教你nginx跳转配置的四种方式
前言
最近工作用到了nginx,但是路由配置特殊,业务场景复杂,因此整理了集中nginx跳转的配置方式,如servername的正则,location的匹配顺序,rewrite和proxy的示例,相信总有一种满足你的需求。
一、配置server对应的域名
server name 为虚拟服务器的识别路径。因此不同的域名会通过请求头中的HOST字段,匹配到特定的server块,转发到对应的应用服务器中去。server_name匹配规则:后面可以跟多个域名,第1个是主域名
1.1、精确匹配
如下nginx配置
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
listen 8080; server_name test1.com; location / { return 200 "I am test1!\n"; } } server { listen 8080; server_name my.test.com; location / { return 200 "I am mytest!\n"; } } |
请求结果
curl http://my.test.com:8080 返回:I am mytest!
curl http://test1.com:8080 返回:I am test1!
1.2、正则表达式
以*通配符开始的最长字符串,如下示例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
server { listen 8080; server_name test1.*; location / { return 200 "I am test1!\n"; } } |
以*通配符结束的最长字符串
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
listen 8080; server_name *.test.com; location / { return 200 "I am mytest!\n"; }} |
通配符名字只可以在名字的起始处或结尾处包含一个星号,并且星号与其他字符之间用点分隔。所以,“my..com“都是非法的。
例如 :server_name my..com;
报以下错误:
nginx: [emerg] invalid server name or wildcard "my.*.com" on 0.0.0.0:8080
匹配正则表达式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
server { listen 8080; server_name ~^my(?<serno>.+).mydomain.com$; location / { return 200 $serno; } } |
解释说明
- ~: 表示大小写敏感的正则;
- ^:匹配字符串的开始;
- {.+}:换行符以外的任意自读重复一次活更多次;
- (): 分组与取值;
- :表示转义;
- serno:设置提取的变量;
- $:匹配字符串的结束;
请求结果
|
1
2
|
curl http://my02.mydomain.com:8080 返回:02% curl http://my03.mydomain.com:8080 返回:03% |
server_name的配置顺序是怎样的呢?
按照如下顺序匹配:
- 匹配顺序->
- ->精确匹配
- ->*在前的域名
- ->*在后的域名
- ->按文件中的顺序匹配
- ->default server:第一个,listen指定default
二、配置location
2.1、Location 匹配规则:仅匹配URI,忽略参数
|
1
|
location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … } |
匹配的正则符号如下:
- = 严格匹配。如果请求匹配这个location,那么将停止搜索并立即处理此请求
- ~ 区分大小写匹配(可用正则表达式)
- ~* 不区分大小写匹配(可用正则表达式)
- !~ 区分大小写不匹配
- !~* 不区分大小写不匹配
- ^~ 如果把这个前缀用于一个常规字符串,那么告诉nginx 如果路径匹配那么不测试正则表达式
2.2、举例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
1、匹配任意请求location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … }2、不区分大小写匹配以js、php结尾的请求location ~* .(js|php)$ { … }3、区分大小写匹配以.txt结尾的请求location ~ ^.+\.txt$ |
2.3、匹配顺序如下图

按照上面的规则配置了如下location
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
location = /documents { return 200 'configuration A'}location /documents { return 200 'configuration B'}location /documents/txt1 { return 200 'configuration C'}location ^~ /documents/ { return 200 'configuration D'}location ~* /documents/(\w+)$ { return 200 'configuration E'}location ~ /documents/$ { return 200 'configuration F'} |
- curl http://test1.com:8080/documents,精确匹配返回 configuration A
- curl http://test1.com:8080/documents/ ^~匹配上后不在匹配,返回 configuration D
- curl http://test1.com:8080/documents/txt1 走到了正则匹配,不会走到/documents/txt1(正则没走完) 返回configuration E
- curl http://test1.com:8080/documents/txt1/,返回configuration C,因为正则都不匹配
2.4、如何debug正则呢?
编译的时候加上 --with-debug选项,例如 ./configure --with-debug
conf文件加上要debug的host,debug_connection对应要debug的连接。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
events { worker_connections 1024; debug_connection 192.168.1.3; debug_connection 127.0.0.1;} |
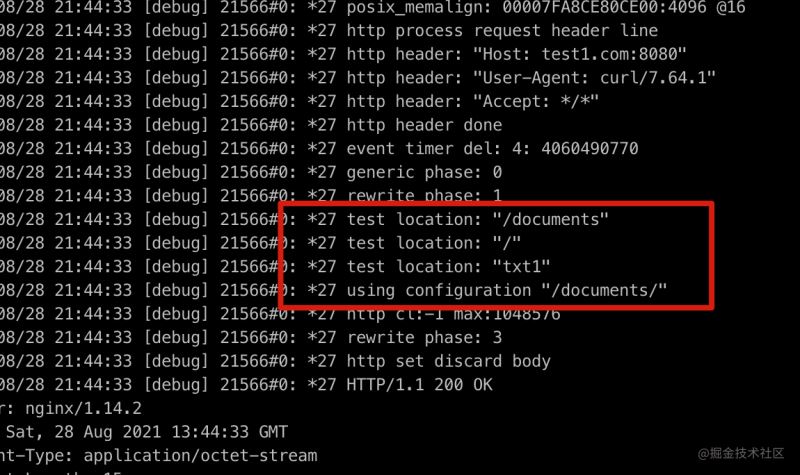
error.log查看debug日志,图中test location就是正则匹配的过程
三、配置rewrite
语法如下:
指令语法:rewrite regex replacement[flag];
默认值:none
应用位置:server、location、if
rewrite是实现URL重定向的重要指令,他根据regex(正则表达式)来匹配内容跳转到replacement,结尾是flag标记.
| flag标记 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| last | 本条规则匹配完成后继续向下匹配新的location URI规则 |
| break | 本条规则匹配完成后终止,不在匹配任务规则 |
| redirect | 返回302临时重定向 |
| permanent | 返回301永久重定向 |
3.1、重定向
return三种code,code url和url。
返回状态码:444表示关闭连接 301表示http1。0中永久重定向,302表示临时重定向,进制缓存。http1.1后,303表示临时重定向,允许改变方法,进制缓存,307表示临时重定向,不允许改变方法,禁止被缓存,308表示永久重定向,不允许改变方法。
返回code
|
1
2
3
|
location / { return 301 https://www.xxxx.com$request_uri;} |
通过$request_uri变量匹配所有的URI。
|
1
|
rewrite ^ https://www.xxxx.com$request_uri? permanent; |
通过正则匹配所有的URI后再去掉开头第一个/(反斜线)。
|
1
|
rewrite ^/(.*)$ https://www.xxxx.com/$1; |
与if指令结合
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
server { listen 80; server_name test1.net test2.net; if ($host != 'test1.net' ) { rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.baidu.net/$1 permanent; }} |
3.2、如何查看rewrite日志
打开日志开关rewrite_log on;
可以配置到http,server,location和if上下文中
示例:curl http://test1.com:8080/first/2.txt
|
1
2
3
4
|
location /first { rewrite_log on; rewrite /first(.*) /second$1 last; } |
效果图如下

四、配置 proxy
对上游服务使用http/https协议进行反向代理。proxy_pass后面跟url,可以仿造location,if in location和limit_except上下文中。 这个功能是默认编译到nginx中的。本文重点讨论http proxy。
url参数规则
- url必须以http或者https开头,接下来是域名、ip、unix socket或者upstream名字,都可以就端口。后面是可选的uri
http示例
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000/uri/;
UNIX域套接字路径来定义示例
proxy_pass http://unix:/tmp/backend.socket:/uri/;
url中是否携带uri,结果也不一样,如果在proxy_pass后面的url加/,相当于是绝对根路径,则nginx不会把location中匹配的路径部分代理走;如果没有/,则会把匹配的路径部分给代理走。
目录结构如下
├── first
│ └── index.html
├── index.html
└── second
└── index.html
nginx配置如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
server { listen 8081; server_name my.test.com; } server { listen 8082; # 第一种情况 location /first { proxy_pass http://my.test.com:8081; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } # 第二种情况 location /first { proxy_pass http://my.test.com:8081/; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } } |
不带/,然后 curl http://127.0.0.1:8082/first/index.html 返回index html
带/,然后 curl http://127.0.0.1:8082/first/index.html 返回first index
- Url参数中可以携带变量
proxy_pass http://$host$uri; - 可以配合rewrite break语句
|
1
2
3
4
|
location /nameb/ { rewrite /nameb/([^/]+) /test?nameb=$1 break; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8801/; } |
五、小结
配置nginx的路由,有多种方式,域名可以用server_name配置,uri可以用location配置,复杂的可以加rewrite配置修改请求。还有就是配置proxy代理,在代理中转发id等。
到此这篇关于nginx跳转配置的四种方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关nginx跳转配置内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享4款.NET开源、免费、实用的商城系统
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了