8数组
一维数组声明
<存储类别> <元素类型> <数组名>[<元素个数> ];
如:
int a[10];
static double b[20];
说明
1.一组连续的存储单元
2.具有相同的名字和类型
3.第一个元素的序号是 0
4.10 个元素的数组a: a[0], a[1] ... a[9]
初始化
int a[10]={4};
float r[20]={0.1, 5.1};
double d[3]={10.0,5.0,1.0};
初始值的数目小于数组元素个数时,剩余元素被初始化为0,不允许初始值的数目大于数组元素个数。
省略数组元素数目的数组声明
int x[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
等同于:
int x[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
数组元素可以逐个赋值
int x[5] ;
x[0] = 1;
x[1] = 2;
注意:
x = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; //语法错
x[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; //语法错
x[5] = 5; //编译正确,但有语义错
示例:输出数组并对数组元素求和
#define SIZE 10
#include <iostream.h>
int main( )
{ int n[SIZE] = { 12, 34, 55, 71, 1, 65, 423, 19, 540, 10 };
int i , sum = 0;
for ( i = 0; i <= SIZE - 1; i++ )
{ cout << "n[" << i << "] = " << n[ i ] << endl;
sum += n[ i ];
}
cout << "The summary is: " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
一维数组(作函数参数)
1.数组名有值,其值是数组的第一个元素的地址
2.数组作为函数参数传递时,实参获得的是数组的首地址
3.被调用函数通过数组首地址能访问数组每个元素
示例:数组作为函数的参数
#include <iostream.h>
#define SIZE 10
void modifyArray( int [ ], int);
int main( )
{ int a[ SIZE ] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
modifyArray ( a, SIZE );
cout << "After calling modifyArray: " << endl;
for (int index = 0; index <= SIZE - 1; index ++ )
cout<<"a["<<index<<"]="<< a[index] << endl;
return 0;
}
void modifyArray ( int b[ ], int len )
{ for (int index = 0; index <= len - 1; index++ )
b[ index ] ++ ;
}
多维数组
1.有多个下标的数组称为多维数组
int a[3][4];
char c[4][3][5];
2.n+1维数组可以看成元素是n维数组的一维数组
a[3][4]包含3个元素:a[0]、a[1]、a[2],每个元素都是包含4个元素的一维数组
初始化
1.多维数组可以在声明时初始化
2.可以给出全部元素的值,没有足够的值时,剩余元素初始化为0
int mat[2][2] = {{1},{3, 4}};
int a[3][4] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int m[2][2][2] = {{{1},{5}},{3, 4}};
字符串
1.字符串是用一对双引号括起来的一串字符
"string" "Visual C++" "a+b="
2.字符串的长度等于双引号内所有字符的长度之和(汉字长度为2)
3.字符串可以包含一般字符,也可以包含转义字符
"\"cout<<ch\"\n" 中包含有11个字符
存储
1.字符串的存储是利用一维字符数组来实现的(字符串的值即为该数组的首地址)
2.字符数组的长度为待存字符串的长度加1,字符串以字符‘\0’ 结尾
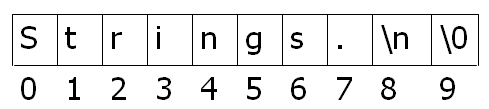
3.如字符串“Strings.\n” 的存储内容为:
字符数组初始化
char a[10]= "array";
等价于
char a[10]={'a','r','r','a','y','\0'};
又如
char b[20]= "This is a pen. ";
char c[8]= "";
但 a = "struct"; //错误
a[0]= ‘A’; //正确
char week[7][11] = {"Sunday",
"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday",
"Thursday", "Friday","Saturday"};
char grade[][10] = { "excellent",
"good", "middle", "pass","bad"};
char typeName[6][10] = {"int",
"double", "char"};
char d[10][20]={""};
I/O
char a[30];
cin >> a; //输入字符串
cout << a //输出字符串
cin >> a[3]; //输入字符
cout << a[4]; //输出字符
例子:二分法查找数组元素
#include <iostream.h>
#define SIZE 10
int binarySearch ( int [ ], int, int, int );
void displayArray ( int [ ], int, int, int );
int main( )
{ int a[ SIZE ], i , key, result;
for ( i = 0; i <= SIZE - 1; i++ ) a[ i ] = 2 * i;
cout << "Enter a number: " ; cin >> key;
result = binarySearch( a, key, 0, SIZE - 1 );
if ( result != -1 )
cout<<key<< " found: No." << result << "."<< endl;
else
cout<<key << " not found." << endl;
return 0;
}
int binarySearch(int b[ ], int searchKey, int low, int high )
{ int middle;
while ( low <= high )
{ middle = ( low + high ) / 2;
displayArray( b, low, middle, high );
if ( searchKey == b[ middle ] )
return middle;
else if ( searchKey < b[ middle ] )
high = middle - 1;
else
low = middle + 1;
}
return -1; /* searchKey not found */
}
void displayArray ( int b[ ], int low, int mid, int high )
{ for ( int i = 0; i <= SIZE - 1; i ++ )
{ if ( i == low)
cout << "["; // 标记搜索的起点
if ( i == mid )
cout << "*"; // 标记被比较的元素
cout << b[ i ];
if ( i == high)
cout << "]" ; // 标记搜索的终点
if ( i != SIZE - 1)
cout << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}




