【LevelDB源码阅读】SkipList
是什么
skiplist特点
- 有几个层组成,每层是一个有序的链表
- 第一层包含所有元素,如果元素x出现在第i层,则所有比i小的层都包含x
- 头指针指向最高处的第一个元素
参考LevelDB源码剖析之基础部件-SkipList中示意图:
skiplist结构
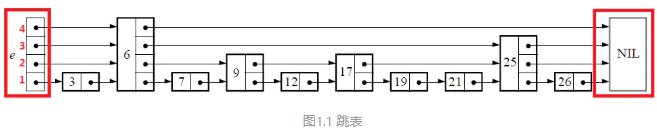
图1.1中红色部分为初始化状态,即head各个level中next节点均为NULL。
查找和插入示例:
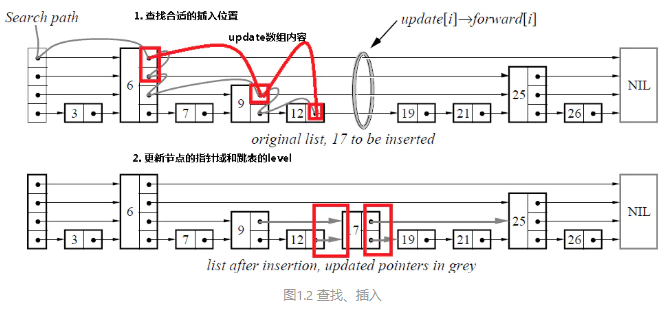
为什么要用
- 实现比平衡树简单,性能和平衡树媲美
学到什么
- 通过类模板解决多种数据类型
源码分析
SkipList是一个模板类
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
class SkipList
其中Key是要存储的数据类型,Comparator实现Key的比较。
对外接口
主要提供两个接口Insert和Contains,即插入和查找,没有Delete接口。
// Insert key into the list.
// REQUIRES: nothing that compares equal to key is currently in the list.
void Insert(const Key &key);
// Returns true iff an entry that compares equal to key is in the list.
bool Contains(const Key &key) const;
数据成员
enum { kMaxHeight = 12 }; //最大层数
// Immutable after construction
Comparator const compare_;
Arena* const arena_; // Arena used for allocations of nodes
Node* const head_; // SkipList头节点
// Modified only by Insert(). Read racily by readers, but stale
// values are ok.
std::atomic<int> max_height_; // Height of the entire list
// Read/written only by Insert().
Random rnd_;
构造函数
初始化head_高度为kMaxHeight,并设置每一层的后继节点为nullptr。
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena *arena)
: compare_(cmp),
arena_(arena),
head_(NewNode(0 /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)),
max_height_(1),
rnd_(0xdeadbeef) {
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
head_->SetNext(i, nullptr); // 设置每层后继节点为nullptr
}
}
Node和NewNode
Node对应SkipList中的节点,包含了key以及若干层级信息。
// Implementation details follow
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key &k) : key(k) {}
Key const key;
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
Node *Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return next_[n].load(std::memory_order_acquire);
}
void SetNext(int n, Node *x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].store(x, std::memory_order_release); // 设置当前节点下一个节点
}
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
Node *NoBarrier_next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return next_[n].load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node *x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].store(std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
std::atomic<Node *> next_[1];
};
所有Node对象都通过NewNode构造,先通过arena_分配内存,然后通过placement new的方式调用Node的构造函数。
为什么使用placement new?
主要为了在预分配的内存上构建对象。
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key, Comparator>::NewNode(
const Key &key, int height) {
char *const node_memory = arena_->AllocateAligned(
sizeof(Node) + sizeof(std::atomic<Node*>) * (height - 1));
return new (node_memory) Node(key);
}
插入
插入时需要找到多个前后节点。
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Insert(const Key &key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreatOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == nullptr || !Equal(key, x->key));
int height = RandomHeight(); // 随机决定插入节点高度
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; ++i) {
prev[i] = head_; //如果当前节点的高度大于最高节点,则高出部分的的前节点都是头节点
}
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (nullptr), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since nullptr sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
max_height_.store(height, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
x = NewNode(key, height); // 构造节点,高度为height
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i) { // 每层断开链表插入新节点
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x); // 先修改x节点,再修改prev节点
}
}
其中RandomHeight通过破硬币的方法随机决定该节点高度
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key, Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd.Next() % kBranching) == 0)) {
++height;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
}
FindGreatOrEqual实现如下:
//返回第一个大于等于key的节点
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindGreatOrEqual(const Key &key, Node **prev) const {
Node *x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1; // 下标从0层开始
while (true) {
Node *next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else { // key <= next->key
if (prev != nullptr) prev[level] = x;
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
--level;
}
}
}
}
其中KeyIsAfterNode实现如下:
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key, Comparator>::KeyIsAfterNode(const Key &key, Node *n) const {
// null n is considered infinite
return (n != nullptr) && (compare_(n->key, key) < 0);
}
查找
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Contains(const Key &key) const {
Node *x = FindGreatOrEqual(key, nullptr);
if (x != nullptr && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
迭代器
MemTable在读取时使用的是SkipList::Iterator,定义如下:
// Iteration over the contents of a skip list
class Iterator {
public:
// Initialize an iterator over the specified list.
// The returned iterator is not valid.
explicit Iterator(const SkipList *list);
// Returns true iff the iterator is positioned at a valid node.
bool Valid() const;
// Returns the key at the current position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
const Key &key() const;
// Advances to the next position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Next();
// Advances to the previous position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Prev();
// Advance to the first entry with a key >= target
void Seek(const Key &target);
// Position at the first entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToFirst();
// Position at the last entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToLast();
private:
const SkipList *list_; // 需迭代的skiplist
Node *node_; // 当前迭代的节点
// Intentionally copyable
};




