第17章:MySQL之二级索引
第17章:MySQL之二级索引
目录
修订日期:2021-01-08
一. Secondary Index(二级索引)
1.1. Secondary Index 介绍
- Clustered Index(聚集索引)
- 叶子节点存储所有记录(all row data)

- Secondary Index(二级索引)
- 也可以称为非聚集索引
- 叶子节点存储的是索引和主键信息
- 在找到索引后,得到对应的主键,再回到聚集索引中找主键对应的记录(row data)
- Bookmark Lookup (书签查找)
- 俗称回表
- 回表不止多一次IO
- 而是多N次IO(N=树的高度)

- Secondary Index 查找数据
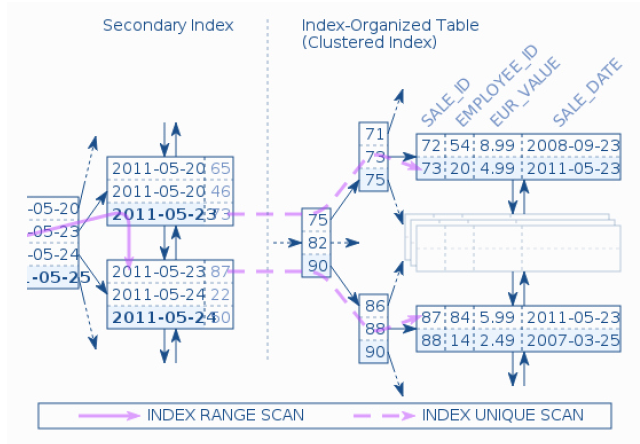
1.2. Secondary Index 回表
create table userinfo (
userid int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(30),
registdate datetime,
email varchar(50),
primary key(userid),
unique key idx_username(username),
key idx_registdate(registdate)
);
- 假设查找
username为Tom,先找二级索引idx_username,通过找到key为Tom,并得到对应的primary key:userid_a。 - 得到了
userid_a后,再去找聚集索引中userid_a的记录(row data)。 - 上述一次通过二级索引得到数据(row data)的查找过程,即为
回表。整个过程都是MySQL自动帮你做的。
- 可以将上述的userinfo 表进行人工拆分,从而进行人工回表,拆分如下:
-- 表1 : 创建一个只有主键userid的表,将原来的二级索引人工拆分成独立的表
create table userinfo(
userid int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(30),
registdate datetime,
email varchar(50),
primary key(userid)
);
-- 表2:idx_username表,将userid和username作为表的字段,并做一个复合主键(对应原来的idx_username索引)
create table idx_username(
userid int not null,
username varchar(30),
primary key(username, userid)
);
-- 表3:idx_registdate表,将userid和registdate作为表的字段,并做一个复合主键(对应原来的idx_registdate 索引)
create table idx_registdate(
userid int not null,
registdate datetime,
primary key(registdate, userid)
);
-- 表4:一致性约束表
create table idx_username_constraint(
username varchar(30),
primary key(username)
);
-- 插入数据,使用事物,要么全插,要么全不插入
start transaction;
insert into userinfo values(1, 'Tom', '1990-01-01', 'tom@123.com');
insert into idx_username_constraint values('Tom');
insert into idx_username values(1, 'Tom');
insert into idx_registdate values(1, '1990-01-01');
commit;
--
-- 执行sql
--
(root@localhost) 10:49:12 [(none)]> use mytest;
Database changed
(root@localhost) 09:45:19 [mytest]> create table userinfo (
-> userid int not null auto_increment,
-> username varchar(30),
-> registdate datetime,
-> email varchar(50),
-> primary key(userid),
-> unique key idx_username(username),
-> key idx_registdate(registdate)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
(root@localhost) 09:45:46 [mytest]> create table idx_username(
-> userid int not null,
-> username varchar(30),
-> primary key(username, userid)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
(root@localhost) 09:46:19 [mytest]> create table idx_registdate(
-> userid int not null,
-> registdate datetime,
-> primary key(registdate, userid)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 09:46:29 [mytest]> create table idx_username_constraint(
-> username varchar(30),
-> primary key(username)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:14:23 [mytest]> start transaction;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:15:36 [mytest]> insert into userinfo values(1, 'Tom', '1990-01-01', 'tom@123.com');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:15:36 [mytest]> insert into idx_username_constraint values('Tom');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:15:36 [mytest]> insert into idx_username values(1, 'Tom');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:15:36 [mytest]> insert into idx_registdate values(1, '1990-01-01');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:15:36 [mytest]> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
- 假设要查找TOM的
email:- 先查找
Tom对应的userid,即找的是idx_username表(对应之前就是在idx_username索引中找tom) - 得到
userid后,再去userinfo表,通过userid得到email字段的内容(对应之前就是在聚集索引中找userid的记录(row data)) - 上述两次查找就是
人工回表
- 先查找
拆表后,就需要开发自己去实现
回表的逻辑;而开始的一张大表,则是MySQL自动实现该逻辑。
1.3. 堆表的二级索引
- 在堆表中,是
没有聚集索引的, 所有的索引都是二级索引; - 索引的叶子节点存放的是
key和指向堆中记录的指针(物理位置)
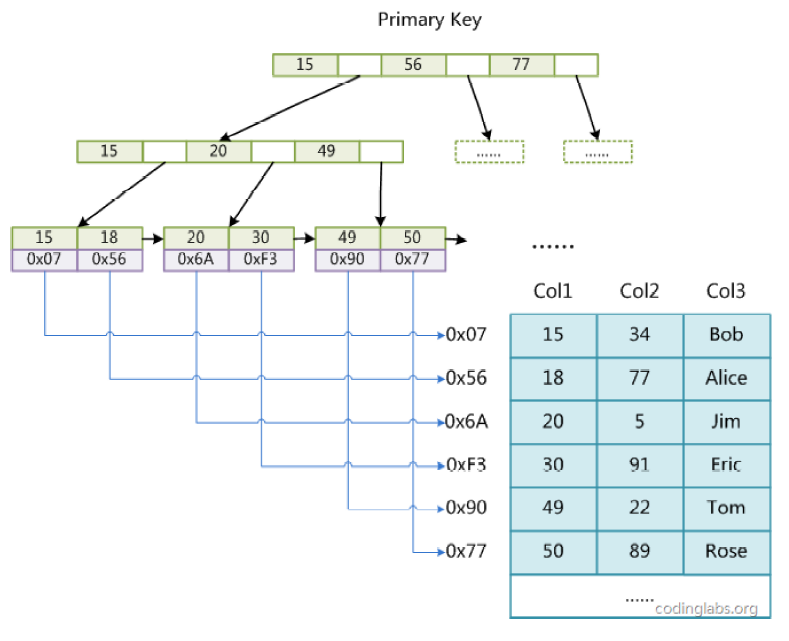
1.4. 堆表和索引组织表(IOT)二级索引的对比
堆表中的二级索引查找不需要回表,且查找速度和主键索引一致,因为两者的叶子节点存放的都是指向数据的指针;反之IOT表的的二级索引查找需要回表。- 堆表中某条记录(row data)
发生更新且无法原地更新时,该记录(row data)的物理位置将发生改变;此时, 所有索引中对该记录的指针都需要更新(代价较大);反之,IOT表中的记录更新,且主键没有更新时,二级索引都无需更新(通常来说主键是不更新的)- 实际数据库设计中,堆表的数据无法原地更新时,且在一个
页内有剩余空间时,原来数据的空间位置不会释放,而是使用指针指向新的数据空间位置,此时该记录对应的所有索引就无需更改了; - 如果
页内没有剩余空间,所有的索引还是要更新一遍;
- 实际数据库设计中,堆表的数据无法原地更新时,且在一个
- IOT表页内是
有序的,页与页之间也是有序的,做range查询很快。
1.5. index with included column(含列索引)
在上面给出的userinfo 的例子中,如果要查找某个用户的email ,需要回表,如何不回表进行查询呢?
- 方案一:复合索引
-- 表结构
create table userinfo (
userid int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(30),
registdate datetime,
email varchar(50),
primary key(userid),
unique key idx_username(username, email), -- 索引中有email,可以直接查到,不用回表
key idx_registdate(registdate)
);
-- 查询
select email from userinfo where username='Tom';
该方案可以做到
只查一次索引就可以得到用户的email,但是复合索引中username和email都要排序
而含列索引的意思是索引中只对username 进行排序,email是不排序的,只是带到索引中,方便查找。
- 方案二:拆表
create table userinfo (
userid int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(30),
registdate datetime,
email varchar(50),
primary key(userid),
key idx_registdate(registdate)
);
create table idx_username_include_email (
userid int not null,
username varchar(30),
email varchar(50),
primary key(username, userid),
unique key(username)
);
-- 两个表的数据一致性可以通过事物进行保证
通过拆表的方式,查找
idx_username_include_email表,既可以通过username找到
- 对于含有多个索引的IOT表,可以将索引拆成不同的表,进而提高查询速度
- 但是实际使用中,就这个例子而言,使用复合索引,代价也不会太大。
二. Multi-Range Read 多范围读(MRR)
2.1. 回表的代价
(root@localhost) 10:53:33 [employees]> alter table employees add index idx_date (hire_date); -- 给 employees 增加一个普通索引
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.89 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
(root@localhost) 10:54:16 [employees]> show create table employees \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: employees
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `employees` (
`emp_no` int(11) NOT NULL,
`birth_date` date NOT NULL,
`first_name` varchar(14) NOT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(16) NOT NULL,
`gender` enum('M','F') NOT NULL,
`hire_date` date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`emp_no`),
KEY `idx_date` (`hire_date`) --新增的索引dx_date
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查询语句1
select * from employees where emp_no between 10000 and 20000; -- 主键查找1W条数据
-- 查询语句2
select * from employees where hire_date >= '1990-01-01' limit 10000; -- select * 操作,每次查找需要回表
- 对于查询语句1 ,假设一个页中有100条记录,则只需要
100次IO; - 对于查询语句2 ,此次查询中,假设
聚集索引和hire_date索引(二级索引)的高度都是3 ,且查找1W 条(假设不止1W条),则需要查询的IO数为(3+N)+3W3为第一次找到hire_date>=1990-01-01所在的页(二级索引)的IO次数N为从第一次找到的页往后读页的IO次数(注意二级索引也是连续的, 不需要从根再重新查找)- 所以
3+N就是在hire_date (二级索引)中读取IO的次数
- 所以
3W为在IOT表中进行回表的次数
- 在MySQL5.6之前,实际使用过程中,优化器可能会选择直接进行
扫表,而不会进行如此多的回表操作。
2.2. MRR 介绍
MRR:它的作用针对基于辅助/第二索引的查询(磁盘的随机访问),随机转顺序,空间换时间。
- 开辟一块
内存空间作为cache- 配置为
8M,注意是线程级的,不建议设置的很大;
- 配置为
- 参数
read_rnd_buffer_size用来控制键值的缓冲区大小,当大于该值,执行器对已经缓存的数据根据RowID进行排序,并通过RowID来取得行数据
(root@localhost) 10:45:04 [employees]> show variables like "%read_rnd%";
+----------------------+---------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+----------------------+---------+
| read_rnd_buffer_size | 8388608 | --8M
+----------------------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:45:12 [employees]>
- 将
需要回表的主键放入上述的内存空间中(空间换时间), 放满后进行排序(随机转顺序); - 将
排序好数据(主键)一起进行回表操作,以提高性能;- 在
IO Bound的SQL场景下,使用MRR比不使用MRR系能提高将近10倍(磁盘性能越低越明显); - 如果
数据都在内存中,MRR的帮助不大, 已经在内存中了,不存在随机读的概念了(随机读主要针对物理访问)
- 在
SSD 仍然需要开启该特性,多线程下的随机读确实很快,但是我们这里的操作是一条SQL语句,是
单线程的,所以顺序的访问还是比随机访问要更快。
(root@localhost) 10:15:38 [mytest]> show variables like 'optimizer_switch'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Variable_name: optimizer_switch
Value: index_merge=on,index_merge_union=on,index_merge_sort_union=on,index_merge_intersection=on,engine_condition_pushdown=on,index_condition_pushdown=on,mrr=on,mrr_cost_based=on,block_nested_loop=on,batched_key_access=off,materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,firstmatch=on,duplicateweedout=on,subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,use_index_extensions=on,condition_fanout_filter=on,derived_merge=on
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 其中MRR默认是打开的 mrr=on,不建议关闭
(root@localhost) 10:57:39 [employees]> (root@localhost) 10:57:39 [employees]> explain select * from employees where hire_date >= '1990-01-01';
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | ALL | idx_date | NULL | NULL | NULL | 299423 | 50.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:57:44 [employees]>
-- 虽然mrr=on打开了,但是没有使用MRR
(root@localhost) 10:57:44 [employees]> set optimizer_switch='mrr_cost_based=off'; -- 将该值off,不让MySQL对MRR进行成本计算(强制使用MRR)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:58:47 [employees]> explain select * from employees where hire_date >= '1990-01-01';
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_date | idx_date | 3 | NULL | 149711 | 100.00 | Using index condition; Using MRR |
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 10:58:52 [employees]>
-- 使用了MRR
三. 求B+树的高度
3.1 B+树

3.1 B+树高度

如上图所示,每个页的Page Header 中都包含一个PAGE_LEVEL 的信息,表示该页所在B+树中的层数, 叶子节点的PAGE_LEVEL为0 。
所以树的高度就是root页的PAGE_LEVEL + 1
3.3. PAGE_LEVEL
从一个页的第64字节开始读取,然后再读取2个字节,就能得到PAGE_LEVEL 的值
3.4. 获取root页
(root@localhost) 10:58:52 [employees]> use information_schema;
Database changed
(root@localhost) 13:45:37 [information_schema]> desc INNODB_SYS_INDEXES;
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| INDEX_ID | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | |
| NAME | varchar(193) | NO | | | |
| TABLE_ID | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | |
| TYPE | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| N_FIELDS | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| PAGE_NO | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| SPACE | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| MERGE_THRESHOLD | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 13:45:56 [information_schema]> select * from INNODB_SYS_INDEXES where space<>0 limit 1\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
INDEX_ID: 32
NAME: PRIMARY
TABLE_ID: 27
TYPE: 3
N_FIELDS: 2
PAGE_NO: 3 -- 根据官方文档,该字段就是B+树root页的PAGE_NO
SPACE: 16
MERGE_THRESHOLD: 50
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
(root@localhost) 13:46:27 [information_schema]> desc INNODB_SYS_TABLES;
+---------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| TABLE_ID | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | |
| NAME | varchar(655) | NO | | | |
| FLAG | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| N_COLS | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| SPACE | int(11) | NO | | 0 | |
| FILE_FORMAT | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| ROW_FORMAT | varchar(12) | YES | | NULL | |
| ZIP_PAGE_SIZE | int(11) unsigned | NO | | 0 | |
| SPACE_TYPE | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) 13:46:56 [information_schema]> SELECT
-> b. NAME,
-> a. NAME,
-> index_id,
-> type,
-> a.space,
-> a.PAGE_NO
-> FROM
-> INNODB_SYS_INDEXES AS a,
-> INNODB_SYS_TABLES AS b
-> WHERE
-> a.table_id = b.table_id
-> AND a.space <> 0
-> AND b. NAME LIKE "dbt3/%";
+----------------------+-----------------------+----------+------+-------+---------+
| NAME | NAME | index_id | type | space | PAGE_NO |
+----------------------+-----------------------+----------+------+-------+---------+
| dbt3/customer | PRIMARY | 2166 | 3 | 1644 | 3 |
| dbt3/customer | i_c_nationkey | 2167 | 0 | 1644 | 4 |
| dbt3/lineitem | PRIMARY | 2168 | 3 | 1645 | 3 |
| dbt3/lineitem | i_l_shipdate | 2169 | 0 | 1645 | 4 |
| dbt3/lineitem | i_l_suppkey_partkey | 2170 | 0 | 1645 | 5 |
| dbt3/lineitem | i_l_suppkey | 2172 | 0 | 1645 | 7 |
| dbt3/lineitem | i_l_receiptdate | 2173 | 0 | 1645 | 8 |
| dbt3/lineitem | i_l_orderkey_quantity | 2175 | 0 | 1645 | 10 |
| dbt3/lineitem | i_l_commitdate | 2176 | 0 | 1645 | 11 |
| dbt3/nation | PRIMARY | 2177 | 3 | 1646 | 3 |
| dbt3/nation | i_n_regionkey | 2178 | 0 | 1646 | 4 |
| dbt3/orders | PRIMARY | 2179 | 3 | 1647 | 3 |
| dbt3/orders | i_o_orderdate | 2180 | 0 | 1647 | 4 |
| dbt3/orders | i_o_custkey | 2181 | 0 | 1647 | 5 |
| dbt3/part | PRIMARY | 2182 | 3 | 1648 | 3 |
| dbt3/partsupp | PRIMARY | 2183 | 3 | 1649 | 3 |
| dbt3/partsupp | i_ps_suppkey | 2185 | 0 | 1649 | 5 |
| dbt3/region | PRIMARY | 2186 | 3 | 1650 | 3 |
| dbt3/supplier | PRIMARY | 2187 | 3 | 1651 | 3 |
| dbt3/supplier | i_s_nationkey | 2188 | 0 | 1651 | 4 |
| dbt3/time_statistics | GEN_CLUST_INDEX | 2189 | 1 | 1652 | 3 |
+----------------------+-----------------------+----------+------+-------+---------+
21 rows in set (0.01 sec)
(root@localhost) 13:47:27 [information_schema]>
-- 聚集索引页的root页的PAGE_NO一般就是3
3.5. 读取PAGE_LEVEL
(root@localhost) 13:49:04 [information_schema]> select count(*) from dbt3.lineitem;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 6001215 |
+----------+
1 row in set (43.47 sec)
[root@localhost-m(252) /r2/mysqldata/dbt3]# hexdump -s 24640 -n 2 -Cv lineitem.ibd
00006040 02 22 |."|
00006042
[root@localhost-m(252) /r2/mysqldata/dbt3]#
24640 = 8192 * 3 + 64- 其中
8192是页大小 root页的PAGE_NO为3,表示是第4个页,则需要跳过前面3个页,才能定位到root页,所以要*3- 然后加上
64个字节的偏移量,即可定位到PAGE_LEVEL
- 其中
-n 2表示读取的字节数,这里读取2个字节,即可以读到PAGE_LEVEL
根据上述hexdump的结果,root页中的PAGE_LEVEL为2,表示该索引的高度为3(从0开始计算)


