c潭州课堂25班:Ph201805201 MySQL第二课 (课堂笔记)
![]()
![]()
mysql> create table tb_2(
-> id int,
-> name varchar(10) not null
-> );
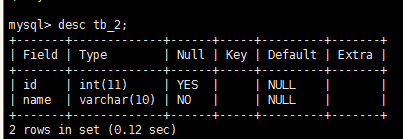
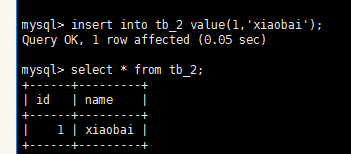
插入数据 insert into tb_2 value(1,'xiaobai'); 在非空时,NOT NULL 必须有值,
2,在已有的表中设置一个字段的非空约束
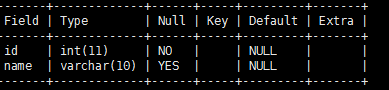
mysql> alter table tb_2
-> modify id int not null;
取消非空约束
mysql> alter table tb_2
-> modify id int:
![]()
![]()
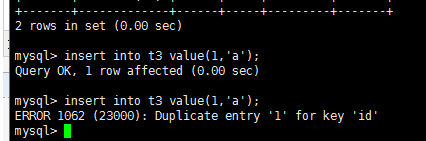
mysql> create table t3
-> (id int unique key,
-> name varchar(10);

unique key 字段不可重复,否则报错,
2, 在已有的表中添加唯一约束
方法1
mysql> alter table t3
-> add unique key(name);
方法2
alter table t3
-> modify name varchar(10) unique key;
alter table t3 modify id int unique key;
删除唯一
mysql> alter table t3
-> drop key name;
![]()
主键的作用: 可以唯一标识一条数据,每张表里只能 有一个主键,
主键特性: 非空且唯一,当表里没有主键时,第一个非空且唯一的列,被当成主键,
创建定有主键的表
create table t4(
-> id int primary key,
-> name varchar(10));
在已有的表中设定主键
方法1
> alter table t4
-> add primary key(id);
方法2
> alter table t4
>modify id int primary key;

删除主键
mysql> alter table t4
-> drop primary key;
![]()
auto_increment 自动编号,要与键一起使用,一般与主键一起使用,一个表里只有一个自增长,
默认情况下起始值为 1,每次的增量为 1,
新建个有自增长的表
create table tb5(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(10)
->)auto_increment = 100; 设 auto_increment 从100开始

插入 name 的值,
insert into tb5 (name) values('a'),('b'), ('c');
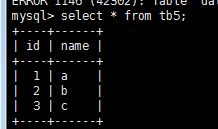
这里的 ID 字段自增长,
给已有表添加自增长:
alter table tb5
-> modify id int auto_increment;
删除:
alter table tb5
-> modify id int;

default 初始值设置,插入数据时,如果没有给该字段赋值,则会给以默认值,
新建个表
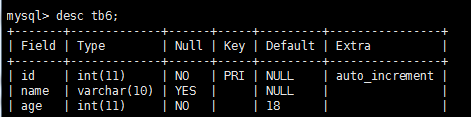
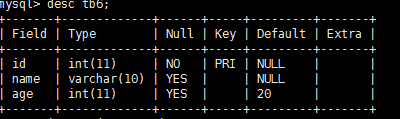
create table tb6(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(10),
-> age int not null default 18
-> );
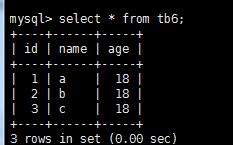
插入 name 值 ,这里 id 自增长,age 不传值则默认18
insert tb6 (name) values('a'),('b'),('c');
insert into tb6 set name='qq',age=20;
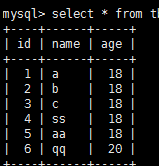
删除默认约束
alter table tb6
-> modify age int;
给已有的表添加默认约束
alter table tb6 modify age int default 20;
![]()
fofeign key 保持数据一致性完整性,实现一对一,一对多,多对多的关系,
外键必须关联到键上,一般是关联另一个表的主键,
因为一个表只存一类信息,所以用键来做参照,可以减少数据冗余,
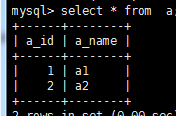
建 a 表
create table a(
-> a_id int primary key auto_increment, 唯一性,自增长,
-> a_name varchar(20) not null 非空
-> );
insert into a values(1,'a1'),(2,'a2'); 插入数据
建个 b 表
create table b(
-> b_id int primary key,
-> b_name varchar(20) not null,
-> fy_id int not null,
-> constraint AB_id foreign key(fy_id) references a(a_id)
-> );
b 表中 fy_id 的字段只能添加 a 表中的 a_id 中已有的数据,
此时 ,a 表 a_id 的数据不能被修改和删除,
删除外键
alter table b drop foreign key AB_id;
添加外键
alter table `b`
-> add constraint AB_id foreign key(fy_id) references a(a_id);
![]()
通常一个学校可以有很多学生,而一个学生只属于一个学校,
学校与学生的关系就是一对多的关系,通过外键关联实现,
创建学院表
create table tanzhou(
-> t_id int primary key auto_increment, 学院 id
-> t_name varchar(10) not null 学院名
-> );
创建学生表
create table stu(
-> s_id int primary key auto_increment, 学生 id
-> s_name varchar(10), 学生名
-> tz_id int not null, 所属学院 id
-> foreign key(tz_id) references tanzhou(t_id)
-> );
创建学生详情表
create table stu_d(
-> id int primary key,
-> age int ,
-> address varchar(20) comment '家庭住址',
-> home_num varchar(20),
-> foreign key (id) references stu(s_id)
-> );
创建一张课程表
create table k_c_b(
-> kid int primary key not null,
-> kname varchar(10),
-> ke_shii int
-> );
创建选课表
create table x_k_b(
-> xid int primary key not null,
-> kid int unique key,
-> sid int,
->primary key(kid, sid), 这行为联合组键,意义在同一学生不能选两次一样的课程,
-> foreign key(kid) references k_c_b(kid), 引课程表
-> foreign key(sid) references stu(s_id) 引学生表
-> );
补充
数据类型
tinyint 1 字节 -128 --》》127
smallint 2字节 -12768--》12768
int 4字节 -2147483643--》2147483643
bigint 8字节
float 4字节
double 8字节
double(5,2) 表示 5位数,2位小数, 如:999.99
char
char(3) 3个字节
varchar
varchar(20) 从0到20个字节
tmestamp
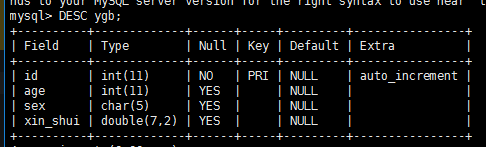
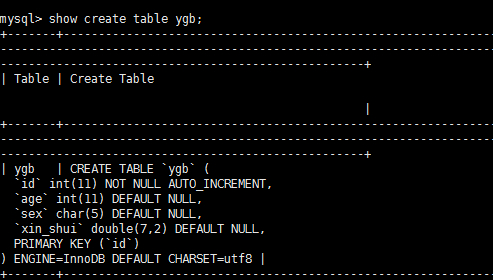
创建个员工表
主键,自增
create table ygb(
id int primary key auto_increment,
age int,
sex char(5),
xin_shui DOUBLE(7,2)
);
desc ygb;
添加字段
alter table ygb ADD 入值时间 tinyint
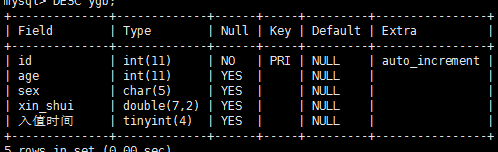
alter table ygb ADD 入值时间2 DATE NOT NULL ;
一次多个字段
alter table ygb ADD a int,
ADD b INT ,
add c INT ;
删除字段
alter table ygb DROP a;
alter table ygb DROP b,
DROP c;
改字段 默认值为 18 放在 id 的后边
alter table ygb modify age SMALLINT DEFAULT 18 after id;
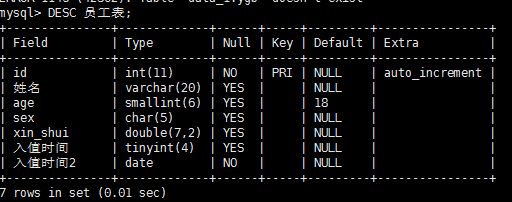
改字段名
alter table ygb change name 姓名 VARCHAR (20);
改表名
rename table ygb to 员工表;
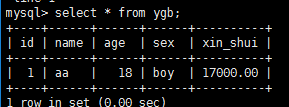
插入数据
insert into ygb (id,name,age,sex,xin_shui)
values(1,'aa',18,'boy',17000.00)
查询
select * from ygb;
insert into ygb (name,sex,xin_shui)
values('ab','boy',17000.00);
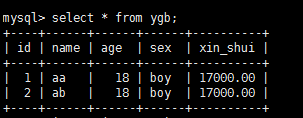 id 自增,gae 默认值,
id 自增,gae 默认值,
这样写要对应着字段写全
insert into ygb VALUES (10,'bb',20,'g',5000);
插入多组
insert into ygb (name,sex,xin_shui)
values('ac','boy',17000.00),
('ad','g',3000),
('af','b',3000);
set 插入
insert into ygb set name = 'cc'
改:
update ygb set xin_shui=xin_shui+2000 where id=10;
在原有基础上加,如果不加条件,将对所有添加
删除
delete from ygb where id=11 or id=12;
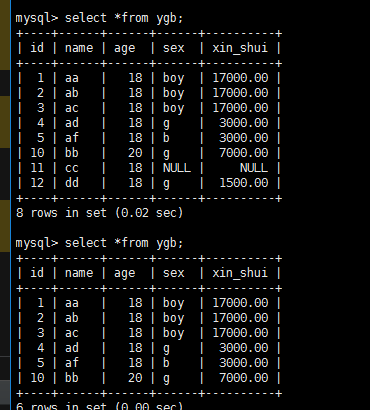
删除字段 alter table 表名 drop 字段名;:
删表:留下空表,
delete from ygb ; 一条条删
truncate table ygb; 整个删除,重建 个空表
查
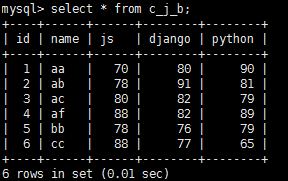
建一成绩表
create table c_j_b(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
js DOUBLE,
django DOUBLE,
python DOUBLE );
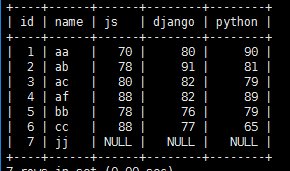
insert into c_j_b(name,js,django,python)
values('aa',70,80,90),
('ab',78,91,81),
('ac',80,82,79),
('af',88,82,89),
('bb',78,76,79),
('cc',88,77,65);
select name from c_j_b;
select name,js from c_j_b;
重复只出现一次 distinct
select distinct js from c_j_b;
这只是显示,并没有改库,
elect name,js+10,django+10,python+10 from c_j_b;
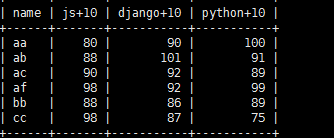
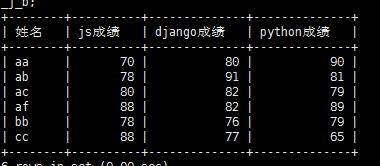
select name as 姓名,js as js成绩,django as django成绩,
python as python成绩 from c_j_b;_j_b;
select name js from c_j_b where js>80;
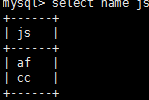
查 70 到 90 内的 between
select name, js from c_j_b where js between 70 and 90;
查 in里边的是否有
select name ,js from c_j_b where js in (78,90,70);
模糊匹配 like'a%' like'a__'
select name ,js from c_j_b where name like'a%';
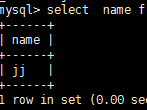
select name from c_j_b where js is null;\
排序
select name,JS from c_j_b ORDER BY JS;
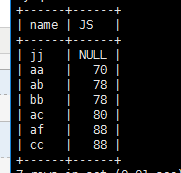
select name,JS from c_j_b ORDER BY JS desc;
select name,JS+django+python as 总成绩 from c_j_b;
+------+-----------+
| name | 总成绩 |
+------+-----------+
| aa | 240 |
| ab | 250 |
| ac | 241 |
| af | 259 |
| bb | 233 |
| cc | 230 |
| jj | NULL |
+------+-----------+
总成绩排序,从低到高,
select name,JS+django+python as 总成绩 from c_j_b order by 总成绩 desc;
+------+-----------+
| name | 总成绩 |
+------+-----------+
| af | 259 |
| ab | 250 |
| ac | 241 |
| aa | 240 |
| bb | 233 |
| cc | 230 |
| jj | NULL |
+------+-----------+
分组 group by
select name from c_j_b group by name;
分组后
分组后 js 的和, 按名字分组
select name sum(js) from c_j_b group by name;
把分组后,js 的总分大于150的打印,group by 后不可用 where ,要用 havin,
select name sum(js) from c_j_b group by name having sum(js) >150;
group by 前用 where, 其后用 having,
说明,如果 字段中有 null,此时他与谁计算都 分得到个 null,
所以 ifnull(js,0), 如果 js 里有null 那就让他 = 0.
显示
select * from c_j_b; limit 3;
select * from c_j_b; limit 1:4;

