Linux-基础学习(四)-部署图书管理系统项目
部署图书管理项目需要以下软件
- 项目文件(django项目文件夹)
- 数据库文件(django项目对应的数据库文件)
- centos7(linux本体)
- nginx(反向代理以及静态文件收集)
- uWSGI(代理服务器与后端的application应用服务器之间的中间件)
- virtualenv(虚拟环境)
- supervisor(自动守护)
1.项目部署
1.1 项目文件上传
上传图书管理系统项目到linux服务器上
- Lrzsz工具进行上传
- xftp工具进行上传(推荐方式)
- scp命令
在/opt/目录下传输项目文件,数据库文件同样存放在这个文件夹下
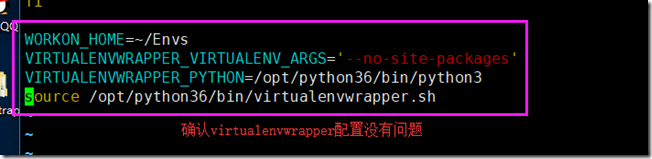
1.2 虚拟环境配置virtualenv
通过virtualenvwrapper工具的配置,解决虚拟环境问题
创建虚拟环境mkvirtualenv book_manage_env
1.3 数据库安装
在centos7本体下安装配置mariadb数据库,且创建数据库数据,迁移导入图书管理系统数据
- 安装mariadb数据库(和mysql一模一样只是为了免费)
- 导出开发过程中的book_manage项目的数据
- 第一种方法:使用navicat导出,转储SQL文件,(如果需要数据则使用结构与数据,反之则使用结构)
- 第二种方法,使用mysqldump命令, 此命令适用于windows和linux下
- 将数据导入到服务器mariadb数据库中
- 进入数据库,先创建一个数据库book_manage (create database book_manage)
- 进入此数据库 use book_manage
- 导入数据库 source /opt/book_manage.sql
- 允许root用户远程登陆数据库
- 第一种方法, 在初始化数据库的时候,就允许root用户远程登录
- 第二种方法 使用SQL语句进行授权(grant all privileges on *.* to root@"%" identified by "你的密码";)
-测试使用linux的python解释器去运行项目 切换到 项目中运行(注意要解决解释器的模块问题,才能正常运转项目)
1.4 uWSGI配置
完成uWSGI命令学习,使用uWSGI启动图书管理系统项目,支持多进程
1.4.1 安装Uwsgi
(1)使用pip安装uwsgi模块
pip3 install uwsgi
(2)创建一个测试文件testuwsgi.py, 运行简单的uWSGI站点
第一步vim /opt/book_homework/testuwsgi.py 写入以下文件
def application(env, start_response): start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type','text/html')]) return [b"Hello World"]
第二步 使用uwsgi命令启动此文件
uwsgi --http :9000 --file testuwsgi.py
第三步 在浏览器通过IP加端口进行访问
(3)使用uwsgi.ini文件,简单的命令就可以将uwsgi启动起来
cd /opt/book_manage
vim uwsgi.ini
写入配置文件
[uwsgi] # Django-related settings # the base directory (full path) # 写上项目的绝对路径 chdir = /opt/book_manage # Django's wsgi file # 填写找到django的wsgi文件,填写相对路径,以chdir参数为相对路径 module = book_manage.wsgi # the virtualenv (full path) # 填写虚拟环境的绝对路径 home = /root/Envs/book_manage_env/ # process-related settings # master #启动uwsgi主进程 master = true # maximum number of worker processes processes = 1 # the socket (use the full path to be safe #如果你使用了nginx,做反向代理,必须填写socket链接,而不是http参数 socket = 0.0.0.0:8000 #如果你不用nginx,直接使用uwsgi,运行一个http服务端,就用这个http参数 http = 0.0.0.0:8000 # ... with appropriate permissions - may be needed # chmod-socket = 664 # clear environment on exit vacuum = true
使用uwsgi命令指定配置文件启动,单个项目是可以这么启动
uwsgi -ini /opt/book_homework/uwsgi.ini
1.5 nginx配置
1.5.1 收集django静态文件
收集django静态文件
vim /opt/book_homework/book_homework/settings.py
加入一行配置,静态文件
STATIC_ROOT='/opt/static'
回到django项目主目录下(有manage.py文件的目录), 输入命令进行收集静态文件
python3 manage.py collectstatic
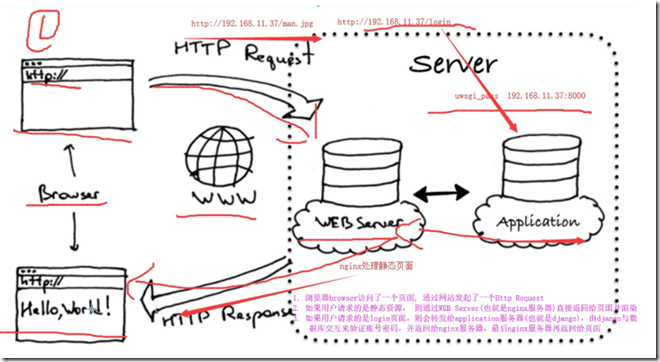
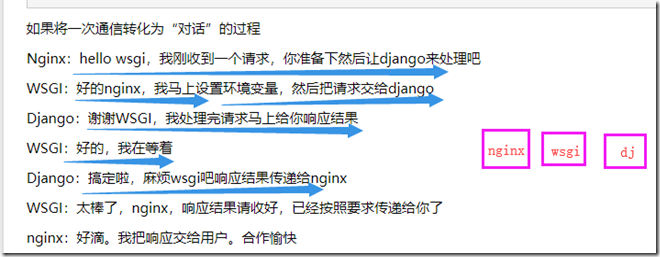
1.5.2 配置nginx与uwsgi结合
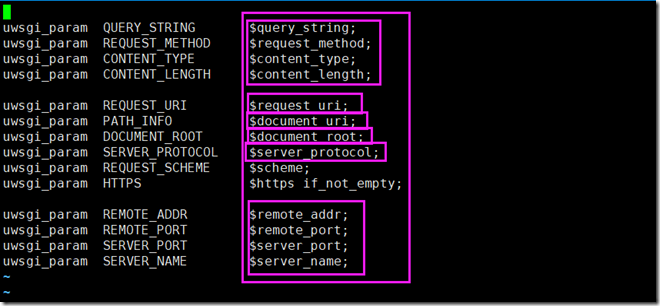
下图为/opt/nginx112/conf/uwsgi_params文件
1.5.3 修改nginx的配置文件/opt/nginx112/conf/nginx.conf
添加以下配置
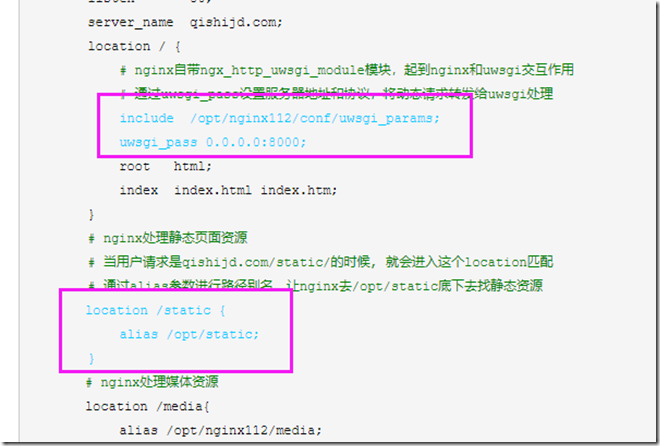
location / { # nginx自带ngx_http_uwsgi_module模块,起到nginx和uwsgi交互作用 # 通过uwsgi_pass设置服务器地址和协议,将动态请求转发给uwsgi处理 include /opt/nginx112/conf/uwsgi_params; uwsgi_pass 0.0.0.0:8000; root html; index index.html index.htm; } ************************************************************************************************************* location /static { alias /opt/static; }
如图配置
nginx.conf全部配置文件如下
worker_processes 1; error_log logs/error.log; pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; # nginx反向代理uwsgi server { listen 80; server_name qishijd.com; location / { # nginx自带ngx_http_uwsgi_module模块,起到nginx和uwsgi交互作用 # 通过uwsgi_pass设置服务器地址和协议,将动态请求转发给uwsgi处理 include /opt/nginx112/conf/uwsgi_params; uwsgi_pass 0.0.0.0:8000; root html; index index.html index.htm; } # nginx处理静态页面资源 # 当用户请求是qishijd.com/static/的时候, 就会进入这个location匹配 # 通过alias参数进行路径别名,让nginx去/opt/static底下去找静态资源 location /static { alias /opt/static; } # nginx处理媒体资源 location /media{ alias /opt/nginx112/media; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } }
1.5.4 平滑重启nginx
/opt/nginx112/sbin/nginx -s reload
1.5.5 确保uwsgi已经正常启动
这个主要是用于守护进程
/root/Envs/book_manage/bin/uwsgi --ini /opt/book_manage/uwsgi.ini
ps -ef | grep uwsgi
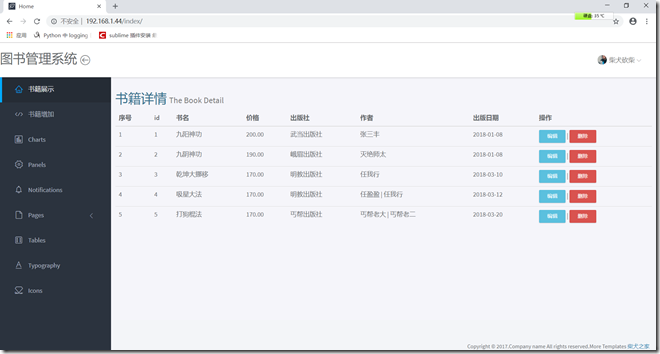
在浏览器访问http://192.168.1.44已经可以正常访问,静态文件也可以正常加载了,修改数据也没有问题, 说明数据库连接正常
2.安装配置supervisor
supervisor 是基于 python 的任务管理工具,用来自动运行各种后台任务,当然你也能直接利用 nohup 命令使任务自动后台运行,但如果要重启任务,每次都自己手动 kill 掉任务进程,这样很繁琐,而且一旦程序错误导致进程退出的话,系统也无法自动重载任务。
这里我们要配置基于virtualenv的supervisor,但是请注意:由于supervisor在python3下无法使用,因此只能用python2去下载!!!!!!
2.1 安装suprvisor
安装suprvisor
easy_install supervisor # 这个是python2下面的安装模块命令,等同于python3下面的pip
如果没有easy_install这个命令,就需要安装setuptools工具
yum install python-setuptools
2.2 使用命令生成supervisor.conf配置文件
echo_supervisord_conf > /etc/supervisord.conf
2.3 在/etc/supervisord.conf末尾添加上如下代码
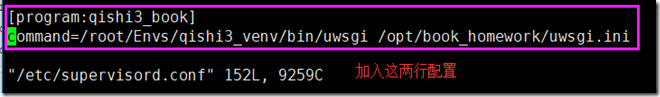
[program:book_manage] command=/root/Envs/book_manage_env/bin/uwsgi /opt/book_manage/uwsgi.ini stopasgroup=true # 如果发现关闭supervisor进程后,结束uwsgi进 killasgroup=true # 程无效,就需要加上这两个参数
如图所示
2.4 启动supervisor, 完成uWSGI启动django,nginx反向代理
supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf
2.5 upervisor启动命令参数有两种
# 任务管理命令如下:有两种,一个是参数形式, 一个是交互式 # 参数形式 supervisorctl -c /etc/supervisor.conf stop/start/restart all supervisorctl -c /etc/supervisor.conf start crm_knight # 交互式形式 supervisorctl -c /etc/supervisor.conf
2.6 重新加载supervisor(了解即可)
一、添加好配置文件后 二、更新新的配置到supervisord supervisorctl update 三、重新启动配置中的所有程序 supervisorctl reload 四、启动某个进程(program_name=你配置中写的程序名称) supervisorctl start program_name 五、查看正在守候的进程 supervisorctl 六、停止某一进程 (program_name=你配置中写的程序名称) pervisorctl stop program_name 七、重启某一进程 (program_name=你配置中写的程序名称) supervisorctl restart program_name 八、停止全部进程 supervisorctl stop all 注意:显示用stop停止掉的进程,用reload或者update都不会自动重启。
a