VIS RAYTRACING 2
1, Triangle SDF

发现Houdini行列式竟然会出问题????有人测试过matrix2吗。。。。。
float area_tri(vector2 a, b ,c){ float m11 = b.x - a.x; float m12 = c.x - a.x; float m21 = b.y - a.y; float m22 = c.y - a.y; // THIS WILL CAUSE ERROR ----- //matrix2 m = set( m11,m12,m21,m22) ; //float area = determinant(m); //return area * 0.5f; // THIS WILL CAUSE ERROR ------ return 0.5f*(a.x*b.y + b.x*c.y + c.x*a.y -a.x*c.y - b.x*a.y - c.x*b.y); } // int in_tri(float abs_AF,abs_BT,abs_GM) { if (abs_AF > 0.99999f) return 0; if (abs_BT > 0.99999f) return 0; if (abs_GM > 0.99999f) return 0; if( abs_AF + abs_BT +abs_GM> 1.0f) return 0; return 1; } // define our triangle vector2 a = set(-2.0f, 0.0f); vector2 b = set(2.0f, 0.0f); vector2 c = set(0.0f, 2.0f); vector2 inp = set(@P.x, @P.y); float A = area_tri(a, b, c); float Aa = area_tri(inp, b,c); float Ab = area_tri(inp, a,c); float Ac = area_tri(inp, a,b); float AF = Aa / A; float BT = Ab / A; float GM = Ac / A; float abs_AF = abs(AF); float abs_BT = abs(BT); float abs_GM = abs(GM); f@sdf = 0; if (in_tri(abs_AF,abs_BT,abs_GM) ) // if exist in tri; { f@sdf = min(abs_GM, min(abs_AF,abs_BT) ); } else{ f@sdf = 0 ; }
2,map 2d points to sphere:
假如一些随机点应用:
phi = u * phi_max theta= theta_min + v* (theta_max- theta_min) x = r sin(theta) cos(phi) y = r sin(theta) sub(phi) z = r cos(theta)

float r = chf("radius"); float u = chf("u"); float v = chf("v"); float phi_max = rand(@ptnum*10058) * 2.0f * PI; float theta_min = rand(@ptnum*1000); float theta_max = rand(@ptnum*500) * PI; float phi = u * phi_max; float theta = theta_min + v*( theta_max - theta_min); float x = r * sin(theta) * cos(phi); float y = r * sin(theta) * sin(phi); float z = r * cos(theta); @P.x = x; @P.y = y; @P.z = z;
This form is particularly useful for texture mapping, where it can be directly used to map a texture defined over[0,1]^2 to the sphere
u = 0.0 v=1.0
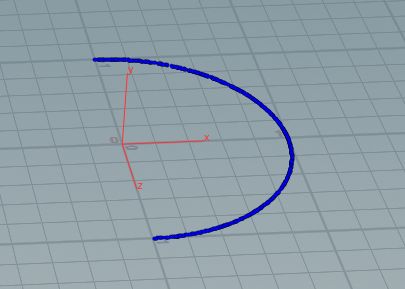
u=0.5 v=1
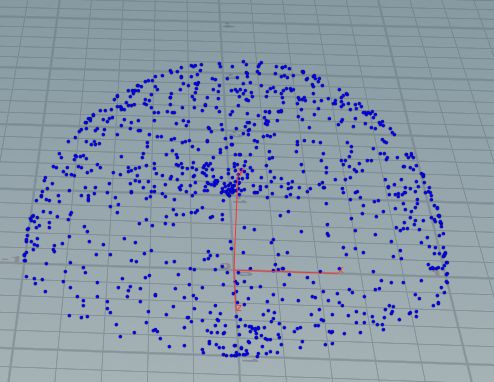
u=v=1
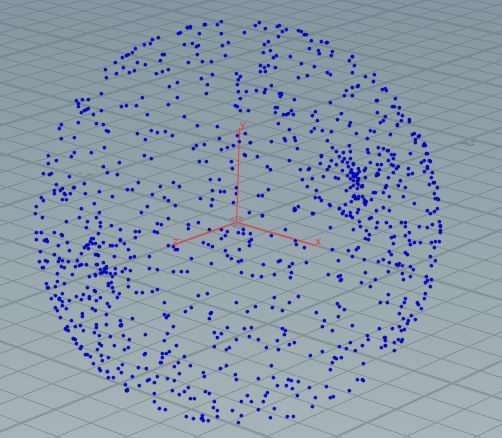
均匀分布在全球:
参考https://github.com/diharaw/GPUPathTracer/blob/master/src/shader/path_tracer_cs.glsl
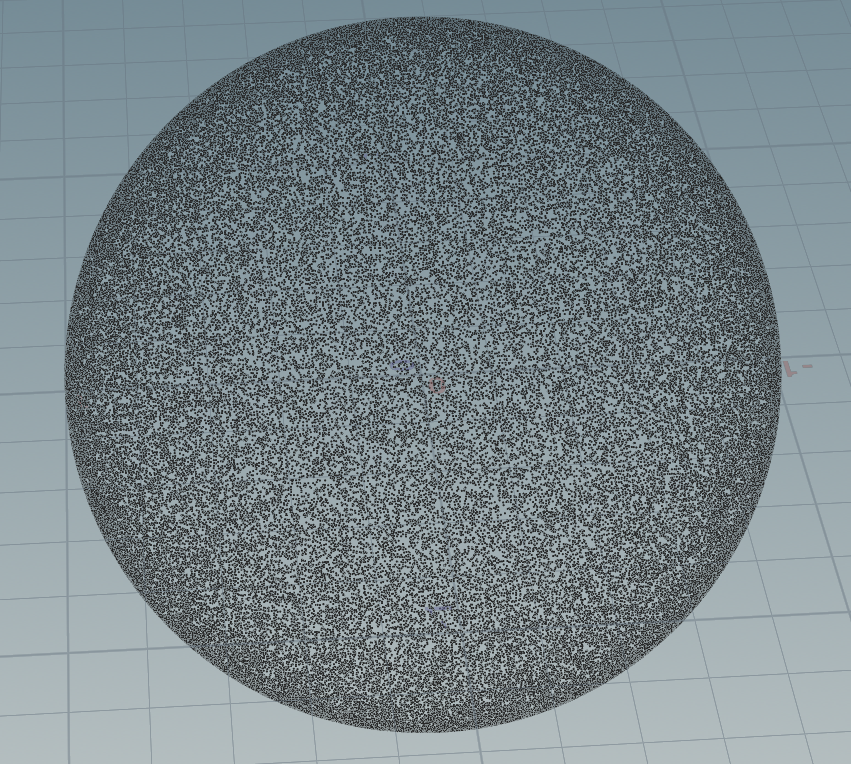

vector random_in_unit_sphere(int state) { float z = rand(state*131) * 2.0f - 1.0f; float t = rand(state*12) * 2.0f * 3.1415926f; float r = sqrt(max(0.0, 1.0f - z * z)); float x = r * cos(t); float y = r * sin(t); vector res = set(x, y, z); return res; } for(int i=0;i<100000;i++) { addpoint(geoself(),random_in_unit_sphere(i) ) ; }
分布很均匀。
方法2:
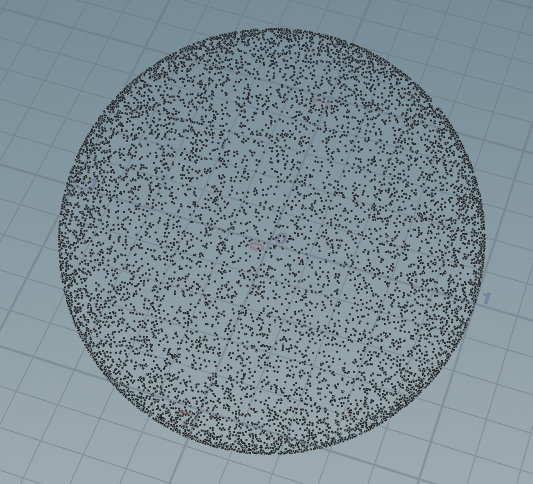

vector random_unit_vector(int i) { float a = rand(i*502) * 2 * PI; float z = fit(rand(i*50000),0,1,-1,1); float r = sqrt(1 - z*z); return set(r*cos(a), r*sin(a), z); } for(int i=0 ; i< 10000;i++){ addpoint(geoself(),random_unit_vector(i)); }
用球坐标分布在球内:

vector random_in_unit_sphere(int state) { float u = rand(state); float v = rand(state+56465); float theta = u * 2.0 * PI; float phi = acos(2.0 * v - 1.0); float r = cbrt(rand(state+561) ); float sinTheta = sin(theta); float cosTheta = cos(theta); float sinPhi = sin(phi); float cosPhi = cos(phi); float x = r * sinPhi * cosTheta; float y = r * sinPhi * sinTheta; float z = r * cosPhi; return set( x, y, z); } for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) { addpoint(geoself(),random_in_unit_sphere(i) ) ; }
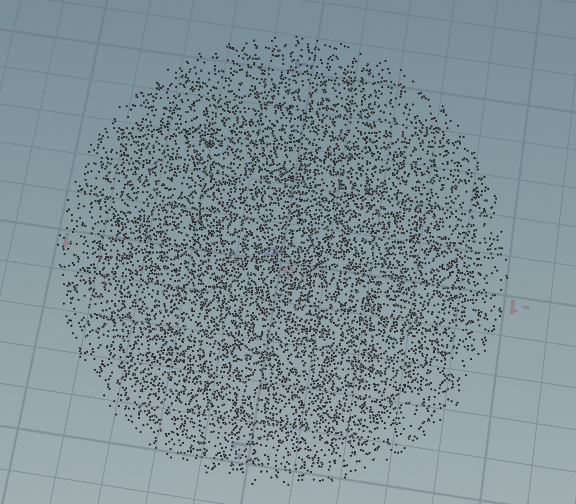
跟这个相关的分布http://corysimon.github.io/articles/uniformdistn-on-sphere/
http://datagenetics.com/blog/january32020/index.html
https://www.jasondavies.com/maps/random-points/
Raytracing in one weekend用球坐标分布在球内:
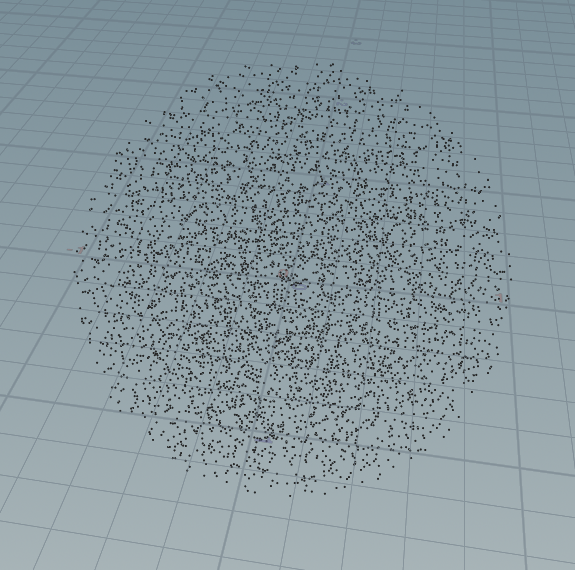
vector random_in_unit_sphere(int seed) { while (true) { float vx = rand((seed + 1 ) * 2); float vy = rand(seed + 320); float vz = rand(seed + 1744); vx = fit(vx, 0,1, -1,1); vy = fit(vy, 0,1, -1,1); vz = fit(vz, 0,1, -1,1); vector v = set(vx,vy,vz); if (length(v) >=1 ) break; // 按道理说这里应该是continue,不知道houdini应该处理不了? else return v; } return 0; } for(int i =0;i<10000;i++){ vector p = random_in_unit_sphere(i*20); addpoint(geoself(), p); }
但是经过我测试,for循环竟然完美支持continue:
vector random_in_unit_sphere(int seed) { for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ float vx = rand((seed + 1 ) * 2); float vy = rand(seed + 320); float vz = rand(seed + 1744); vx = fit(vx, 0,1, -1,1); vy = fit(vy, 0,1, -1,1); vz = fit(vz, 0,1, -1,1); vector v = set(vx,vy,vz); if (length(v) >=1 ) continue; else return v; } return 0; } for(int i =0;i<10000;i++){ vector p = random_in_unit_sphere(i*20); addpoint(geoself(), p); }
True lambertian里面还说了一些:
稍微对这个方法修改,就可以达到球表面分布:
https://raytracing.github.io/books/RayTracingInOneWeekend.html
Picking random points on the unit sphere can be achieved by picking random points in the unit sphere, and then normalizing those.
vector random_in_unit_sphere(int seed) { for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ float vx = rand((seed + 1 ) * 2); float vy = rand(seed + 320); float vz = rand(seed + 1744); vx = fit(vx, 0,1, -1,1); vy = fit(vy, 0,1, -1,1); vz = fit(vz, 0,1, -1,1); vector v = set(vx,vy,vz); if (length(v) >=1 ) continue; else return v; } return 0; } for(int i =0;i<10000;i++){ vector p = random_in_unit_sphere(i*20); addpoint(geoself(), normalize(p) ); // Normalize就行 }
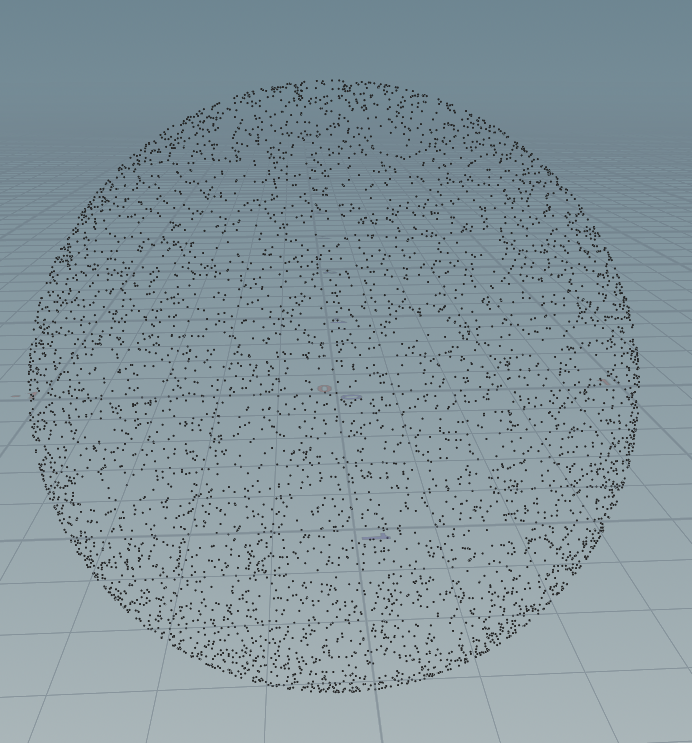
误区修复,我突然发现houdini的seed的问题,不是while循环的问题:
xy平面的disk撒点。houdini rand依赖seed所以关键问题必须给seed做一份copy,然后让rand_range()函数种子每次都不能一样。这个是关键。!
float rand_range(int seed; float low; float high){ return fit(rand(seed), 0,1, low, high); } vector random_in_unit_disk(int seed) { int seed_copy = seed+13727; while(1) { vector p = set(rand_range(seed_copy, -1.0,1.0), rand_range(seed_copy + 100, -1,1), 0); if (length(p) >= 1) { seed_copy+=7; seed_copy*=2; continue; } else return p; } } for(int i=0;i<80;i++){ vector v = random_in_unit_disk(i); addpoint(geoself(), v); }
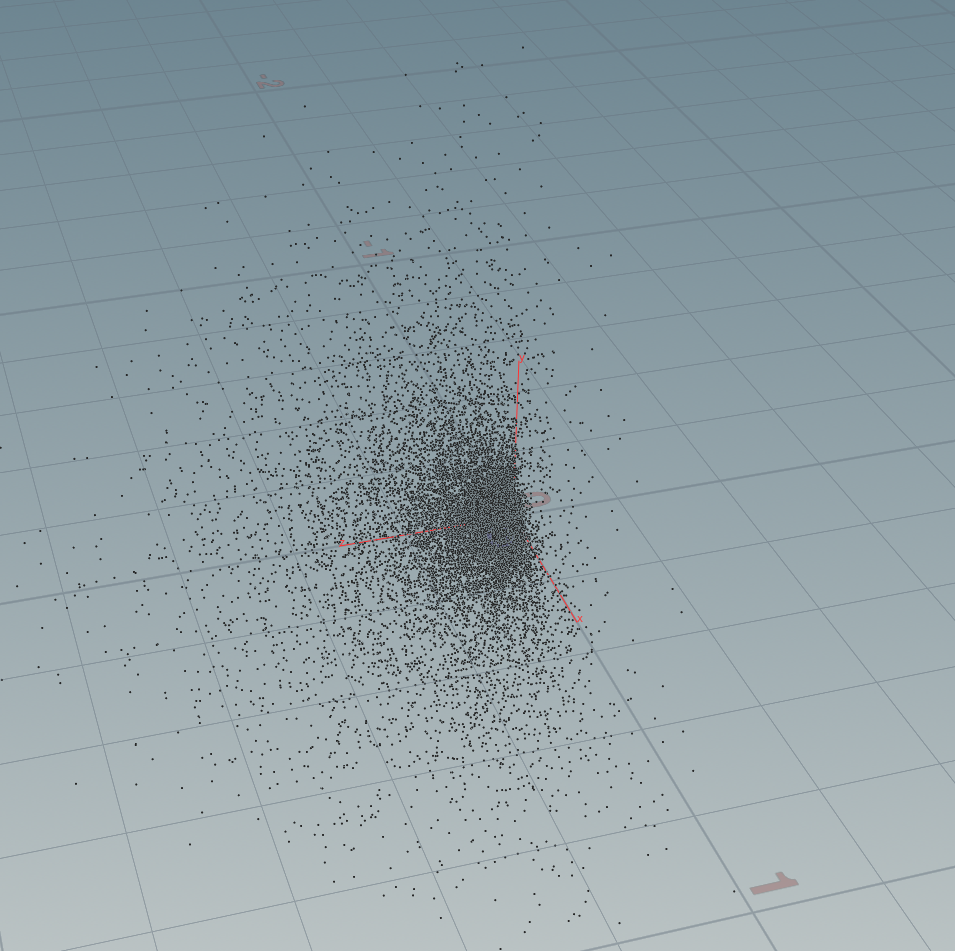
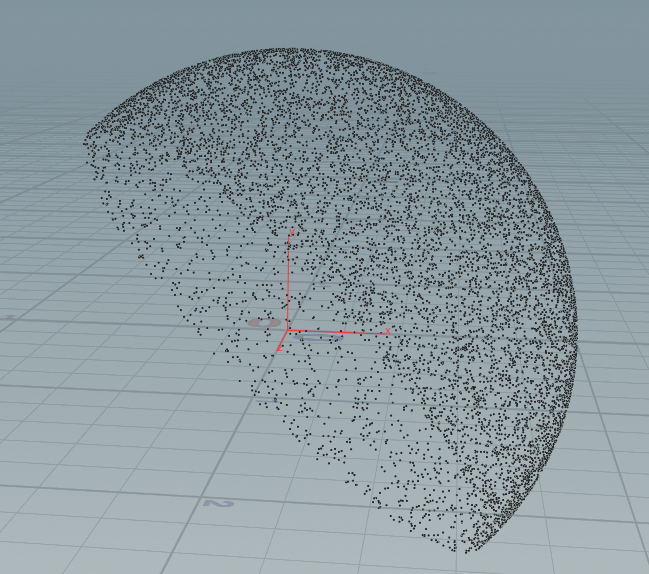
3:填充的半球点 openglSSAO一章提到:

float llerp(float a;float b;float f) { return a + f * (b - a); } int nsamples = 14164; for (int i = 0; i < nsamples; ++i) { vector sample = set( rand(i)* 2.0 - 1.0, rand(i*51400) * 2.0 - 1.0, rand(i*5024713)); sample = normalize(sample); sample *= rand(i*50723); float scale = float(i) / float(nsamples); scale = lerp(0.1f, 1.0f, scale * scale); sample *= scale; addpoint(geoself(),sample); }
4,Sphere mapping:
开局给你一个球,怎么贴HDR?实际就是求UV
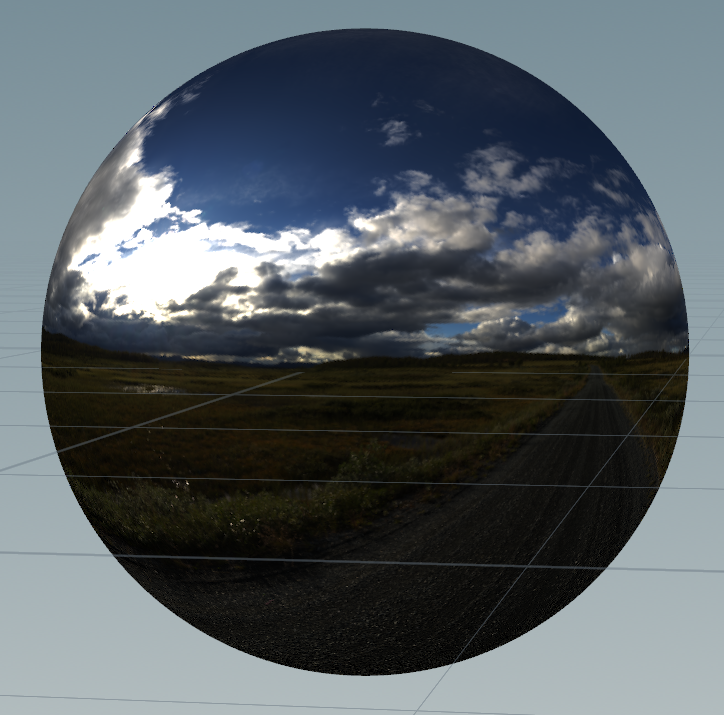

float u = atan(@P.z , @P.x); u/= (2 * PI); float v = acos(@P.y); v/= PI; v = 1- v; string tex = chs("texture"); @Cd = texture(tex, u ,v);
开局给你一个向量,这个向量为任何向量:
float phi = atan2(dir.x, dir.z); float theta = acos(dir.y); float u = phi / (2.000 *d_pi ); float v = 1 - theta / d_pi; //u = clamp(u,0,1); //v = clamp(v,0,1); vector imgL = texture(ch("img"),u,v);
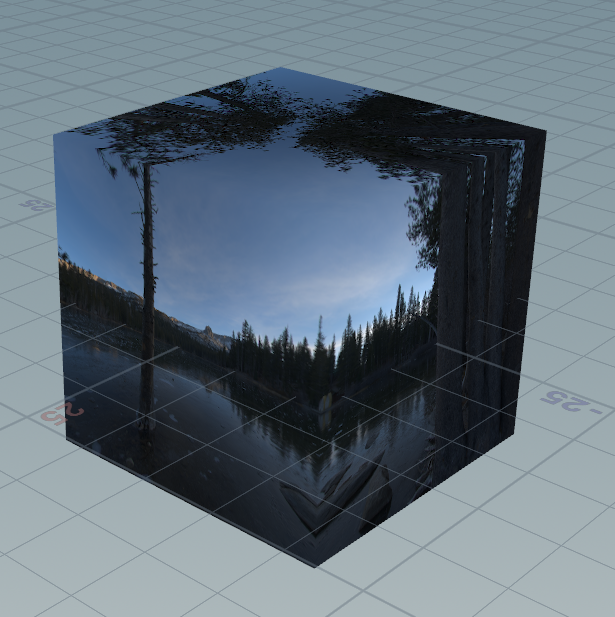
5, sample Cube map

string img = chs("img"); vector2 SampleSphericalMap(vector v) { vector2 invAtan = set(0.1591, 0.3183); vector2 uv = set(atan(v.z, v.x), asin(v.y)); uv *= invAtan; uv += 0.5; return uv; } vector dir = normalize(@P); vector2 uv = SampleSphericalMap(dir); vector color = texture(img, uv.x, uv.y); @uv = uv; @Cd = color;
6, 球坐标与直角转换:
只要注意你画半圆:
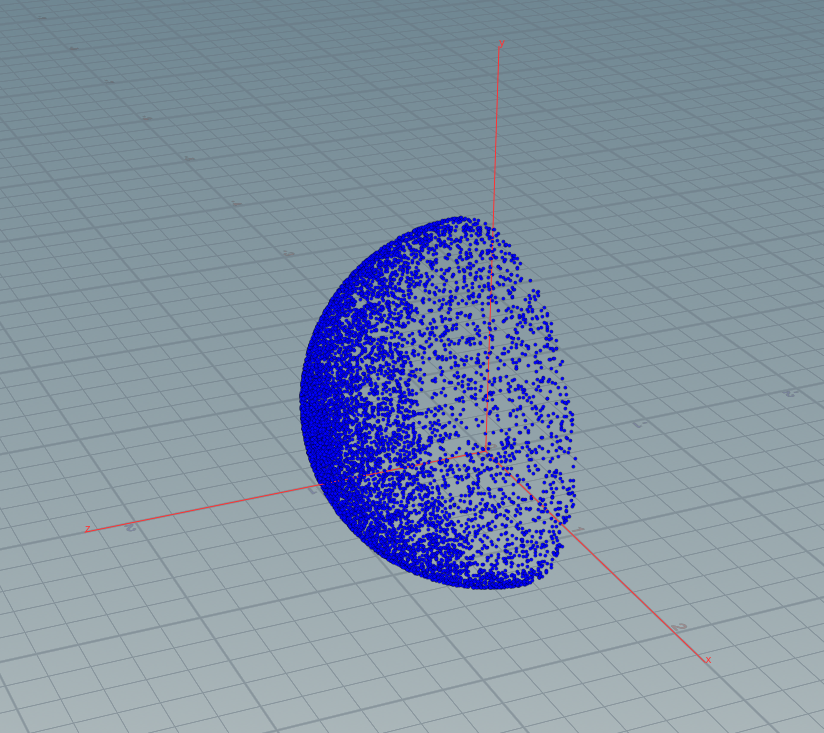
for(int i=0 ;i < 10000; i++) { float theta = rand(i+4573) * (PI/2.0f); float phi = rand(i*211020) * (2.0f* PI); float x=sin(theta)*cos(phi); float y=sin(theta)*sin(phi); float z=cos(theta); addpoint(geoself(), set(x,y,z)); }
只要看你得theta的 区间是PI/2 ,所以 半圆在Z轴。一般都放到z轴,然后要把变换到法线位置(一下是线性变换,矩阵也可以)
// spherical to cartesian (in tangent space) vec3 tangentSample = vec3(sin(theta) * cos(phi), sin(theta) * sin(phi), cos(theta)); // tangent space to world vec3 sampleVec = tangentSample.x * right + tangentSample.y * up + tangentSample.z * N;
7,ImportanceSampleGGX && "CosWeightedSampleGGX" && Align-to-normal-method
两者都是从[0-1] [0-1]的范围采样变成半球。
ImportanceSampleGGX:
带有roughtness的参数.注意下面的代码roughness 是平方的,disney和epic的区别就是epic平方了


float VanDerCorpus(int n; int base) { float invBase = 1.0f / float(base); float denom = 1.0f; float result = 0.0f; for(int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) { if(n > 0) { denom = float(n) % 2.0f; result += denom * invBase; invBase = invBase / 2.0f; n = int(float(n) / 2.0f); } } return result; } // ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- vector2 HammersleyNoBitOps(int i; int N) { return set(float(i)/float(N), VanDerCorpus(i, 2)); } vector ImportanceSampleGGX(vector2 Xi;vector N;float roughness) { float a = roughness*roughness; float phi = 2.0 * PI * Xi.x; float cosTheta = sqrt((1.0 - Xi.y) / (1.0 + (a*a - 1.0) * Xi.y)); float sinTheta = sqrt(1.0 - cosTheta*cosTheta); // from spherical coordinates to cartesian coordinates vector H; H.x = cos(phi) * sinTheta; H.y = sin(phi) * sinTheta; H.z = cosTheta; // from tangent-space vector to world-space sample vector vector up = abs(N.z) < 0.999 ? set(0.0, 0.0, 1.0) : set(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); vector tangent = normalize(cross(up, N)); vector bitangent = cross(N, tangent); vector sampleVec = tangent * H.x + bitangent * H.y + N * H.z; return normalize(sampleVec); } int n = 4096; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ int test = i; vector2 xy = HammersleyNoBitOps(test,n); vector testNormal = chv("normal"); vector newpos = ImportanceSampleGGX(xy,testNormal, chf("roughtness")); addpoint(geoself(),newpos); }
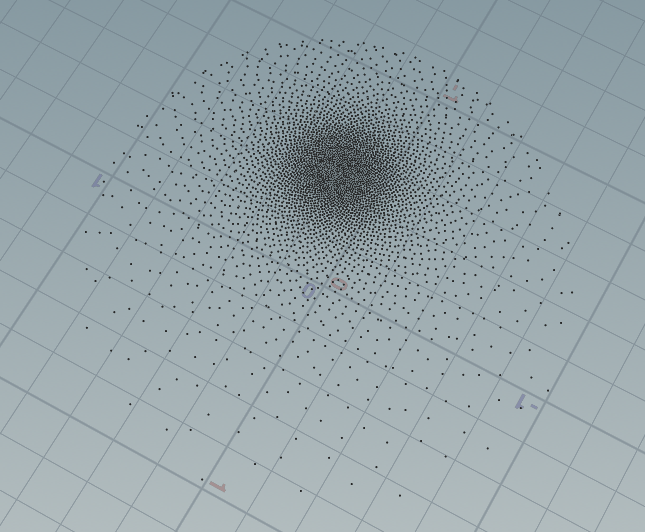
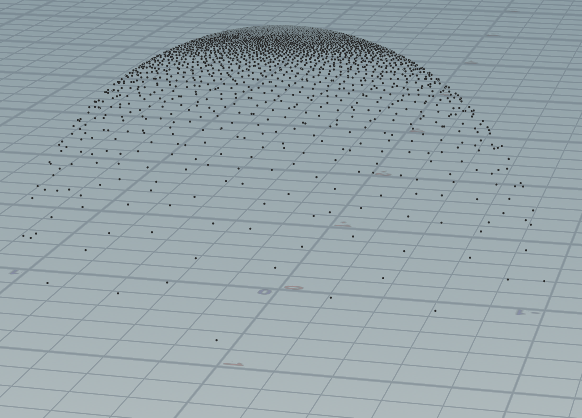
CosWeightedSampleGGX:
带个指数级衰减:


vector2 genSamplers(int i){ float sx = i; float sy = i*100; return set(rand(sx),rand(sy)); } vector CosWeightedSampled(vector2 Xi;vector N;float e){ float cos_phi = cos(2.0f * PI * Xi.x); float sin_phi = sin(2.0f * PI * Xi.x); float cos_theta = pow((1.0f - Xi.y) , 1.0f / (e+1.0)); float sin_theta = sqrt(1.0f - cos_theta * cos_theta); // Generation Z based sphere float pu = sin_theta * cos_phi; float pv = sin_theta * sin_phi; float pw = cos_theta; vector H = set(pu,pv,pw); // from tangent-space vector to world-space sample vector vector up = abs(N.z) < 0.999 ? set(0.0, 0.0, 1.0) : set(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); vector tangent = normalize(cross(up, N)); vector bitangent = cross(N, tangent); vector sampleVec = tangent * H.x + bitangent * H.y + N * H.z; return sampleVec; } int n = 4096; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ int test = i; vector2 xy = genSamplers(test); vector N = chv("normal"); float e = chf("e"); vector sampleVec = CosWeightedSampled(xy,N,e); addpoint(geoself(), sampleVec ); }
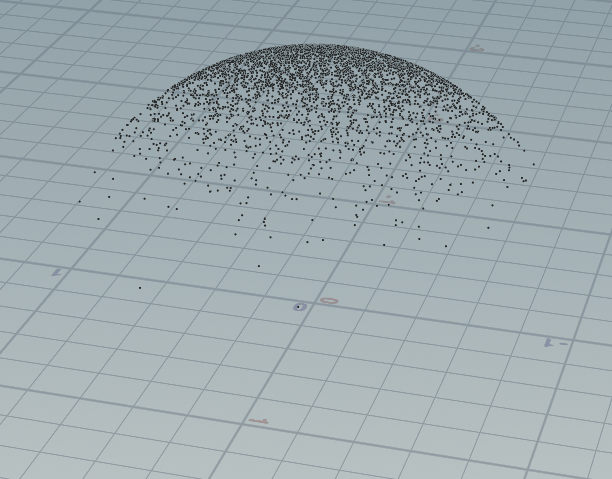
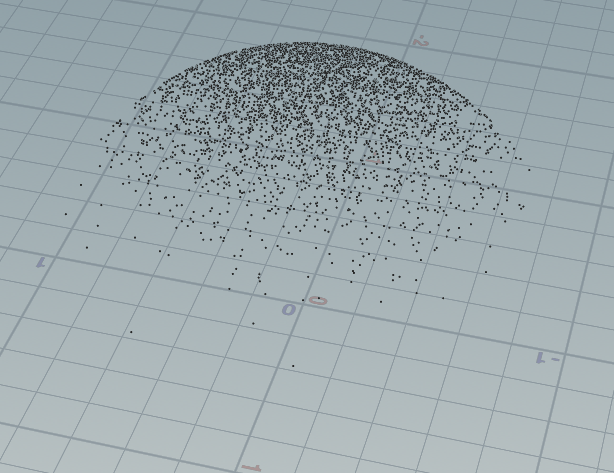
这里带入一种直接对齐方法,原理简单,直接对其到N方向上的半球,这种方法比上面的简单的多,输入方向N:


vector random_unit_vector(int i) { float a = rand(i*502) * 2 * PI; float z = fit(rand(i*50000),0,1,-1,1); float r = sqrt(1 - z*z); return set(r*cos(a), r*sin(a), z); } vector N = chv("N"); N = normalize(N); for(int i=0 ; i< 10000;i++){ vector dir = random_unit_vector(i); if(dot(dir, N) < 0){ dir = -dir; } addpoint(geoself(),dir); }
所以raytracing in one weekend 里的半球diffuse也可以这么写:

8, From RayTracing from ground up
Review the Regular Sampling in a pixel:


注意这种采样是在一个像素里生成5 * 5 个采样。实际上这种方法问题请大的:

Random Sampling:
只用把4.1里的内部代码替换下即可:

Jittered Sampling: 一个像素25个采样点:
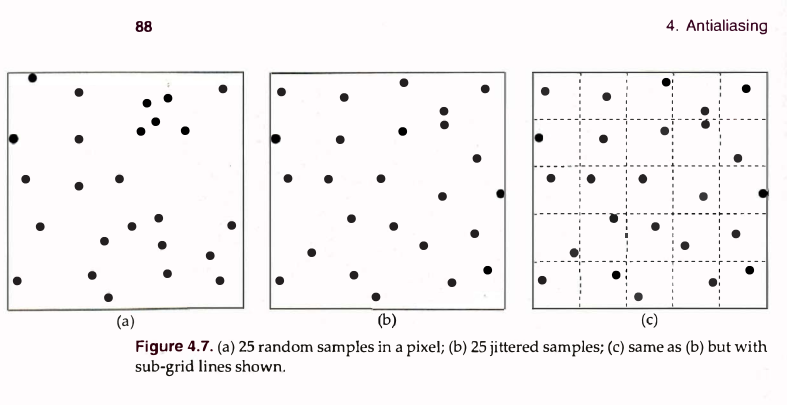
修改4.1的代码就行: replace the expressions q + 0.5 and p+0.5 to -> q + rand_float() and p+ rand_float()
有时间一定要实现一下:
https://graphics.pixar.com/library/MultiJitteredSampling/paper.pdf
随机
1, 有全局seed的 random[0-1]

static unsigned int seed = 0x13371337; static inline float random_float() { float res; unsigned int tmp; seed *= 16807; tmp = seed ^ (seed >> 4) ^ (seed << 15); *((unsigned int *) &res) = (tmp >> 9) | 0x3F800000; return (res - 1.0f); } int main() { for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ cout << random_float() << endl; } }
参考:fundamentals of computer graphics
http://learnopengl.com/#!Advanced-Lighting/SSAO
PBRT2
Raytracing from ground up




