mysql分库分表实战及php代码操作完整实例
**当单表达到几千万时,查询一次要很久,如果有联合查询,有可能会死在那
分库分表主要就是解决这个问题,减小数据库的负担,缩短查询时间**
分库:
1)按功能分
用户类库、商品类库、订单类库、日志类、统计类库…
2)按地区分
每个城市或省市一个同样的库,加上后缀或前缀如:db_click_bj、db_click_sh…
分表:
1、横向分表 解决表记录太大问题
1)按某个字段分,
如:discuz的附件表分成10个附件分表pre_forum_attachment_0到pre_forum_attachment_9,还有1个附件索引表pre_forum_attachment存储tid和附件id关系
根据主题的tid最后一位来决定附件要保存在哪个分表,
2)按日期分表
一些日志、统计类的可以按年、月、日、周分表
如:点击量统计click_201601、click_201602
3)使用mysql的merge
先把分表创建好,然后创建总表指定engine= MERGE UNION=(table1,table2) INSERT_METHOD = LAST;
2、纵向分表 解决列过多问题
1)经常组合查询的列放在一个表,常用字段的表可考虑Memory引擎
2)不经常使用的字段单独成表
3)把text、blob等大字段拆分放在附表
如:phpcms的文章表分成主表v9_news和从表v9_news_data,主表存标题、关键字、浏览量等,从表存具体内容、模板等
很多主流mvc框架都提供了切换数据库访问方法
thinkphp切换数据库
$this->db(1,"mysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/test")->query("查询sql");//数据库连接信息可放在配置文件 $this->db(1)->query("查询sql");//下次直接使用编号1定位
分表的话 在查询前先根据分表规则把表名查出
演示
这里用两台机子简单以同个业务库分库,同个表分表,演示插入、查询如何定位库和表并最终成功执行
两台机子:
server1:192.168.1.198
server2:192.168.1.199
两台机子都执行下面操作
1、先创建10个数据库,每个数据库10个表
当然也可以改成百库百表,也可手动创建,我为了方便写了个脚本批量创建
create.php
<?php ini_set('memory_limit', '-1'); $con=mysql_connect("192.168.1.198","open","123456"); if($con){ for($i=0;$i<10;$i++){//10个库 $sql="drop database cloude_{$i};";//删库 谨慎 mysql_query($sql); $sql="create database cloude_{$i} default character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;"; $do=mysql_query($sql,$con)or die(mysql_error()); if($do){ mysql_select_db("cloude_{$i}",$con); mysql_query("set name gtf8"); for($j=0;$j<10;$j++){ //10个表 $sql="drop table if exists user_{$j};"; mysql_query($sql); $sql="create table user_{$j} ( id char(36) not null primary key, name char(15) not null default '', password char(32) not null default '', sex char(1) not null default '男' )engine=InnoDB;"; $do=mysql_query($sql,$con) or die(mysql_error()); if($do){ //echo "create table user_{$j} successful! <br/>"; }else{ //echo "create error!"; } } } } }else{ echo "connect error!!!!"; }
2、分库分表路由实现
Config.php
<?php class Config{ public $dsn; public $user; public $password; public $dbname; //分库分表后得到的数据库名 public $table; //分库分表后得到的表名 private static $config;//mysql配置数组 private static $configFile = 'mysql.php'; //配置文件路径 public function __construct($dbname, $table, $id = 0){ if (is_null(static::$config)) { $config = include(static::$configFile); static::$config = $config; } $config = static::$config; if (isset($config['shared']) && isset($config['shared'][$dbname])) { $dbconfig = $config['shared'][$dbname]; $id = is_numeric($id) ? (int)$id : crc32($id); $database_id = ($id / $dbconfig['database_split'][0]) % $dbconfig['database_split'][1]; $table_id = ($id / $dbconfig['table_split'][0]) % $dbconfig['table_split'][1]; foreach ($dbconfig['host'] as $key => $conf) { list($from, $to) = explode('-', $key); if ($from <= $database_id && $database_id <= $to) { $the_config = $conf; } } $this->dbname = $dbname . '_' . $database_id; $this->table = $table . '_' . $table_id; } else { $this->dbname = $dbname; $this->table = $table; $the_config = $config['db'][$dbname]; } $c = $the_config; if (isset($c['unix_socket']) && $c['unix_socket']) { $this->dsn = sprintf('mysql:dbname=%s;unix_socket=%s', $this->dbname, $c['unix_socket']); } else { $this->dsn = sprintf('mysql:dbname=%s;host=%s;port=%s', $this->dbname, $c['host'], $c['port']); } $this->user = $c['user']; $this->password = $c['password']; } }
3、数据库配置文件
mysql.php
<?php $default = array( 'unix_socket' => null, 'host' => '192.168.1.198', 'port' => '3306', 'user' => 'open', 'password' => '123456', ); $db_199 = array( 'unix_socket' => null, 'host' => '192.168.1.199', 'port' => '3306', 'user' => 'open', 'password' => '123456', ); $config = array( // 不进行分库分表的数据库 'db' => array( 'hadoop' => $default, ), // 分库分表 'shared' => array( 'cloude' => array( 'host' => array( /** * 编号为 0 到 4 的库使用的链接配置 */ '0-4' => $default, /** * 编号为 5 到 9 的库使用的链接配置 */ '5-9' => $db_199, ), // 分库分表规则 /** * 下面的配置对应10库10表 * 如果根据 uid 进行分表,假设 uid 为 224,对应的库表为: * (224 / 1) % 10 = 4 为编号为 4 的库 * (224 / 10) % 10 = 1 为编号为 2 的表 */ 'database_split' => array(1, 10), 'table_split' => array(10, 10), ), ), ); return $config;
4、模型类操作数据库
Model.php
<?php require_once 'Config.php';//引入配置信息 class Model{ public $config; //数据库配置 public $connection; //pdo protected $dbnamePrefix; //库前缀如cloude_50 前缀为cloude protected $tablePrefix; //表前缀 protected $dbname; //分库分表后对应的库 protected $table; //分库分表后对应的库表 public function __construct($id){ $this->config = new Config($this->dbnamePrefix, $this->tablePrefix, $id); //根据id找到对应库和表 $this->connection = new Pdo($this->config->dsn, $this->config->user, $this->config->password);//实例化pdo $this->connection->exec("set names utf8"); $this->dbname = $this->config->dbname; $this->table = $this->config->table; } public function update(array $data, array $where = array()){ } public function select(array $condition){ $sqlwhere=''; if(!empty($condition)){ foreach ($condition as $field => $value) { $where[] = '`'.$field.'`='."'".addslashes($value)."'"; } $sqlwhere .= ' '.implode(' and ', $where); } $sql="select * from ".$this->dbname.'.'.$this->table; if($sqlwhere){ $sql.=" where $sqlwhere"; } $res=$this->connection->query($sql); $data['data']=$res->fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC); $data['info']=array("dsn"=>$this->config->dsn,"dbname"=>$this->dbname,"table"=>$this->table,"sql"=>$sql); return $data; } public function insert(array $arrData) { $name = $values = ''; $flag = $flagV = 1; $true = is_array( current($arrData) );//判断是否一次插入多条数据 if($true) { //构建插入多条数据的sql语句 foreach($arrData as $arr) { $values .= $flag ? '(' : ',('; foreach($arr as $key => $value) { if($flagV) { if($flag) $name .= "$key"; $values .= "'$value'"; $flagV = 0; } else { if($flag) $name .= ",$key"; $values .= ",'$value'"; } } $values .= ') '; $flag = 0; $flagV = 1; } } else { //构建插入单条数据的sql语句 foreach($arrData as $key => $value) { if($flagV) { $name = "$key"; $values = "('$value'"; $flagV = 0; } else { $name .= ",$key"; $values .= ",'$value'"; } } $values .= ") "; } $sql = "insert into ".$this->dbname.'.'.$this->table." ($name) values $values"; if( ($rs = $this->connection->exec($sql) ) > 0 ) { return array("dsn"=>$this->config->dsn,"dbname"=>$this->dbname,"table"=>$this->table,"sql"=>$sql); } return false; } public function query($sql){ return $this->connection->query($sql); } } 1
5、测试
使用主键id作为分表字段,那最好就不要使用自增了,可使用uuid
User.php
<?php require 'Config.php'; require 'Model.php'; class User extends Model { protected $dbnamePrefix = 'cloude'; protected $tablePrefix = 'user'; } //生成唯一uuid function create_uuid($prefix = ""){ //可以指定前缀 $str = md5(uniqid(mt_rand(), true)); $uuid = substr($str,0,8) . '-'; $uuid .= substr($str,8,4) . '-'; $uuid .= substr($str,12,4) . '-'; $uuid .= substr($str,16,4) . '-'; $uuid .= substr($str,20,12); return $prefix . $uuid; } $userId=create_uuid(); $user = new User($userId); $data=array('id'=>$userId,'name'=>'大明'.$userId,'password'=>'14e1b600b1fd579f47433b88e8d85291','sex'=>'男'); if($result=$user->insert($data)){ echo '插入成功:','<pre/>'; print_r($result); } $condition=array("id"=>$userId); $list=$user->select($condition); if($list){ echo '查询成功:','<pre/>'; print_r($list); }
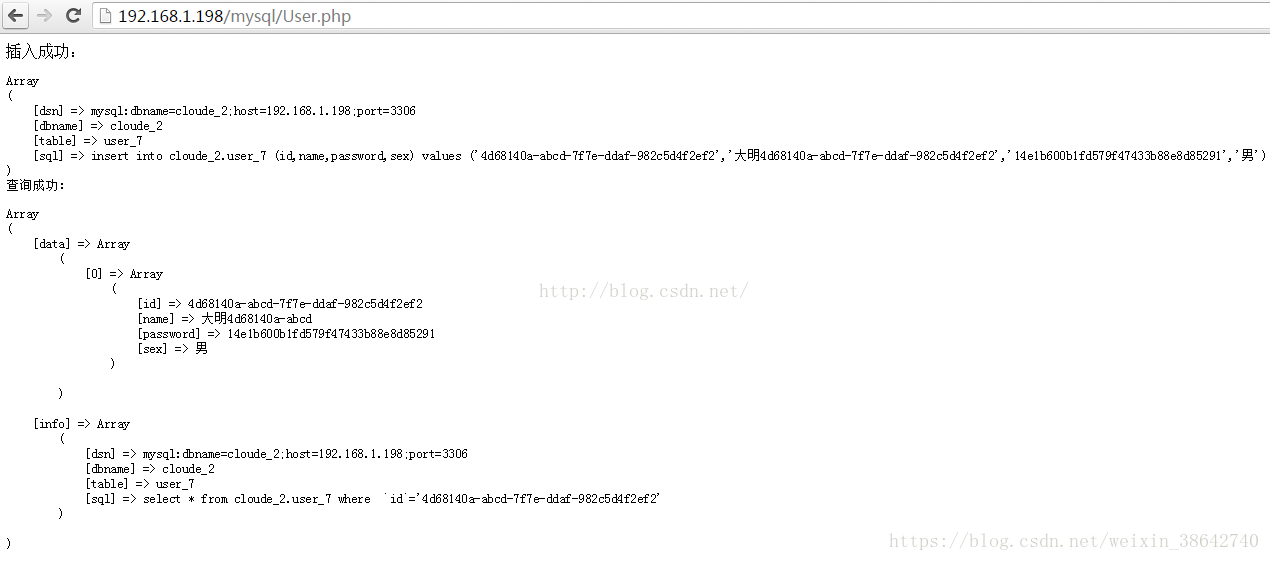
6、结果
插入成功会返回插入到哪个库哪个表,查询成功返回从哪个库哪个表查的
**
分库分表注意事项:
**
1、维度问题
假如用户购买了商品,需 要将交易记录保存取来,如果按照用户的纬度分表,则每个用户的交易记录都保存在同一表中,所以很快很方便的查找到某用户的购买情况,但是某商品被购买的情 况则很有可能分布在多张表中,查找起来比较麻烦。反之,按照商品维度分表,可以很方便的查找到此商品的购买情况,但要查找到买人的交易记录比较麻烦。
所以常见的解决方式有:
通过扫表的方式解决,此方法基本不可能,效率太低了。
记录两份数据,一份按照用户纬度分表,一份按照商品维度分表。
通过搜索引擎解决,但如果实时性要求很高,又得关系到实时搜索
2、避免分表join操作 因为关联的表有可能不在同一数据库中
3、避免跨库事务
避免在一个事务中修改db0中的表的时候同时修改db1中的表,一个是操作起来更复杂,效率也会有一定影响
4、分表宜多不宜少;这样做主要是为了尽量避免后期可能遇到的二次拆分
5、尽量把同一组数据放到同一DB服务器上
例如将卖家a的商品和交易信息都放到db0中,当db1挂了的时候,卖家a相关的东西可以正常使用。也就是说避免数据库中的数据依赖另一数据库中的数据
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「justPr」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38642740/java/article/details/81448762


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号