6控制结构
程序的基本控制结构
顺序结构:常用的语句有表达式语句和复合语句。
选择结构:if语句、if-else语句、switch语句。
循环结构:while语句、do-while语句、 for语句。
其它:空语句、continue语句、break语句 、goto语句、return语句。
表达式语句示例:
a = a + 3; // 赋值语句
x = y = z = 0; // 多重赋值语句
t = 2,t + x + a; // 逗号表达式语句
z = i < j ? x : x + y ;// 条件表达式语句
f1(); //函数调用语句且f1有返回值
x1 = exp(x); // 函数表达式语句,计算 ex
x2 = pow(x, y); //函数表达式语句,计算xy
if语句
一般形式为:
if ( <条件表达式> ) <语句>
<条件表达式> 可以是任意表达式
(一般为逻辑表达式)
语义:计算<条件表达式>的值,若非零,则执行<语句> ,然后按顺序继续执行if语句的下一条语句(有例外)。否则,跳过 <语句> ,直接执行if语句的下一条语句。
if语句示例:
if (grade>=60)
cout <<"passed \n";
if-else语句
一般形式为:
if ( <条件表达式> ) <语句1>
else <语句2>
注:else和<语句2>必须可分离,即在有些情况下else和<语句2>之间的空格或换行符是必须的。
if-else 语句示例:
if (grade >= 60)
cout <<"Passed !\n";
else
cout <<"Failed !\n";
(错:elsecout <<"Failed !\n";)
if 或if-else的嵌套: if 或if-else 中嵌套 if 或if-else
if(grade>=90)printf(“A”);
else if (grade>=80)printf(“B”);
else if (grade>=70)printf(“C”);
else if (grade>=60)printf(“D”);
else printf(“F”);
注意else和if的匹配:在if语句后面若直接跟else,
则把if语句、else和其后的语句一起作为if-else语句
if 或if-else的嵌套: if 或if-else 中嵌套 if 或if-else
if(grade>=60)
if(grade==100)printf(“AAA”);
else if (grade==0)printf(“FFF”);
不等价于
if(grade>=60)
{if(grade==100)printf(“AAA”);}
else if (grade==0)printf(“FFF”);
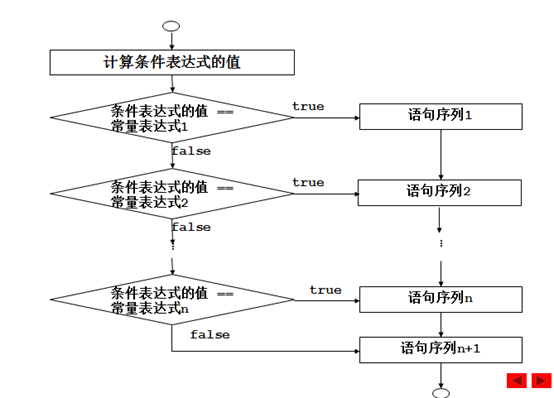
switch 语句
switch 语句一般形式:
switch (<条件表达式> )
{case <常量表达式1> : <语句序列1>
case <常量表达式2> : <语句序列2>
……
case <常量表达式n> : <语句序列n>
default: <语句序列n+1>
}
多个case 分支和可选的 default 分支
<条件表达式>的值为整数类型(int,char,…)
每个<语句序列>的最后一个语句一般为break语句,每个<语句序列>也可以为空
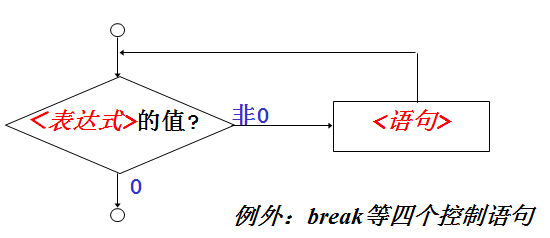
while 语句
一般形式
while( <表达式> )
<语句>
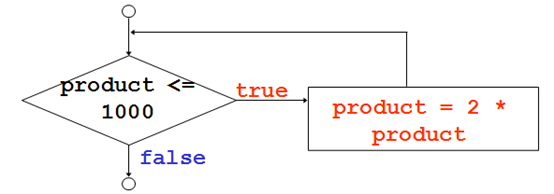
示例
int product = 2;
while ( product <= 1000 )
product = 2 * product;
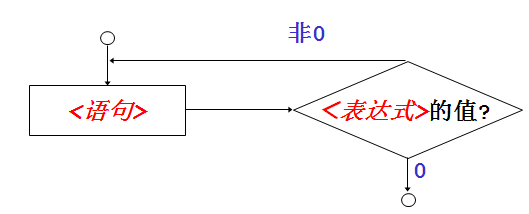
do-while 语句
一般形式
do
{
<语句>
}
while (<表达式>);
示例(打印整数 1 到 10)
int counter = 1;
do
{
printf( “%d\n", counter );
}
while (++counter <= 10);
for 语句
for语句一般形式
for (<初始化语句>[<表达式2>];[<表达式3>])
<语句>
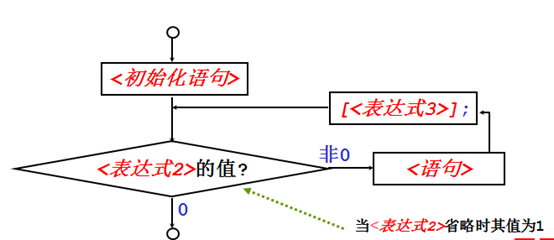
示例(打印整数1到10)
int counter;
for(counter=1;counter<=10;counter++)
printf( “%d\n", counter );
注意:
for 语句和while语句的关系
若<语句>中不含continue语句,则
for (<表达式1>;<表达式2>;<表达式3>)
<语句>
等价于:
<表达式1>;
while (<表达式2>)
{<语句>
<表达式3> ;
}
break 语句
语法: break;
只能用于循环体或switch语句中,使程序控制退出 while, for, do/while 或 switch 结构,程序执行这些语句的后继语句
break 语句的用途:
提早退出循环
跳出 switch 结构
continue 语句
语法: continue ;
只能用于循环体中,跳过while, for 或 do/while 循环体中的剩余语句 ,程序开始执行下一次循环
while 和 do/while
continue 语句执行后,马上测试循环条件
for 语句
continue 语句执行后, 计算递增表达式,然后测试循环条件
return 语句
语法:
return <表达式>; 或 return;
语义:
在主函数体中执行return语句,使整个程序结束
在其它函数体中执行return语句,返回到调用函数的相应位置继续执行
例子一:用switch语句实现成绩转换
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{int score,scorePhrase;
cout<<"Please input the score: \n";
cin >> score;
if (score < 0 || score > 100)
{cout << "The score is illegal!";
return 0; //不是最好的实现,有多出口
}
// 计算分数段
scorePhrase = score / 10;
// 判断并输出等级
switch ( scorePhrase )
{
case 10:
case 9: //p76未考虑100分的情况
cout<<"Grade is "<<'A'<<'.'<< endl;
break;
case 8:
cout<<"Grade is "<<'B'<<'.'<< endl;
break;
case 7:
cout<<"Grade is "<<'C'<<'.'<< endl;
break;
case 6:
cout<<"Grade is "<<'D'<<'.'<< endl;
break;
// 判断并输出等级
case 0:
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
cout<<"Grade is "<<'E'<<'.'<< endl;
break;
default:
cout<<"The score is illegal!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
例子二:while 语句和switch 语句的应用
/* 计算各级成绩的人数 */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{int grade;
int aCount=0;
int bCount=0
cCount=dCount=fCount=0;
printf("Enter the letter grades.\n");
printf("Enter the EOF character "
" to end input.\n");
while ( ( grade = getchar() ) != EOF )
switch ( grade )
{case 'A': case 'a':
++aCount; break;
case 'B': case 'b':
++bCount; break;
case 'C': case 'c':
++cCount; break;
case 'D': case 'd':
++dCount; break;
case 'F': case 'f':
++fCount; break;
case '\n': case' ':
break;
default:
printf("Incorrect letter grade entered.");
printf("Enter a new grade.\n"); break;
}
printf( "\nTotals for each letter "
" grade are:\n" );
printf( "A: %d\n", aCount );
printf( "B: %d\n", bCount );
printf( "C: %d\n", cCount );
printf( "D: %d\n", dCount );
printf( "F: %d\n", fCount );
return 0;
}
例子三:while 语句应用1:计数控制循环(循环反复执行,直到计数器达到特定的值,是定数循环:即循环次数是已知的。)
-------------------计算10个学生的平均成绩
/* Class average program with
counter-controlled repetition */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{int counter, grade, total, average;
/* initialization phase */
total = 0;
counter = 1;
/* processing phase */
while ( counter <= 10 )
{printf( "Enter grade: " );
scanf( “%d", &grade );
total = total + grade;
counter = counter + 1;
}
/* termination phase */
average = total / 10; /*平均值*/
printf("Class average is %d\n",
average);
return 0;
}
示例四:while 语句应用2:条件控制循环(当用户输入信号量(标记值)时,循环结束)
/* Class average program with
sentinel-controlled repetition */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{float average; /* new data type */
int counter, grade, total;
/* initialization phase */
total = 0;
counter = 0;
/* processing phase */
printf("Enter grade, -1 to end: ");
scanf( “%d", &grade );
while ( grade != -1 )
{total = total + grade;
counter = counter + 1;
printf("Enter grade, -1 to end: " );
scanf(“%d", &grade);
}
/* termination phase */
if ( counter != 0 )
{average = (float)total/counter;
printf("Class average is %.2f",
average);
}
else
printf("No grades were entered\n" );
return 0;
}
示例五:for 循环 求和
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int sum = 0, number;
for (number = 2;number <= 100;number+=2)
sum += number;
printf( "Sum is %d\n", sum );
return 0;
}
示例六: for 循环结构中使用 break 语句
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{int x;
for ( x = 1; x <= 10; x++ )
{if ( x == 5 )
break;
printf( "%d ", x );
}
printf( "\nBroke out of loop”
“ at x == %d\n", x );
return 0;
}
示例七:for 循环结构中使用 continue 语句
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{int x;
for ( x = 1; x <= 10; x++ )
{if ( x == 5 )
continue;
printf( "%d ", x );
}
printf("\nUsed continue to skip”
“printing the value 5\n");
return 0;
}




