简易计算器
需求分析与设计思路:
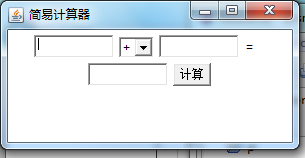
创建一个简易计算器,首先要创建一个窗体,并且要有简单的输入数据的框架。
向窗体中添加三个TextField 便于用户输入要计算的数,添加choice下拉选择框,
便于用户输入+-* /符号, lable用来显示=,Button按钮用来显示"计算"以便用
户算出最终结果,最后利 用if语句判断出用户要进行哪种运算。
代码实现:
package pp;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Choice;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("简易计算器");
frame.setSize(300,150);
frame.addWindowListener(new Listener());
final TextField tf1 = new TextField(8);
final Choice choice = new Choice();
choice.addItem("+");
choice.addItem("-");
choice.addItem("*");
choice.addItem("/");
final TextField tf2 = new TextField(8);
Label label = new Label("=");
final TextField tf3 = new TextField(8);
Button button = new Button("计算");
frame.add(tf1);
frame.add(choice);
frame.add(tf2);
frame.add(label);
frame.add(tf3);
frame.add(button);
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
String s1 = tf1.getText();
String s2 = tf2.getText();
String ch = choice.getSelectedItem();
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
Double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double d = 0;
if (ch.equals("+"))
{
d=d1+d2;
}
else if(ch.equals("-"))
{
d=d1-d2;
}
else if (ch.equals("*"))
{
d=d1*d2;
}
else
{
d=d1/d2;
}
tf3.setText(d + " ");
}
});
frame .setVisible(true);
}
运行测试:
}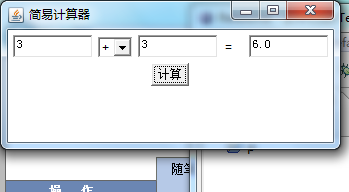
本次代码测试大概用了两个小时。
总结:首先要有清晰的思路,知道第一步是创建一个窗体,然后完整整个窗体的内容,分析用户需求,按用户要求实现代码,最后测试。


