Sentinel整体架构
总体架构
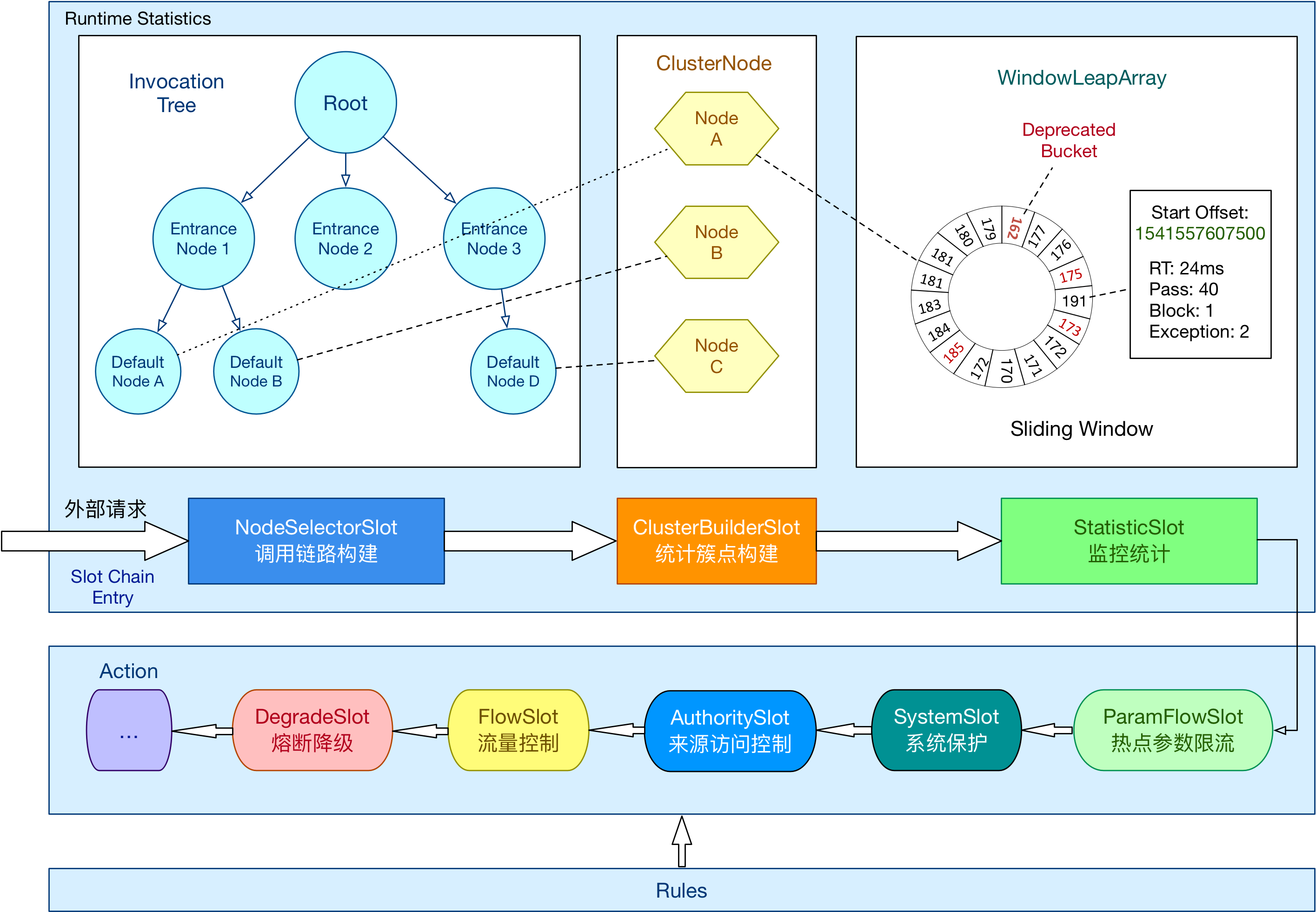
上图是来自官网的总体架构图,这张图上可以清晰的看到整个流量控制以责任链的模式进行的,每一个slot负责特定的处理,后续会给大家具体讲解chain上每一个slot的功能。
NodeSelectorSlot负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;ClusterBuilderSlot则用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;StatisticSlot则用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;FlowSlot则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;AuthoritySlot则根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;DegradeSlot则通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;SystemSlot则通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;
模型设计
上图只是展示了树状结构,无法清晰解释多线程下的执行态。

在这图中可以清晰的看到资源的调用情况及统计的维度,包括早DefaultNode上的统计 ClusterNode上的统计,以及StatisticNode上的统计。
在执行SphU.entry之前,首先会去创建EntranceNode入口 ContextUtil.enter(contextName, origin);
protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) { Context context = contextHolder.get(); if (context == null) { // 一个context name 对应一个线程, 一个contextname又对应一个 EntranceNode Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap; DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name); // DCL if (node == null) { // 超过2000个context、 则返回null_context if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) { setNullContext(); return NULL_CONTEXT; } else { LOCK.lock(); try { node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name); if (node == null) { if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) { setNullContext(); return NULL_CONTEXT; } else { // 每一个资源名称都会对应 node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null); // Add entrance node. /** * root 本身就是EntranceNode 资源名为machine-root" * addChild,相当于放在上层node的list里面 */ Constants.ROOT.addChild(node); // copy-on-write Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1); newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap); // 缓存顶层资源对应的EntranceNode newMap.put(name, node); contextNameNodeMap = newMap; } } } finally { LOCK.unlock(); } } } // 保存了context name 以及对应的EntranceNode context = new Context(node, name); context.setOrigin(origin); // 设置到ThreadLocal中 contextHolder.set(context); } return context; }
实际上建立了线程与Context关系一对一关系 ,context name与EntranceNode一对一关系。接下来开始执行SphU.entry -> CtSph#entryWithPriority, 在此之前会做一些初始化,这块后续再讲解。
private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws BlockException { // 获取当前线程中context ThreadLocal<Context>中获取 Context context = ContextUtil.getContext(); // 如果是 NullContext,那么说明 context name 超过了 2000 个,参见 ContextUtil#trueEnter // 这个时候,Sentinel 不再接受处理新的 context 配置,也就是不做这些新的接口的统计、限流熔断等 if (context instanceof NullContext) { // The {@link NullContext} indicates that the amount of context has exceeded the threshold, // so here init the entry only. No rule checking will be done. return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context); } if (context == null) { // Using default context. context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME); } // Global switch is close, no rule checking will do. if (!Constants.ON) { return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context); } ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper); /* * Means amount of resources (slot chain) exceeds {@link Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE}, * so no rule checking will be done. */ if (chain == null) { return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context); } Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context); try { chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args); } catch (BlockException e1) { e.exit(count, args); throw e1; } catch (Throwable e1) { // This should not happen, unless there are errors existing in Sentinel internal. RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1); } return e; }
这边根据资源名称去获取对应的ProcessSlotChain调用链。也就是说相同资源名称的DefaultNode共享同一个chain。
责任链构建
调用链是是一个单向链表,上一个slot通过Next变量来持有下一个slot的引用,下图展示了责任链模式的数据结构。
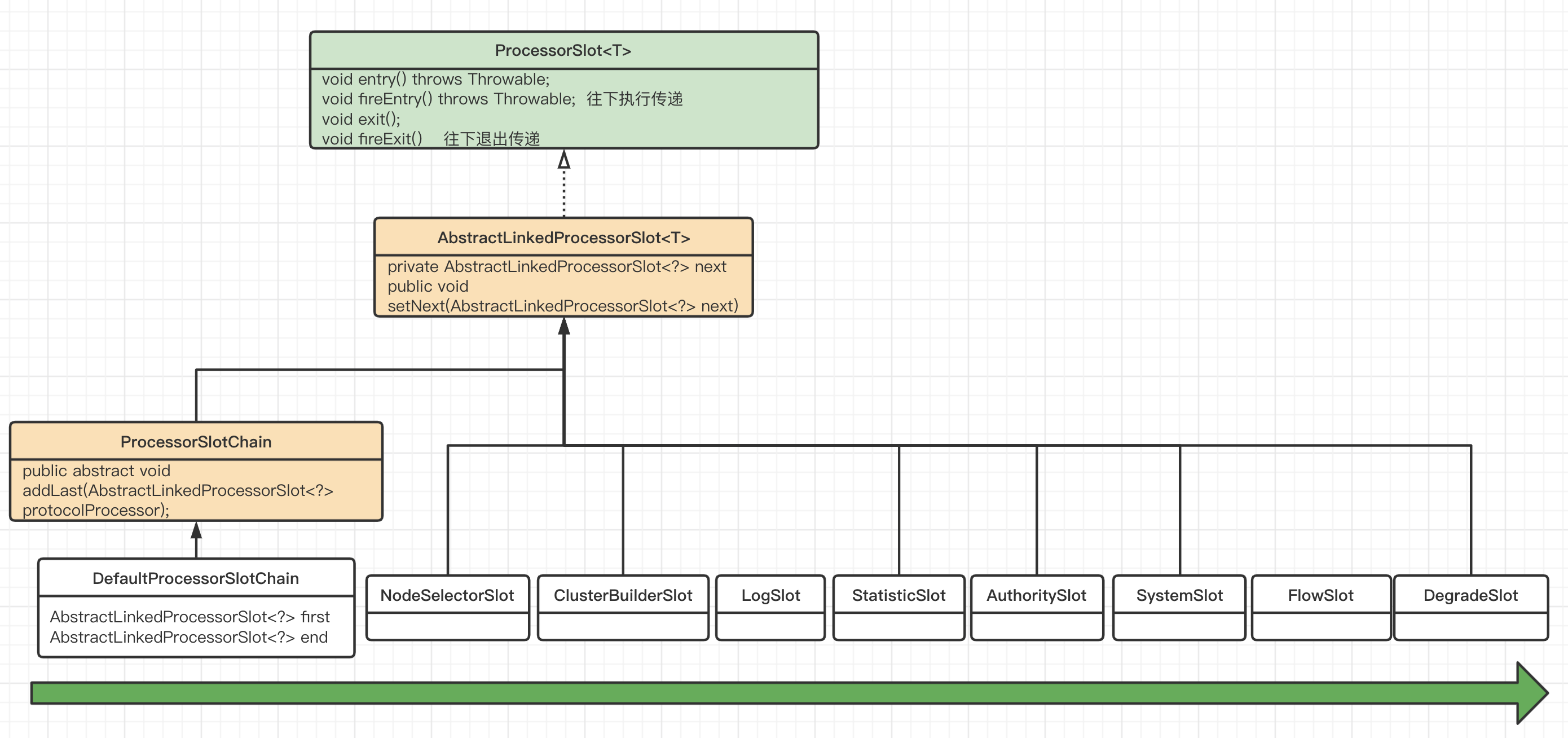
接下来看一下如何初始化调用链的,CtSph#lookProcessChain
这边有一个概念 就是一个class类型 对应一个SpiLoader对象并缓存在内存中
ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) { ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper); // DCL if (chain == null) { synchronized (LOCK) { chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper); if (chain == null) { // Entry size limit. if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) { return null; } // 创建资源调用链 chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain(); Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>( chainMap.size() + 1); newMap.putAll(chainMap); newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain); chainMap = newMap; } } } return chain; }
接下来会涉及到SPI相关的内容,对SPI不太熟悉的小伙伴,可以自行查阅资料。从SPI加载slot构建器
slotChainBuilder = SpiLoader.of(SlotChainBuilder.class).loadFirstInstanceOrDefault();
首先获取对应class类型的SpiLoader,根据classname保存在内存中
public static <T> SpiLoader<T> of(Class<T> service) { AssertUtil.notNull(service, "SPI class cannot be null"); AssertUtil.isTrue(service.isInterface() || Modifier.isAbstract(service.getModifiers()), "SPI class[" + service.getName() + "] must be interface or abstract class"); String className = service.getName(); SpiLoader<T> spiLoader = SPI_LOADER_MAP.get(className); if (spiLoader == null) { synchronized (SpiLoader.class) { spiLoader = SPI_LOADER_MAP.get(className); if (spiLoader == null) { SPI_LOADER_MAP.putIfAbsent(className, new SpiLoader<>(service)); spiLoader = SPI_LOADER_MAP.get(className); } } } return spiLoader; }
接下来看一下loadFirstInstanceOrDefault方法
public S loadFirstInstanceOrDefault() { // 加载class load(); // 相同接口的实现类中 加载第一个 for (Class<? extends S> clazz : classList) { if (defaultClass == null || clazz != defaultClass) { return createInstance(clazz); } } // 如果没有 加载默认实现类 return loadDefaultInstance(); }
/** * Load the Provider class from Provider configuration file */ public void load() { // 如果加载过了 返回 if (!loaded.compareAndSet(false, true)) { return; } // 获取文件路径 String fullFileName = SPI_FILE_PREFIX + service.getName(); ClassLoader classLoader; if (SentinelConfig.shouldUseContextClassloader()) { // 线程上下文加载器 classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); } else { // 使用加载service的加载器 可能是系统类子加载器 classLoader = service.getClassLoader(); } if (classLoader == null) { // 使用系统类加载器加载 classLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(); } Enumeration<URL> urls = null; try { urls = classLoader.getResources(fullFileName); } catch (IOException e) { fail("Error locating SPI configuration file, filename=" + fullFileName + ", classloader=" + classLoader, e); } if (urls == null || !urls.hasMoreElements()) { RecordLog.warn("No SPI configuration file, filename=" + fullFileName + ", classloader=" + classLoader); return; } while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); InputStream in = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { in = url.openStream(); br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { // 每次读取一行 if (StringUtil.isBlank(line)) { // Skip blank line continue; } line = line.trim(); int commentIndex = line.indexOf("#"); if (commentIndex == 0) { // 跳过注释 // Skip comment line continue; } // 如果行开头不是# 取行头到#之间的字符串 if (commentIndex > 0) { line = line.substring(0, commentIndex); } line = line.trim(); Class<S> clazz = null; try { // 加载到JVM clazz = (Class<S>) Class.forName(line, false, classLoader); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { fail("class " + line + " not found", e); } // clazz 是否是service 的子类 或相同 if (!service.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) { fail("class " + clazz.getName() + "is not subtype of " + service.getName() + ",SPI configuration file=" + fullFileName); } // 缓存实现类 classList.add(clazz); Spi spi = clazz.getAnnotation(Spi.class); String aliasName = spi == null || "".equals(spi.value()) ? clazz.getName() : spi.value(); if (classMap.containsKey(aliasName)) { Class<? extends S> existClass = classMap.get(aliasName); fail("Found repeat alias name for " + clazz.getName() + " and " + existClass.getName() + ",SPI configuration file=" + fullFileName); } // 别名与class 缓存 classMap.put(aliasName, clazz); if (spi != null && spi.isDefault()) { if (defaultClass != null) { fail("Found more than one default Provider, SPI configuration file=" + fullFileName); } defaultClass = clazz; } RecordLog.info("[SpiLoader] Found SPI implementation for SPI {}, provider={}, aliasName={}" + ", isSingleton={}, isDefault={}, order={}", service.getName(), line, aliasName , spi == null ? true : spi.isSingleton() , spi == null ? false : spi.isDefault() , spi == null ? 0 : spi.order()); } } catch (IOException e) { fail("error reading SPI configuration file", e); } finally { closeResources(in, br); } } // 根据order进行排序 sortedClassList.addAll(classList); Collections.sort(sortedClassList, new Comparator<Class<? extends S>>() { @Override public int compare(Class<? extends S> o1, Class<? extends S> o2) { Spi spi1 = o1.getAnnotation(Spi.class); int order1 = spi1 == null ? 0 : spi1.order(); Spi spi2 = o2.getAnnotation(Spi.class); int order2 = spi2 == null ? 0 : spi2.order(); return Integer.compare(order1, order2); } }); }
至此完成了chain构建器的类加载。后面通过构建器build一个调用链,同样使用SPI技术,slotChainBuilder.build();
@Override public ProcessorSlotChain build() { ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain(); // 获取到所有的slot 并排好序 List<ProcessorSlot> sortedSlotList = SpiLoader.of(ProcessorSlot.class).loadInstanceListSorted(); for (ProcessorSlot slot : sortedSlotList) { // 校验 if (!(slot instanceof AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot)) { RecordLog.warn("The ProcessorSlot(" + slot.getClass().getCanonicalName() + ") is not an instance of AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot, can't be added into ProcessorSlotChain"); continue; } // ProcessorSlotChain中的end一直引用最新的slot //每一次的addlast 都会将当前最后一个slot的next引用到新的slot上 //同时更新ProcessorSlotChain中的end为新的slot chain.addLast((AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?>) slot); } return chain; }
这就是整个资源调用链初始化的过程,也是基于单向链表的责任链模式的构建。



