剑指offer 学习笔记 从上到下打印二叉树
面试题32:从上到下打印二叉树。
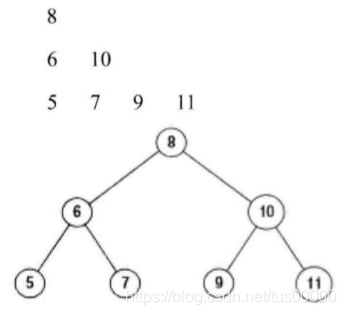
(1)从上到下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。

以上图为例,按层打印先打印根节点8,之后把第二层的6、10保存在队列中,现在队列中有两个节点,按从左到右的打印要求,我们先取出值为6的节点打印,之后把它的节点5、7入队列,然后出队列的值是10,出队列后,将10的两个节点9、11入队列,现在第三层也是从左到右的顺序入队列了。我们不用再定义队列,因为标准库已经实现了一个很好的deque(双向队列):
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
struct BinaryTreeNode {
int m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;
};
BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startPreorder, int* endPreorder, int* startInorder, int* endInorder) { // 创建树
BinaryTreeNode* root = new BinaryTreeNode();
root->m_nValue = *startPreorder;
root->m_pLeft = root->m_pRight = nullptr;
if (startPreorder == endPreorder) { // 当递归到前序遍历只含一个元素时
if (startInorder == endInorder && *startPreorder == *startInorder) { // 此时若中序遍历也只含一个元素并且这个元素值与前序遍历的元素值相同时,递归到底成功返回
return root;
} else { // 否则当前序和中序遍历的个数不相等(前序遍历只含一个元素但中序遍历有多个元素)或值不相等(前序遍历和中序遍历元素数都为1但这两个值不等)时
throw exception("Invalid input."); // 说明输入的前序和中序遍历不匹配
}
}
int* rootInorder = startInorder;
while (rootInorder < endInorder && *rootInorder != *startPreorder) { // 遍历中序序列找到根节点
++rootInorder;
}
if (rootInorder == endInorder && *rootInorder != *startPreorder) { // 若以上循环结束仍未找到根节点,说明输入有误
throw exception("Invalid input");
}
int leftLength = rootInorder - startInorder; // 左子树长度
int* leftPreorderEnd = startPreorder + leftLength; // 左子树尾边界
if (leftLength > 0) { // 当左子树仍存在时
root->m_pLeft = ConstructCore(startPreorder + 1, leftPreorderEnd, startInorder, rootInorder - 1); // 继续递归左子树
}
if (leftLength < endPreorder - startPreorder) { // 左子树长度小于当前遍历的树节点数-1(去掉根节点)时,说明存在右子树
root->m_pRight = ConstructCore(startPreorder + leftLength + 1, endPreorder, rootInorder + 1, endInorder); // 继续递归右子树
}
return root;
}
BinaryTreeNode* Construct(int* preorder, int* inorder, int length) { // 创建树
if (preorder == nullptr || inorder == nullptr || length <= 0) {
return nullptr;
}
return ConstructCore(preorder, preorder + length - 1, inorder, inorder + length - 1);
}
void PrintFromTopToBottom(BinaryTreeNode* pTreeRoot) {
if (pTreeRoot == nullptr) {
return;
}
deque<BinaryTreeNode*> dequeTreeNode;
dequeTreeNode.push_back(pTreeRoot);
while (dequeTreeNode.size()) {
BinaryTreeNode *pNode = dequeTreeNode.front(); // 获取此次循环队首节点,由于在pop之后还要检查队首节点的子节点,因此需保存它
dequeTreeNode.pop_front();
cout << pNode->m_nValue << " ";
if (pNode->m_pLeft != nullptr) {
dequeTreeNode.push_back(pNode->m_pLeft);
}
if (pNode->m_pRight != nullptr) {
dequeTreeNode.push_back(pNode->m_pRight);
}
}
}
int main() {
int preorder[] = { 8,6,5,7,10,9,11 };
int inorder[] = { 5,6,7,8,9,10,11 };
BinaryTreeNode* pRoot = Construct(preorder, inorder, 7);
PrintFromTopToBottom(pRoot);
}
扩展题目:如何广度优先遍历一幅有向图?也可以基于队列实现,树是图的一种特殊退化形式,从上到下按层遍历二叉树,本质上就是广度优先遍历二叉树。
(2)分行从上到下打印二叉树,每层打印一行:
与前面题类似,也可以用队列来保存将要打印的节点,但还需两个变量,一个表示在当前层中还没有打印的节点数,另一个变量表示下一层节点的数目:
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
struct BinaryTreeNode {
int m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;
};
BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startPreorder, int* endPreorder, int* startInorder, int* endInorder) { // 创建树
BinaryTreeNode* root = new BinaryTreeNode();
root->m_nValue = *startPreorder;
root->m_pLeft = root->m_pRight = nullptr;
if (startPreorder == endPreorder) { // 当递归到前序遍历只含一个元素时
if (startInorder == endInorder && *startPreorder == *startInorder) { // 此时若中序遍历也只含一个元素并且这个元素值与前序遍历的元素值相同时,递归到底成功返回
return root;
} else { // 否则当前序和中序遍历的个数不相等(前序遍历只含一个元素但中序遍历有多个元素)或值不相等(前序遍历和中序遍历元素数都为1但这两个值不等)时
throw exception("Invalid input."); // 说明输入的前序和中序遍历不匹配
}
}
int* rootInorder = startInorder;
while (rootInorder < endInorder && *rootInorder != *startPreorder) { // 遍历中序序列找到根节点
++rootInorder;
}
if (rootInorder == endInorder && *rootInorder != *startPreorder) { // 若以上循环结束仍未找到根节点,说明输入有误
throw exception("Invalid input");
}
int leftLength = rootInorder - startInorder; // 左子树长度
int* leftPreorderEnd = startPreorder + leftLength; // 左子树尾边界
if (leftLength > 0) { // 当左子树仍存在时
root->m_pLeft = ConstructCore(startPreorder + 1, leftPreorderEnd, startInorder, rootInorder - 1); // 继续递归左子树
}
if (leftLength < endPreorder - startPreorder) { // 左子树长度小于当前遍历的树节点数-1(去掉根节点)时,说明存在右子树
root->m_pRight = ConstructCore(startPreorder + leftLength + 1, endPreorder, rootInorder + 1, endInorder); // 继续递归右子树
}
return root;
}
BinaryTreeNode* Construct(int* preorder, int* inorder, int length) { // 创建树
if (preorder == nullptr || inorder == nullptr || length <= 0) {
return nullptr;
}
return ConstructCore(preorder, preorder + length - 1, inorder, inorder + length - 1);
}
void PrintFromTopToBottom(BinaryTreeNode* pTreeRoot) {
if (pTreeRoot == nullptr) {
return;
}
deque<BinaryTreeNode*> dequeTreeNode;
dequeTreeNode.push_back(pTreeRoot);
int nextLevel = 0, toBePrinted = 1;
while (dequeTreeNode.size()) {
BinaryTreeNode *pNode = dequeTreeNode.front(); // 获取此次循环队首节点,由于在pop之后还要检查队首节点的子节点,因此需保存它
dequeTreeNode.pop_front();
cout << pNode->m_nValue << " ";
if (pNode->m_pLeft != nullptr) {
dequeTreeNode.push_back(pNode->m_pLeft);
++nextLevel;
}
if (pNode->m_pRight != nullptr) {
dequeTreeNode.push_back(pNode->m_pRight);
++nextLevel;
}
--toBePrinted; // 把下一层的所有节点都入队后再检查是否该打印下一层了
if (toBePrinted == 0) {
cout << endl;
toBePrinted = nextLevel; // 开始打印下一层
nextLevel = 0;
}
}
}
int main() {
int preorder[] = { 8,6,5,7,10,9,11 };
int inorder[] = { 5,6,7,8,9,10,11 };
BinaryTreeNode* pRoot = Construct(preorder, inorder, 7);
PrintFromTopToBottom(pRoot);
}
(3)之字形打印二叉树:
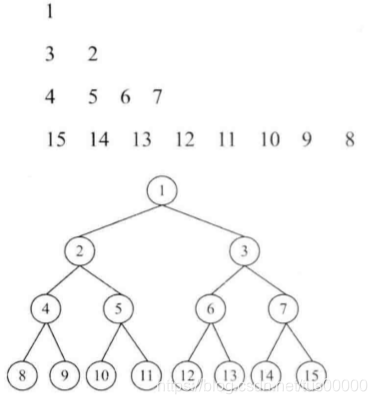
在打印完根节点后,可以将它的左右子节点先后保存在一个栈中,这样第二层就可以实现从右向左打印数据了,在打印第三层的节点时,先打印节点2的两个子节点,再打印节点3的两个子节点,因此第三层的压栈顺序是7654,即奇数层的节点的压栈顺序是先左后右,偶数层节点的压栈顺序是先右后左。
因此完成程序需要两个栈,再打印某层节点时,将下一层的子节点保存在另一个栈中。如打印的是奇数层,那么把它们的子节点从左到右压栈,如打印的是偶数层,则把它们的子节点从右往左压栈:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
struct BinaryTreeNode {
int m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;
};
BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startPreorder, int* endPreorder, int* startInorder, int* endInorder) { // 创建树
BinaryTreeNode* root = new BinaryTreeNode();
root->m_nValue = *startPreorder;
root->m_pLeft = root->m_pRight = nullptr;
if (startPreorder == endPreorder) { // 当递归到前序遍历只含一个元素时
if (startInorder == endInorder && *startPreorder == *startInorder) { // 此时若中序遍历也只含一个元素并且这个元素值与前序遍历的元素值相同时,递归到底成功返回
return root;
} else { // 否则当前序和中序遍历的个数不相等(前序遍历只含一个元素但中序遍历有多个元素)或值不相等(前序遍历和中序遍历元素数都为1但这两个值不等)时
throw exception("Invalid input."); // 说明输入的前序和中序遍历不匹配
}
}
int* rootInorder = startInorder;
while (rootInorder < endInorder && *rootInorder != *startPreorder) { // 遍历中序序列找到根节点
++rootInorder;
}
if (rootInorder == endInorder && *rootInorder != *startPreorder) { // 若以上循环结束仍未找到根节点,说明输入有误
throw exception("Invalid input");
}
int leftLength = rootInorder - startInorder; // 左子树长度
int* leftPreorderEnd = startPreorder + leftLength; // 左子树尾边界
if (leftLength > 0) { // 当左子树仍存在时
root->m_pLeft = ConstructCore(startPreorder + 1, leftPreorderEnd, startInorder, rootInorder - 1); // 继续递归左子树
}
if (leftLength < endPreorder - startPreorder) { // 左子树长度小于当前遍历的树节点数-1(去掉根节点)时,说明存在右子树
root->m_pRight = ConstructCore(leftPreorderEnd + 1, endPreorder, rootInorder + 1, endInorder); // 继续递归右子树
}
return root;
}
BinaryTreeNode* Construct(int* preorder, int* inorder, int length) { // 创建树
if (preorder == nullptr || inorder == nullptr || length <= 0) {
return nullptr;
}
return ConstructCore(preorder, preorder + length - 1, inorder, inorder + length - 1);
}
void Print(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot) {
if (pRoot == nullptr) {
return;
}
vector<stack<BinaryTreeNode *>> levels(2);
int current = 0, next = 1;
levels[current].push(pRoot);
while (levels[current].size()) {
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = levels[current].top();
cout << pNode->m_nValue << " ";
levels[current].pop();
if (current == 0) { // 如果是奇数层
if (pNode->m_pLeft != nullptr) {
levels[next].push(pNode->m_pLeft);
}
if (pNode->m_pRight != nullptr) {
levels[next].push(pNode->m_pRight);
}
} else {
if (pNode->m_pRight != nullptr) {
levels[next].push(pNode->m_pRight);
}
if (pNode->m_pLeft != nullptr) {
levels[next].push(pNode->m_pLeft);
}
}
if (levels[current].empty()) {
current = 1 - current;
next = 1 - next;
cout << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
int preorder[] = { 8,6,5,7,10,9,11 };
int inorder[] = { 5,6,7,8,9,10,11 };
BinaryTreeNode* pRoot = Construct(preorder, inorder, 7);
Print(pRoot);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号