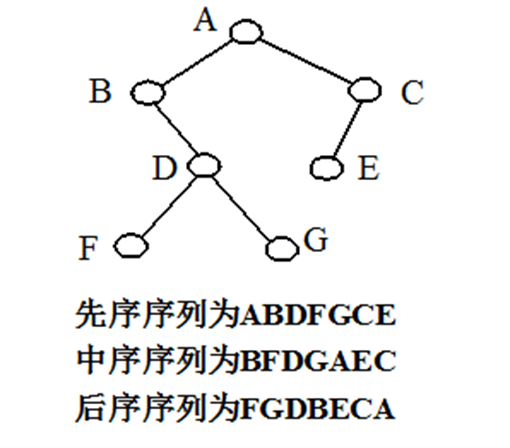
13二叉树的遍历
二叉树的遍历与构建
遍历(traversal)指的是对树中每个结点访问一次且仅一次。
访问(visit)是指对结点进行某种处理,比如输出结点值,查找某个(或某些)结点,计算结点的层号、高度、子孙个数等等。
注意:遍历必须按“一定的规律”进行,因为二叉树是非线性结构。
遍历方法(即规律)很多,常见的有:
先序遍历(preorder traversal): DLR遍历(先根结点,后左子树,再右子树)
中序遍历(inorder traversal): LDR遍历 (先左子树,后根结点,再右子树)
后序遍历(postorder traversal): LRD遍历(先左子树,后右子树,再根结点)
先序遍历算法:
步骤1)如果当前遇到的结点为空,则直接返回。
步骤2)访问当前结点x(D)。
步骤3)递归地遍历x的左子树(L)。
步骤4)递归地遍历x的右子树(R)。
步骤5)完成对以x为根的二叉树的遍历,返回。
步骤2、3、4交换语句次序,变为中序遍历、后序遍历。
二叉树算法
二叉树的存储结构(双链式):
typedef struct Bnode //结点类型定义
{ element_type data; //值域
struct Bnode *Lson, *Rson; //指向左右儿子的链域
} Bnode, *Bptr; // 结点类型名,和指针类型名
//先序遍历函数
void preorder(Bptr p)
{
if(p==NULL)
return;
visit(p);
preorder(p->Lson);
preorder(p->Rson);
}
//中序遍历函数
void inorder(Bptr p)
{
if(p==NULL)
return;
inorder(p->Lson);
visit(p);
inorder(p->Rson);
}
//后序遍历函数
void pastorder(Bptr p)
{
if(p==NULL)
return;
pastorder(p->Lson);
pastorder(p->Rson);
visit(p);
}
重要点:
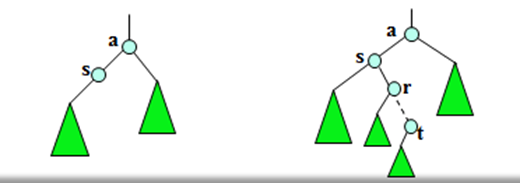
中序前驱
情况1,a有左儿子s(又分二种情况)
[1]若s没有右儿子,则s就是a的中序前趋。
[2]若s有右儿子r,那么r的最右子孙t就是a的中序前趋 。
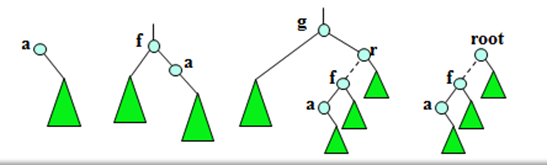
情况2,a没有左儿子(又分三种情况)
[1]若a没有父亲(a是根结点),那么,a没有中序前趋。
[2]若a是其父f的右儿子,那么,f是a 的中序前趋。
[3]若a是其父f的左儿子,如果a在g(最近)的右子树上,则g是a 的中序前趋;否则,a没有中序前趋。
遍历的实例运用
求二叉树各结点层号的算法
结点含有层数域level,采用先序遍历法
void level(Bptr p,int i)
{
if(p==NULL)
return;
p->layer=i;
level(p->Lson,i+1);
level(p->Rson,i+1);
}
主调语句: level(root,1);
求二叉树各结点高度的算法
结点含有高度域height ,采用后序遍历法
int high(Bptr p)
{ int i,j;
if(p==NULL)
return 0; //空树的高度等于0
i=high(p->Lson);
j=high(p->Rson);
p->height=(i>j)? i+1: j+1; //求出结点高度
return (p->height);
}
主调语句:h=high(root);
输出结点a所有子孙的算法
void descents(Bptr p,element_type a)
{
if(p==NULL|| found==3 )
return;
if(p->data==a)
found=1;
if(found==1)
printf("%4d",p->data);
descents(p->Lson,a);
descents(p->Rson,a);
if(p->data==a)
found=3;
}
主调语句:
found=0;
descents(root,a);
给各结点进行中序编号算法
void in_num(Bptr p)
{
if(p==NULL)
return;
in_num(p->Lson);.
p->in_number=count++;
in_num(p->Rson);
}
中序编号性质:
结点在中序序列中的序号(1,2,…… , n)。
任意一个非叶结点v,其中序编号有如下性质:
1)左子树上结点的编号都小于v的编号。
2)右子树上结点的编号都大于v的编号。
3)以v为根的子树中,编号最小的结点,位于该子树的最左端;编号最大的结点,位于该子树的最右端。
4)中序序列中,v的左子树上的结点都排在v的左边,且紧靠v;右子树上的结点都排在v的右边,也紧靠v;v位于其左右子树的子中序序列的中间。
源代码:
// Btree.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//结点的结构体
struct tree
{
int data; //结点的数据域
tree *left, *right; //结点的左、右子树
};
//树的类
class Btree
{
static int n; //记录叶子结点个数
static int m; //记录树结点的个数
public:
tree *root; //跟结点
Btree()
{
root = NULL;
}
void create_Btree(int); //构建二叉树树
void Preorder(tree *); //先序遍历
void inorder(tree *); //中序遍历
void Postorder(tree *); //后序遍历
void display1() { Preorder(root); cout << endl; }
void display2() { inorder(root); cout << endl; }
void display3() { Postorder(root); cout << endl; }
int count(tree *); //计算二叉树的个数
int findleaf(tree *); //求二叉树叶子的个数
int findnode(tree *); //求二叉树中度数为1的结点数量,这是当初考数据结构时候的最后一道题目
};
int Btree::n = 0;
int Btree::m = 0;
void Btree::create_Btree(int x)
{
tree *newnode = new tree; //为树结点动态分配内存空间
newnode->data = x; //结点存入数据
newnode->right = newnode->left = NULL; //当前结点的左、右子树为空
//如果不存在根结点,此结点为树的根结点
if (root == NULL)
root = newnode;
//
else
{
tree *back =NULL;
tree *current = root;
//遍历树 找到没有子树的结点
while (current != NULL)
{
back = current;
//左子树
if (current->data>x)
current = current->left;
//右子树
else
current = current->right;
}
//把新结点作为最后结点的左子树
if (back->data>x)
back->left = newnode;
//把新结点作为最后结点的右子树
else
back->right = newnode;
}
}
int Btree::count(tree *p)
{
if (p == NULL)
return 0;
//递归计算树的结点个数
else
return count(p->left) + count(p->right) + 1; //这是运用了函数嵌套即递归的方法。
}
void Btree::Preorder(tree *temp) //这是先序遍历二叉树,采用了递归的方法。
{
if (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
Preorder(temp->left);
Preorder(temp->right);
}
}
void Btree::inorder(tree *temp) //这是中序遍历二叉树,采用了递归的方法。
{
if (temp != NULL)
{
inorder(temp->left);
cout << temp->data << " ";
inorder(temp->right);
}
}
void Btree::Postorder(tree *temp) //这是后序遍历二叉树,采用了递归的方法。
{
if (temp != NULL)
{
Postorder(temp->left);
Postorder(temp->right);
cout << temp->data << " ";
}
}
int Btree::findleaf(tree *temp)
{
if (temp == NULL)return 0;
else
{ //左、右子树为空,叶子节点+1
if (temp->left == NULL&&temp->right == NULL)return n += 1;
else
{
findleaf(temp->left);
findleaf(temp->right);
}
return n;
}
}
int Btree::findnode(tree *temp)
{
if (temp == NULL)return 0;
else
{
if (temp->left != NULL&&temp->right != NULL)
{
findnode(temp->left);
findnode(temp->right);
}
//某结点只存在左子树,结点数+1,再遍历左子树
if (temp->left != NULL&&temp->right == NULL)
{
m += 1;
findnode(temp->left);
}
//某结点只存在右子树,结点数+1,再遍历右子树
if (temp->left == NULL&&temp->right != NULL)
{
m += 1;
findnode(temp->right);
}
}
return m;
}
void main()
{
//实例化对象
Btree A;
int array[] = { 7, 4, 2, 3, 15, 35, 6, 45, 55, 20, 1, 14, 56, 57, 58 };
//数组的长度
int k;
k = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
cout << "建立排序二叉树顺序: " << endl;
//把数组元素依次存进二叉树结构中
for (int i = 0; i<k; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << " ";
A.create_Btree(array[i]);
}
cout << endl;
cout << "二叉树节点个数: " << A.count(A.root) << endl;
cout << "二叉树叶子个数:" << A.findleaf(A.root) << endl;
cout << "二叉树中度数为1的结点的数量为:" << A.findnode(A.root) << endl;
cout << endl << "先序遍历序列: " << endl;
A.display1();
cout << endl << "中序遍历序列: " << endl;
A.display2();
cout << endl << "后序遍历序列: " << endl;
A.display3();
getchar();
}



