数据结构-链表
一. 链表(Linked List)介绍
链表是有序的列表,但存储方式不一定连续
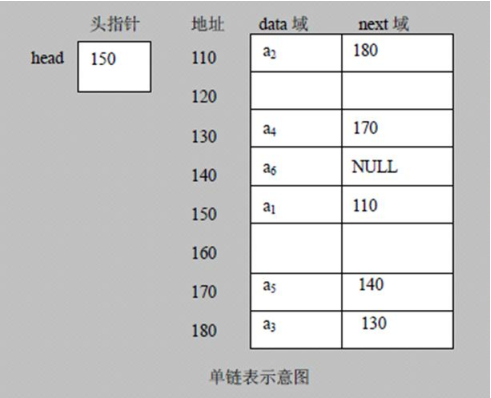
- 链表是以节点的方式来存储,是链式存储
- 每个节点包含 data 域, next 域: 指向下一个节点
二. 代码实现
1.求单链表中有效节点的个数 (遍历链表)
2. 查找单链表中的倒数第 k 个结点
public class LinkList {
//思路
//1. 编写一个方法, 接收 head 节点, 同时接收一个 index
//2. index 表示是倒数第 index 个节点
//3. 先把链表从头到尾遍历, 得到链表的总的长度 getLength
//4. 得到 size 后, 我们从链表的第一个开始遍历 (size-index)个, 就可以得到
//5. 如果找到了, 则返回该节点, 否则返回 nulll
public static Node findLastIndexNode(Node head, int index) {
//判断如果链表为空, 返回 null
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
int size = getLength(head);
Node cur = head.next;
for (int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
cur = head.next;
}
return cur;
}
public static int getLength(Node head) {
if (head.next == null) {
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
Node cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return length;
}
// 链表翻转 头插法
public static void reverseList(Node head) {
if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return;
}
//定义一个辅助的指针(变量), 帮助我们遍历原来的链表
Node cur = head.next;
//当前节点下一节点
Node next = null;
Node reverseHead = new Node(0, null);
while (cur != null) {
//先暂时保存当前节点的下一个节点
next = cur.next;
//将 cur 的下一个节点指向新的链表的最前端
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
reverseHead.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
head.next = reverseHead.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node4 = new Node(4, null);
Node node3 = new Node(3, node4);
Node node2 = new Node(2, node3);
Node node1 = new Node(1, node2);
Node node = new Node(0, node1);
System.out.println(node);
reverseList(node);
System.out.println(node);
}
}
class Node {
public Integer val;
public Node next;
public Node(Integer val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"val=" + val +
", next=" + next +
'}';
}
}
Josephu(约瑟夫、 约瑟夫环) 问题
Josephu 问题为: 设编号为 1, 2, … n 的 n 个人围坐一圈, 约定编号为 k(1<=k<=n) 的人从 1 开始报数, 数
到 m 的那个人出列, 它的下一位又从 1 开始报数, 数到 m 的那个人又出列, 依次类推, 直到所有人出列为止, 由
此产生一个出队编号的序列
class CircleSingleLinkedList {
// 创建一个 first 节点,当前没有编号
private Node first = null;
public void addNode(int nums) {
if (nums < 1) {
System.out.println("nums 的值不正确");
return;
}
// 辅助指针, 帮助构建环形链表
Node curBoy = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= nums; i++) {
// 根据编号, 创建小孩节点
Node boy = new Node(i, null);
// 如果是第一个小孩
if (i == 1) {
first = boy;
first.next = first; // 构成环
curBoy = first; // 让 curBoy 指向第一个小孩
} else {
curBoy.next = boy;//
boy.next = first;//
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
public void showNode() {
if (first == null) {
System.out.println("没有节点");
return;
}
Node cur = first;
while (true) {
System.out.printf("编号 %d\n", cur.val);
if (cur.next == first) {
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
/**
* @param startNo 第几个开始数数
* @param countNum 数几下
* @param nums 最初有个节点
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo, int countNum, int nums) {
// 先对数据进行校验
if (first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums) {
System.out.println("参数输入有误, 请重新输入");
return;
}
Node help = first;
while (true) {
if (help.next == first) {
break;
}
help = first.next;
}
for (int i = 0; i <startNo-1 ; i++) {
first = first.next;
help = help.next;
}
while (true){
if(help == first){
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i <countNum-1 ; i++) {
first = first.next;
help = help.next;
}
System.out.printf("节点 %d 出圈\n", first.val);
first = first.next;
help.next = first;
}
}
}



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步