FutureTask详解
CAS:http://huangyunbin.iteye.com/blog/1942369
Future:http://blog.csdn.net/liulipuo/article/details/39029643
知识储备CAS
CAS基于冲突检测的无锁并发策略,性能也较高。CAS操作有3个操作数,内存值M,预期值E,新值U,如果M==E,则将内存值修改为B,否则啥都不做。
public class TestUnsafe { private static Unsafe unsafe; static{ try { //通过反射获取rt.jar下的Unsafe类 Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); field.setAccessible(true); unsafe = (Unsafe) field.get(null); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Get Unsafe instance occur error"+ e); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class clazz = Target.class; Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); System.out.println("fieldName:fieldOffset"); for (Field f : fields) { // 获取属性偏移量,可以通过这个偏移量给属性设置 System.out.println(f.getName() + ":" + unsafe.objectFieldOffset(f)); } Target target = new Target(); Field intFiled = clazz.getDeclaredField("intParam") ; int a=(Integer)intFiled.get(target ) ; System.out.println("原始值是:"+a); //intParam的字段偏移是12 原始值是3 我们要改为10 System.out.println(unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(target, 12, 3, 10)); int b=(Integer)intFiled.get(target) ; System.out.println("改变之后的值是:"+b); //这个时候已经改为10了,所以会返回false System.out.println(unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(target, 12, 3, 10)); //false //判断target对象的偏移量24位置,即strParam,如果该变量值=null,则给strParam赋值5 System.out.println(unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(target, 24, null, "5")); //true } } class Target{ int intParam=3; long longParam; String strParam; String strParam2; }
测试结果:

FutureTask
futureTask的异步计算功能就不介绍了,主要分析源码,下图是futureTask的结构:
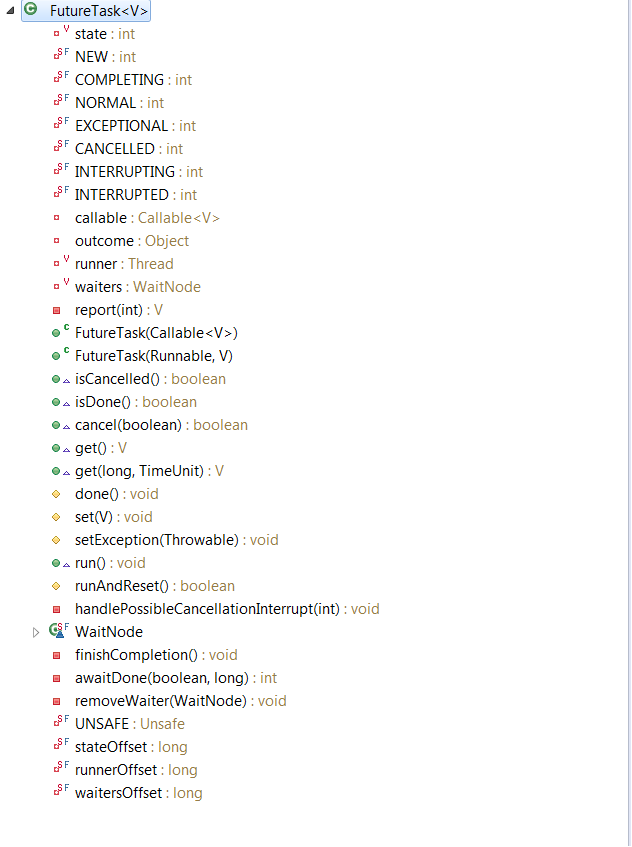
NEW 新建 0
COMPLETING 执行中 1
NORMAL 正常 2
EXCEPTIONAL 异常 3
CANCELLED 取消 4
INTERRUPTING 中断中 5
INTERRUNPED 被中断 6
state的状态变化可以有四种方式
NEW->COMPLETING->NORMAL 正常完成的流程
NEW->COMPLETING->EXCEPTIONAL 出现异常的流程
NEW->CANCELED 被取消
NEW->INTERRUNPING->INTERRRUNPTED 被中断
创建FutureTask
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) { if (callable == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.callable = callable; //state初始化NEW状态 this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable }
run方法:
1 public void run() { 2 //如果当前state不是创建状态,且已经在运行。则直接return。 3 if (state != NEW || 4 !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, 5 null, Thread.currentThread())) 6 return; 7 //开始执行任务 8 try { 9 Callable<V> c = callable; 10 //创建状态,且callable不为空,开始执行调用call() 11 if (c != null && state == NEW) { 12 V result; 13 boolean ran; 14 try { 15 result = c.call(); 16 ran = true; 17 } catch (Throwable ex) { 18 result = null; 19 ran = false; 20 setException(ex); 21 } 22 //成功调用任务,执行set()方法 23 if (ran) 24 set(result); 25 } 26 } finally { 27 // runner must be non-null until state is settled to 28 // prevent concurrent calls to run() 29 //无论是否成功,都要把runner设置为null 30 runner = null; 31 // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent 32 // leaked interrupts 33 int s = state; 34 if (s >= INTERRUPTING) 35 handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); 36 } 37 }
接下来看一下24行的set方法:
1 protected void set(V v) { 2 //CAS设置state NEW -> COMPLETING 3 if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) { 4 //结果赋值outcome 5 outcome = v; 6 //CAS将state设置为NORMAL 7 UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state 8 //唤醒所有的等待线程,同时设置callable=null,调用done(),具体实现后面详细介绍 9 finishCompletion(); 10 } 11 }
cancel()取消
1 public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { 2 //如果state已经不是NEW 或者NEW不能设置成INTERRUPTING , 则直接返回false 。 3 if (!(state == NEW && 4 UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, 5 mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED))) 6 return false; 7 try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception 8 //如果是可中断 那么就 调用系统中断方法 然后把状态设置成INTERRUPTED 9 if (mayInterruptIfRunning) { 10 try { 11 Thread t = runner; 12 if (t != null) 13 //中断执行线程 14 t.interrupt(); 15 } finally { // final state 16 //最后设置state为INTERRUPTED 17 UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED); 18 } 19 } 20 } finally { 21 finishCompletion(); 22 } 23 return true; 24 }
再来看一下get操作:
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { if (unit == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int s = state; //如果还没完成,并且等待timeout也没有完成,则抛出超时异常 if (s <= COMPLETING && (s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING) throw new TimeoutException(); return report(s); }
awaitDone()操作来如何实现超时,已经完成但未超时,则结束等待返回结果,看具体代码:
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException { //超时时间点 final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L; WaitNode q = null; boolean queued = false; //循环执行 for (;;) { //中断处理 if (Thread.interrupted()) { removeWaiter(q); throw new InterruptedException(); } int s = state; //首先判断是否完成,如果完成,直接返回state结果 if (s > COMPLETING) { if (q != null) q.thread = null; return s; } else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet Thread.yield(); //未完成执行,则将当前线程(主线程)设置成等待节点并放入到等待队列中 else if (q == null) q = new WaitNode();
//将waiters设置成q的next节点,并替换,改操作只做一次,将main线程加入到队列中,只加一次 else if (!queued) queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q.next = waiters, q); //如果启动了超时等待 else if (timed) { //计算剩余超时时间 nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime(); //超时,移除队列中的等待线程,返回state,上层判断state,并报出超时异常 if (nanos <= 0L) { removeWaiter(q); return state; } //还未超时,则等待nanos时间,然而如果task执行接受,并不会一直等待,在run()中的set()中,会执行finishCompleted(),将对待队列线性唤醒,调用LockSupport.unpark()方法来唤醒等待线程 LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos); } else //未启用超时功能,在未完成callable,则无限期等待 LockSupport.park(this); } }
最后看一下finishCompletion()方法,调用callable,是如何唤醒main线程
private void finishCompletion() { // assert state > COMPLETING; //遍历等待队列 for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) { //将waiters的头结点中线程设置null,即移除某个等待线程 if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) { for (;;) { Thread t = q.thread; //如果等待线程不为null 调用LockSupport.unpark(t)唤醒,然后操作下一个等待线程 if (t != null) { q.thread = null; LockSupport.unpark(t); } WaitNode next = q.next; if (next == null) break; q.next = null; // unlink to help gc q = next; } break; } } done(); callable = null; // to reduce footprint }
至此,FutureTask的源码解析已经完成,接下来看一下开源对于异步处理的解决方案。
举一反三:
ChannelFuture
ListenableFuture




