[常用类]包装类
包装类:将 基本数据类型 封装成 对象 的好处在于可以在 对象 中定义更多的 功能方法 操作该数据
常用的操作之一:将 基本数据类型 与 字符串 之间进行转换
基本数据类型 与 包装类 的对应:
byte Byte short Short int Integer long Long float Float double Double char Character boolean Boolean
int 转换为 String
- int + ""
- valueOf()将 int 转换为String
Integer 常用方法:
toString() 将Integer转换为String
intValue() 将Integer转换为int
parseInt() 将String转换为int
基本数据类型包装类有8种,其中7种都有 parseXxx() 方法,将这7种字符串表现形式转换为基本数据类型
其中char 的包装类 Character 中没有 parseXxx方法。字符串到字符的转换通过 toCharArray() 可以把字符串转换为字符数组
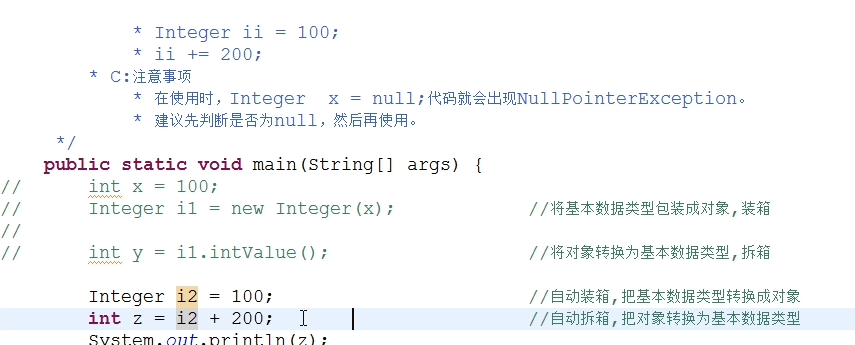
常见面试题:
1 public class Demo5_Integer { 2 3 /** 4 * @param args 5 */ 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 Integer i1 = new Integer(97); 8 Integer i2 = new Integer(97); 9 System.out.println(i1 == i2); //false 10 System.out.println(i1.equals(i2)); //true 11 System.out.println("-----------"); 12 13 Integer i3 = new Integer(197); 14 Integer i4 = new Integer(197); 15 System.out.println(i3 == i4); //false 16 System.out.println(i3.equals(i4)); //true 17 System.out.println("-----------"); 18 19 Integer i5 = 127; 20 Integer i6 = 127; 21 System.out.println(i5 == i6); //true 22 System.out.println(i5.equals(i6)); //true 23 System.out.println("-----------"); 24 25 Integer i7 = 128; 26 Integer i8 = 128; 27 System.out.println(i7 == i8); //false 28 System.out.println(i7.equals(i8)); //true 29 30 /* 31 * -128到127是byte的取值范围,如果在这个取值范围内,自动装箱就不会新创建对象,而是从常量池中获取 32 * 如果超过了byte取值范围就会再新创建对象 33 * 34 * public static Integer valueOf(int i) { 35 assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; 36 if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) //i>= -128 && i <= 127 37 return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; 38 return new Integer(i); 39 } 40 */ 41 } 42 43 }


