end()); cout << "min val:" <<*(min_max.first)<<endl; cout << "max val:" <<*(min_max.second)<<endl; cout << "remove the second elements \n"; va.erase(va.begin()+1,va.begin()+2); for_each(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){cout << x <<endl;}); cout << "remove by condition <5 \n"; va.erase(remove_if(va.begin(),va.end(),[](int x){return x <5;}),va.end()); for_each(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){cout << x <<endl;}); cppRemove_if(); return 0; }
<4>binary_search,sort更加详细的用法:

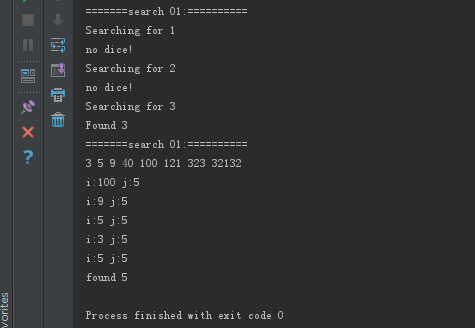
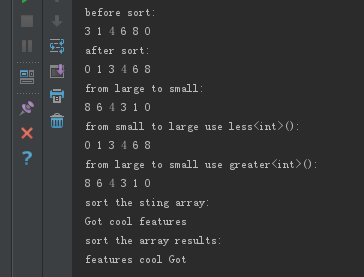
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <functional> using namespace std; template <typename T1> void ShowIntArray(const T1 begin, const T1 end) { for_each(begin,end,[](const int &x){cout << x <<" "; }); cout << "\n"; } template <typename T> void ShowSTLArray(const T&cont) { auto iter = cont.begin(); auto end = cont.end(); for(;iter!=end;iter++) { cout << *iter <<" "; } cout <<endl; }; void cpp_sort() { int a[]= {3,1,4,6,8,0}; int *begin = a; int *end = a + 6; cout << "before sort:\n"; ShowIntArray(begin, end); sort(begin,end); cout << "after sort:\n"; ShowIntArray(begin, end); cout << "from large to small:\n"; sort(begin,end,[](const int &x,const int &y){return x>y;}); ShowIntArray(begin, end); cout << "from small to large use less<int>():\n"; sort(begin,end,less<int>()); ShowIntArray(begin, end); cout << "from large to small use greater<int>():\n"; sort(begin,end,greater<int>()); ShowIntArray(begin, end); vector<string> vecStr{"Got","cool","features"}; cout << "sort the sting array:\n"; ShowSTLArray(vecStr); auto strCmp = [](string &a,string &b) { return a.length() > b.length(); }; cout << "sort the array results:\n"; sort(vecStr.begin(),vecStr.end(),strCmp); ShowSTLArray(vecStr); } void cpp_binary_search() { cout << "=======search 01:==========\n"; std::vector<int> haystack {32132, 121, 3, 5, 9}; std::vector<int> needles {1, 2, 3}; sort(haystack.begin(),haystack.end()); for (auto needle : needles) { cout << "Searching for " << needle << '\n'; if (binary_search(haystack.begin(), haystack.end(), needle)) { cout << "Found " << needle << '\n'; } else { cout << "no dice!\n"; } } cout << "=======search 01:==========\n"; std::vector<int> haystack2 {32132, 121, 3, 5, 9,100,40,323}; sort(haystack2.begin(),haystack2.end(),[](int &x,int &y){return x<y;}); ShowSTLArray(haystack2); auto func =[](int i,int j)->bool{cout<< "i:" << i; cout << " j:"<<j;cout<<"\n";return (i<j);}; if (binary_search(haystack2.begin(),haystack2.end(),5,func)) { cout << "found 5" <<endl; } } int main() { //cpp_sort(); cpp_binary_search(); return 0; }
binarySearch结果:
Sort结果:
<5> 线程大法
(1) hello world thread:

#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <memory> using namespace std; void thread_task() { cout << "thread hello world\n"; } int main() { shared_ptr<thread> t(new thread(thread_task)); t->join(); return 0; }
(2)带参数的函数(bind方法,直接使用thread构造也可以)

void thread_parm(const int &n,const string& name) { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { cout << name <<":thread loop in " << i <<endl; } } void withParam() { thread t0(thread_parm,100,"houdini"); thread t1(bind(thread_parm,100,"maya")); t0.join(); t1.join(); } int main() { withParam(); return 0; }
(3)成员对象函数执行在线程中(也可以作用到智能指针对象)

class HelloObject { public: void sayHello(const string& name,int n) { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { cout << name << " thread: " << i <<endl; } } }; void objectFunction() { HelloObject obj; thread t(&HelloObject::sayHello,&obj,"Json",6); t.join(); // work with shared_ptr shared_ptr<HelloObject> objPtr(new HelloObject()); thread tptr(&HelloObject::sayHello,objPtr,"Houdini",6); tptr.join(); } int main() { objectFunction(); return 0; }
(4)传递引用,头文件functional,std::ref()

class FuncObj { public: void operator()()const { cout << this <<endl; } }; void passRef() { auto obj = FuncObj(); obj(); //pass by value cout << "thread will pass by value\n"; thread t1(obj); t1.join(); //pass by ref cout << "thread will pass by ref\n"; thread t2(ref(obj)); t2.join(); } int main() { passRef(); return 0; }
结果:
0x22fdff
thread will pass by value
0x7c6150
thread will pass by ref
0x22fdff
普通的函数也可以

void increment(int &value) { value++ ; cout << "value :" << value <<endl; } void passRef2() { int a = 10; thread t(increment,ref(a)); t.join(); } int main() { passRef2(); return 0; }
(5)基本功能:
匿名函数:get_id() 区分线程

void lambdaTest() { vector <thread> threads; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { threads.emplace_back(thread([](){cout << "thread id " << this_thread::get_id() << endl;})); } for(auto &t : threads) { t.join(); } } int main() { lambdaTest(); return 0; }
总线程数:
cout << thread::hardware_concurrency() <<endl;
(6)异常与线程
标准处理方法

struct Counter2 { int value; Counter2():value(0){} void increment() { ++value; } void decrement() { if(value == 0) { throw string("value cannot be less than 0"); } --value; } }; struct Wrapper { Counter2 ct; mutex m; void increment() { } void decrement() { m.lock(); try { ct.decrement(); } catch (const string &e) { m.unlock(); cout << e <<endl; throw e; } m.unlock(); } }; void exceptionLock() { Wrapper wap; wap.ct.value = 10; vector<thread> threads; for(int i=0;i<11;i++) { threads.emplace_back(thread([&wap](){ wap.decrement(); })); } for(auto &t:threads) { t.join(); } cout << wap.ct.value << endl; }
(7)模仿Inter TBB parallel_for
串行时间:87
并行时间:19

struct BlockRange { BlockRange():begin(0),end(0) { } int begin; int end; }; class ApplyFoo { public: ApplyFoo(vector<int> *data):mData(data) { } void operator()(const BlockRange &range)const { for(int i=range.begin;i<range.end;i++) { (*mData)[i] += 5; } } private: vector<int> *mData; }; template <typename T> void parallel_for(const T &body,int size,int begin) { auto nThreads = thread::hardware_concurrency(); auto nValuesSize = size; auto perBlockSize =nValuesSize / nThreads; if(nValuesSize < nThreads) { BlockRange range; range.begin = begin; range.end = nValuesSize; body(range); return; } // building blocks vector<BlockRange> blocks; int index = begin; while(index <= nValuesSize) { BlockRange range; range.begin = index; range.end = index+ perBlockSize; blocks.push_back(range); index += (perBlockSize) ; } // fix last block end size; blocks[blocks.size()-1].end = nValuesSize; // thread pool to run typedef shared_ptr<thread> thread_ptr; vector<thread_ptr> pools; for(BlockRange&r:blocks) { pools.emplace_back(new thread(body,r)); } for(auto &t:pools) { t->join(); } } void parallel() { vector<int> values(10000000); fill(values.begin(),values.end(),100); double start,end,cost; start=clock(); parallel_for(ApplyFoo(&values),values.size(),10); end= clock(); cost = end -start; cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl; } void serial() { vector<int> values(10000000); fill(values.begin(),values.end(),100); double start,end,cost; start=clock(); for(int i=0;i<values.size();i++) { values[i] += 5; } end= clock(); cost = end -start; cout << "serial for cost time:" << cost <<endl; } int main() { parallel(); serial(); return 0; }
并行accumulation:
10亿个元素相加:简直他妈的快飞起来了。
串行时间:13063
并行时间:1023

#include <vector> #include <time.h> #include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; struct BlockRange { BlockRange():begin(0),end(0),id(0) { } int begin; int end; int id; }; class ApplyFoo { public: ApplyFoo(vector<int> *data):mData(data) { } void operator()(const BlockRange &range,vector<int> *des)const { auto value = int(0); for(int i=range.begin;i<range.end;i++) { value +=(*mData)[i]; } (*des)[range.id] = value; } private: vector<int> *mData; }; template <typename retType,typename T> retType parallel_add(const T &body,int size,int begin) { vector<retType> partial_accum; auto nThreads = thread::hardware_concurrency(); auto nValuesSize = size; auto perBlockSize =nValuesSize / nThreads; if(nValuesSize < nThreads) { partial_accum.resize(1); BlockRange range; range.begin = begin; range.end = nValuesSize; range.id = 0; body(range,&partial_accum); return accumulate(partial_accum.begin(),partial_accum.end(),retType(0)); } // building blocks vector<BlockRange> blocks; int index = begin; int blockId = 0; while(index <= nValuesSize) { BlockRange range; range.begin = index; range.end = index+ perBlockSize; range.id = blockId; blocks.push_back(range); index += (perBlockSize) ; blockId += 1; } partial_accum.resize(blocks.size()); // fix last block end size; blocks[blocks.size()-1].end = nValuesSize; // thread pool to run typedef shared_ptr<thread> thread_ptr; vector<thread_ptr> pools; for(BlockRange&r:blocks) { pools.emplace_back(new thread(body,r,&partial_accum)); } for(auto &t:pools) { t->join(); } return accumulate(partial_accum.begin(),partial_accum.end(),retType(0)); } void parallel() { vector<int> values(1000000000); fill(values.begin(),values.end(),1); double start,end,cost; start=clock(); cout << "get the result :" <<parallel_add<int>(ApplyFoo(&values),values.size(),0) <<endl; end= clock(); cost = end -start; cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl; } void serial() { vector<int> values(1000000000); fill(values.begin(),values.end(),1); double start,end,cost; start=clock(); cout << "get the result :" <<accumulate(values.begin(),values.end(),0) <<endl; end= clock(); cost = end -start; cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl; } int main() { parallel(); //serial(); return 0; }
<n> boost bind

#include <boost/bind.hpp> #include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp> #include <iostream> using namespace std; void dprint(int x,int y) { cout << x << " " <<y <<endl; } class Bind_test { public: void setData(int x,int y) { _x = x; _y = y; } void printData() { cout << _x << " " <<_y <<endl; } private: int _x; int _y; }; void increnum(int &dg) { dg++; } int main() { boost::bind(&dprint,5,5)(); // 5,5 boost::bind(&dprint,3,_1)(4); // 3, 5 boost::bind(&dprint,_1,_1)(2); // 2, 2 boost::bind(&dprint,_1,_2)(1,2); // 1, 2 boost::bind(&dprint,_2,_1)(1,2); // 2, 1 ->函数参数对掉 cout << "\nbind the class function\n"; boost::shared_ptr<Bind_test> bclass(new Bind_test); boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,bclass,1,2)(); bclass->printData(); Bind_test *bclass_02 = new Bind_test; boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,bclass_02,2,3)(); bclass_02->printData(); // 2 ,3 delete bclass_02; Bind_test bclass_03; boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,4,5)(); bclass_03.printData(); // 4 ,5 boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,_1,_1)(9); bclass_03.printData(); // 9 ,9 boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,_1,_2)(9,10); bclass_03.printData(); // 9 ,10 int dgNum = 0; boost::bind(&increnum,boost::ref(dgNum))(); // 类似C++11 Thread 里要传递引用std::ref(x) cout << dgNum <<endl; cin.get(); return 0; }
额外的:
static_assert 编译时候assertions

下面将输出:hello \n no
cout << R"(hello \n no)" <<endl;
。




