Mybatis深入浅出之工作原理
一、简述
1、Mybatis发展简史

Mybatis前生为apache公司开发的ibatis,2010年交由google公司托管维护管理,并更名为Mybatis,MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架。
2、ORM
ORM:Object Relational Mapping,对象与表映射。ORM实现了将数据库操作映射为对象操作,简化了数据库的操作开发,简单地说:ORM将面向数据库的开发转换为面向对象的开发。Mybatis是ORM的一个实现框架,类似实现有JDBC、Hibernate。Mybatis封装简化了JDBC操作,实现数据的持久化。
3、Mybatis官网
- 官网地址:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
- Mybatis jar包、源码、使用说明文档 都可以从官网中获取。
- 关于Mybatis配置文件、映射文件等xml文件的模板都可以从Mybatis使用说明文档中获取。
二、分层架构

- 接口层: 提供外部接口API,用于开发数据库操作功能。
- 数据处理层:负责具体的SQL实现,执行数据库SQL操作。
- 框架支撑层:主要负责将公共功能抽离独立,为数据处理层提供最基础的组件服务,比如:事务管理、缓存管理。
三、工作流程
Mybatis底层还是采用原生的jdbc实现对数据库的操作,其数据库操作过程是通过 SqlSessionFactory,SqlSession,Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,ResultHandler和TypeHandler等处理器封装实现。其中StatementHandler使用ParameterHandler进行参数预编译,使用ResultHandler进行结果处理。而ParameterHandler与ResultHandler都使用TypeHandler进行数据库类型和javaBean类型的映射;。
执行器:Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
参数处理器:ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
结构处理器 ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
sql查询处理器:StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
流程图:

1、获取配置Configuration对象
- 加载解析配置文件,包括config配置和xml映射文件,创建生成Configuration对象;
2、获取SqlSessionFactory对象:
- 根据Configuration对象创建生成DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象;
3、获取 SqlSession 对象:
- 创建生成包含Executor和Configuration的DefaultSqlSession对象;
4、获取Mapper接口代理对象MapperProxy(若采用接口代理方式执行sql)
- getMapper()使用MapperProxyFactory创建一个MapperProxy的代理对象;
- 代理对象中包含了DefaultSqlSession(Executor);
5、执行SQL
- 依赖DefaultSqlSession对象中的Executor创建的StatementHandler、ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler对象完成向数据库发送SQL语句命令查询转换结果集;
StatementHandler: 设置sql语句,预编译,设置参数等相关工作,以及执行增删改查方法;
ParameterHandler: 设置预编译sql参数;
ResultHandler: 处理查询结果集;
TypeHandler: ParameterHandler和ResultHandler都依赖于TypeHandler,进行数据库类型和javaBean类型的映射。
四、核心接口/类
1、SqlSessionFactory

public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { try { XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } } public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }
2、SqlSession
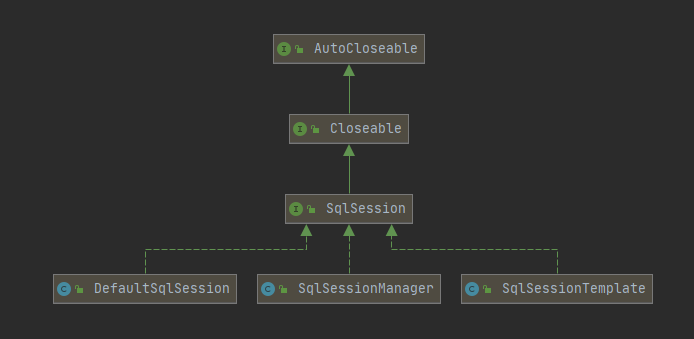
@Override public SqlSession openSession() { return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); } private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } } public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) { this.configuration = configuration; this.executor = executor; this.dirty = false; this.autoCommit = autoCommit; }
3、Executor
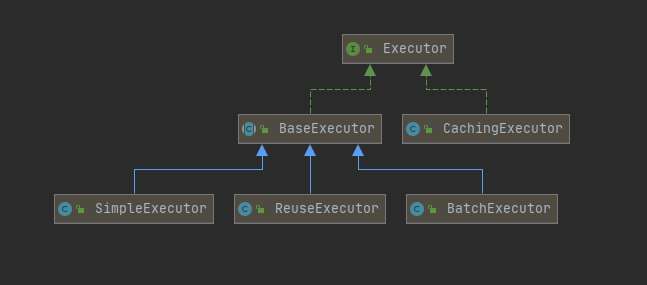
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; } public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) { // Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many. List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter); if (list.size() == 1) { return list.get(0); } else if (list.size() > 1) { throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size()); } else { return null; } } public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
代理方式:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); } public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } } public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); }
五、示例
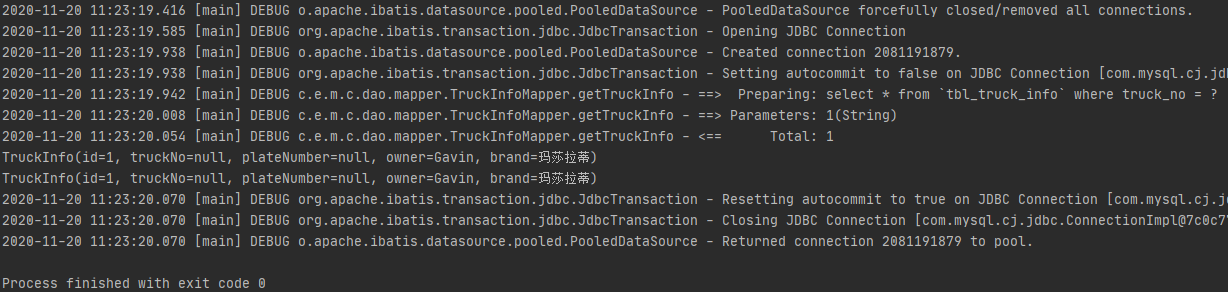
public class CacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.加载配置(Mybaits数据源配置 + 映射xml) Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader); //2. 从SqlSessionFactory中创建一个SqlSession,进行数据库操作 SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(); //3.使用SqlSession查询(基于Statement ID方式) Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<String, Object>(); params.put("truckNo", "1"); String statement = "com.example.mybatis.cache.dao.mapper.TruckInfoMapper.getTruckInfo"; TruckInfo truckInfo = sqlSession.selectOne(statement, params); System.out.println(truckInfo); //4.使用SqlSession查询(基于Mapper接口代理方式) TruckInfoMapper truckInfoMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(TruckInfoMapper.class); TruckInfo truckInfo2 = truckInfoMapper.getTruckInfo("1"); System.out.println(truckInfo2); sqlSession.close(); } }
六、代码
- github:https://github.com/gavincoder/Mybatis.git
- gitee:https://gitee.com/gavincoderspace/mybatis.git
七、参考



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号