OC基础--分类(category) 和 协议(protocol)
OC 中的category分类文件相当于 C#中的部分类;OC 中的protocol协议文件(本质是头文件)相当于 C#中的接口。今天就简单说明一下OC中的这两个文件。
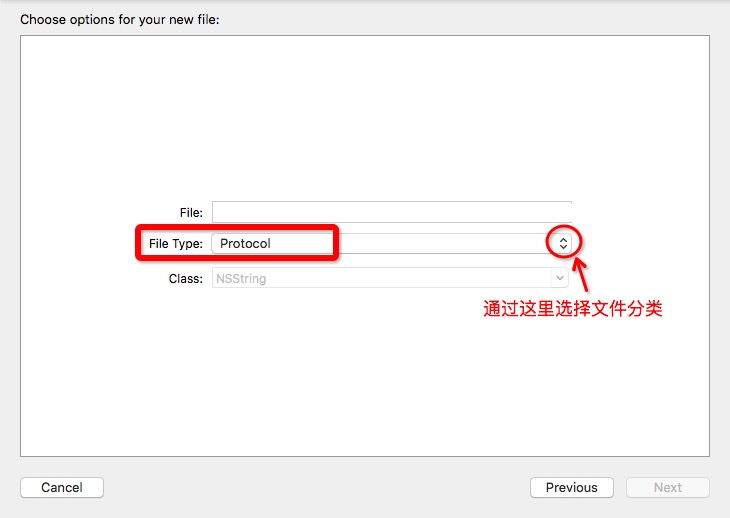
由于视频中的Xcode版本低,导致了分类文件和协议文件没有找到,最后百度得知:
如图:Xcode 7.2版本中的category文件和protocol文件都归类到了Objective-C File 中
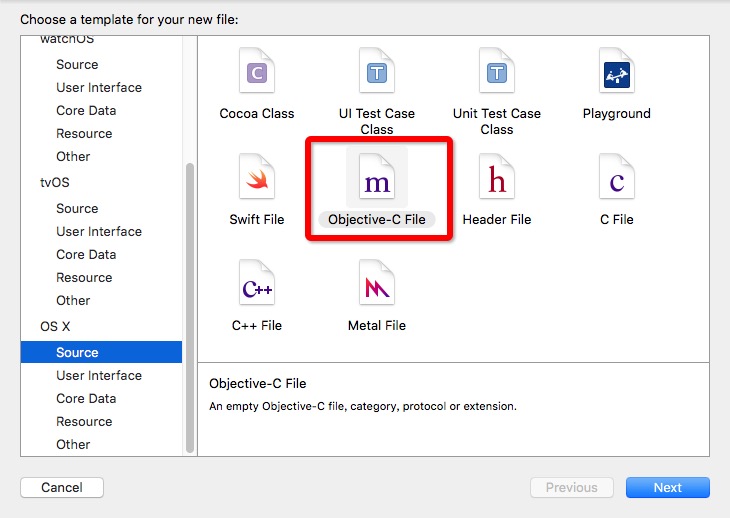
一、category文件:
作用:可以扩展自定义类,或者系统类。下面的实例,是扩展了NSString 类,在类中扩展了计算字符串中数字个数的方法:
NSString类的分类的头文件
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 3 @interface NSString (Number) 4 5 // 计算字符串中阿拉伯数字的个数 6 - (int) numberCount; 7 8 @end
NSString类的分类的.m文件
1 #import "NSString+Number.h" 2 3 @implementation NSString (Number) 4 5 // @"abc123" 6 - (int)numberCount 7 { 8 9 //[self length]; 10 11 int count = 0; 12 13 int len = (int) self.length; 14 15 for (int i = 0; i<len; i++) { 16 // 获取i位置对应的字符(char) 17 char c = [self characterAtIndex:i]; 18 19 if (c>='0' && c<='9') 20 { 21 count++; 22 } 23 } 24 25 return count; 26 } 27 28 @end
main文件:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "NSString+Number.h" 3 4 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) 5 { 6 7 @autoreleasepool { 8 9 NSString *str = @"abc 123fdsf090900sdfds68768867"; 10 11 int count = [str numberCount]; 12 13 NSLog(@"%d", count); 14 } 15 return 0; 16 }
二、protocol文件
作用:声明一系列方法
注意点:分类和协议都只能声明方法,不能声明成员变量
实例:
1 // 声明一系列方法 2 // 分类和协议都只能声明方法,不能声明成员变量 3 @protocol MyProtocol 4 5 // 默认是@required 6 - (void) test4; 7 8 @required // test1必须实现的 9 - (void) test1; 10 11 @optional // test2、test3是可选实现的 12 - (void) test2; 13 - (void) test3; 14 15 @end
1>类遵守协议
@interface 类名:父类名<协议名称1,协议名称2>
@end
2>协议遵守协议
@protocol 协议名称<其他协议名称1,其他协议名称2>
@end
3>协议中方法声明的关键字
(1)@required(默认)
要求实现,如果没有实现,会发出警告
(2)@optional
不要求实现,
4>定义一个变量的时候,限制这个变量保存的对象遵守某个协议
类名<协议名称> *变量名; 或者
id<协议名称> 变量名;
实例:NSObject<MyProtocol> *obj; 或者
id<MyProtocol> obj2;
如果没有遵守相对应协议,编译器会警告
5>@property中声明的属性也可用来做一个遵守协议的限制
@property (nonatomic,strong) 类名<协议名称> *属性;
@property (nonatomic,strong) id<协议名称> 属性;
代码实例:
@property (nonatomic,strong) Dog<MyProtocol> *dog;
@property (nonatomic,strong) id<MyProtocol> dog2;
6>协议可用定义在单独.h文件中,也可用定义在某各类中
(1)如果这个协议只用在某各类中,应该把协议定义在该类中
(2)如果这个协议用在很多类中,就应该定义在单独文件中
7>分类也可用定义在单独.h和.m文件中,也可用定义在原来类中
(1)一般情况下,都是定义在单独文件
(2)定义在原来类中的分类,只要求能看懂语法



