bzoj4605 崂山白花蛇草水
传送门:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4605
【题解】
序列上的第k大我们可以用线段树内套一个能查询序列某些地方有多少数的数据结构来做。
那么平面上很显然就是kdtree。
然后我们要调调重构块大小,大概是2000.
然后发现这样还是很慢,发现一个可以优化的地方,线段树上如果这个节点是父亲的左孩子,那么不用存储。
因为我们只会查询右孩子来判断往那里走。
这样就能过啦!要跑50s啊。。。

# include <stdio.h> # include <assert.h> # include <string.h> # include <iostream> # include <algorithm> // # include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef unsigned long long ull; const int M = 5e5 + 10, N = 5e6 + 10; const int mod = 1e9+7; # define RG register # define ST static int n, Q; int REBUILD_SIZE = 2000; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(!isdigit(ch)) { if(ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while(isdigit(ch)) { x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); } return f == 1 ? x : -x; } int D; struct node { int d[2], mx[2], mi[2], l, r, siz, v, s; friend bool operator ==(node a, node b) { return a.d[0] == b.d[0] && a.d[1] == b.d[1]; } friend bool operator <(node a, node b) { return a.d[D] < b.d[D]; } }; # define ls T[x].l # define rs T[x].r inline void gmax(int &x, int y) { if(x < y) x = y; } inline void gmin(int &x, int y) { if(x > y) x = y; } inline bool in(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int xx1, int yy1, int xx2, int yy2) { return x1 <= xx1 && xx2 <= x2 && y1 <= yy1 && yy2 <= y2; } inline bool out(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int xx1, int yy1, int xx2, int yy2) { return x1 > xx2 || x2 < xx1 || y1 > yy2 || y2 < yy1; } inline bool cmp(int, int); node tmp; struct KDT { node T[N]; int siz; int t[M], tn; inline void set() { siz = 0; T[0].siz = 0, T[0].s = 0; } inline void up(int x) { for (int i=0; i<2; ++i) { T[x].mi[i] = T[x].mx[i] = T[x].d[i]; if(ls) gmin(T[x].mi[i], T[ls].mi[i]); if(rs) gmin(T[x].mi[i], T[rs].mi[i]); if(ls) gmax(T[x].mx[i], T[ls].mx[i]); if(rs) gmax(T[x].mx[i], T[rs].mx[i]); } T[x].s = T[x].v + T[ls].s + T[rs].s; T[x].siz = 1 + T[ls].siz + T[rs].siz; } inline void insert(int &x, int d) { if(!x) { x = ++siz; T[x].d[0] = T[x].mi[0] = T[x].mx[0] = tmp.d[0]; T[x].d[1] = T[x].mi[1] = T[x].mx[1] = tmp.d[1]; T[x].siz = 1; } if(tmp == T[x]) { T[x].v += tmp.v; T[x].s += tmp.v; return ; } if(tmp.d[d] < T[x].d[d]) insert(ls, d^1); else insert(rs, d^1); up(x); } inline int query(int x, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { if(!x) return 0; int ret = 0; if(in(x1, y1, x2, y2, T[x].mi[0], T[x].mi[1], T[x].mx[0], T[x].mx[1])) return T[x].s; if(out(x1, y1, x2, y2, T[x].mi[0], T[x].mi[1], T[x].mx[0], T[x].mx[1])) return 0; if(in(x1, y1, x2, y2, T[x].d[0], T[x].d[1], T[x].d[0], T[x].d[1])) ret += T[x].v; ret += query(ls, x1, y1, x2, y2) + query(rs, x1, y1, x2, y2); return ret; } inline void getnode(int x) { if(!x) return ; getnode(ls); getnode(rs); t[++tn] = x; } inline int build(int l, int r, int d) { if(l>r) return 0; int mid = l+r>>1; D = d; nth_element(t+l, t+mid, t+r+1, cmp); int x = t[mid]; T[x].l = build(l, mid-1, d^1); T[x].r = build(mid+1, r, d^1); up(x); return x; } inline int rebuild(int x, int d) { tn = 0; getnode(x); return build(1, tn, d); } }T; inline bool cmp(int a, int b) { return T.T[a] < T.T[b]; } # undef ls # undef rs int xs, ys, xx, yy; int rt[N], L[N], R[N]; int rb[N], siz, root; inline void modify(int &x, int l, int r, int v, bool b) { if(!x) x = ++siz, rb[x] = REBUILD_SIZE; if(b) { T.insert(rt[x], 0); if(T.T[rt[x]].siz == rb[x]) { rt[x] = T.rebuild(rt[x], 0); rb[x] += REBUILD_SIZE; } } if(l == r) return ; int mid = l+r>>1; if(v <= mid) modify(L[x], l, mid, v, 0); else modify(R[x], mid+1, r, v, 1); } inline int sum(int x, int l, int r, int k) { if(l == r) return l; int t = T.query(rt[R[x]], xs, ys, xx, yy); int mid = l+r>>1; if(k <= t) return sum(R[x], mid+1, r, k); else return sum(L[x], l, mid, k-t); } int main() { // freopen("4605.in", "r", stdin); // freopen("4605.out", "w", stdout); int opt, v, lst = 0; n = read(), Q = read(); T.set(); while(Q--) { opt = read(); if(opt == 1) { // xs = read(), ys = read(), v = read(); xs = read() ^ lst, ys = read() ^ lst, v = read() ^ lst; tmp.d[0] = xs, tmp.d[1] = ys, tmp.v = tmp.s = 1; modify(root, 1, 1e9, v, 1); } if(opt == 2) { // xs = read(), ys = read(), xx = read(), yy = read(), v = read(); xs = read() ^ lst, ys = read() ^ lst, xx = read() ^ lst, yy = read() ^ lst, v = read() ^ lst; int t = T.query(rt[root], xs, ys, xx, yy); if(t < v) puts("NAIVE!ORZzyz."), lst = 0; else printf("%d\n", lst = sum(root, 1, 1e9, v)); } // if(Q % 10000 == 0) cerr << Q << endl; } return 0; }
当然放在外面写不大好
正宗的替罪羊式kdtree,是在里面写的,插入的时候顺便记录深度。
取参数A约在0.7左右,然B=log(1.0/A)
那么当深度超过子树大小/B的时候就加入重构标志。
如果同时满足子树大小>总子树大小*A,那么就重构。
(记住就好啦。。。)
然后这复杂度就很优秀了。

# include <math.h> # include <stdio.h> # include <assert.h> # include <string.h> # include <iostream> # include <algorithm> // # include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef unsigned long long ull; const int M = 5e5 + 10, N = 5e6 + 10; const int mod = 1e9+7; # define RG register # define ST static int n, Q; const double REBUILD_FAC = 0.713, REBUILD_LOG = log(1.0 - REBUILD_FAC); const int REBUILD_SIZE = 2000; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(!isdigit(ch)) { if(ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while(isdigit(ch)) { x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); } return f == 1 ? x : -x; } int D; struct node { int d[2], mx[2], mi[2], l, r, siz, v, s; friend bool operator ==(node a, node b) { return a.d[0] == b.d[0] && a.d[1] == b.d[1]; } friend bool operator <(node a, node b) { return a.d[D] < b.d[D]; } }; # define ls T[x].l # define rs T[x].r inline void gmax(int &x, int y) { if(x < y) x = y; } inline void gmin(int &x, int y) { if(x > y) x = y; } inline bool in(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int xx1, int yy1, int xx2, int yy2) { return x1 <= xx1 && xx2 <= x2 && y1 <= yy1 && yy2 <= y2; } inline bool out(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int xx1, int yy1, int xx2, int yy2) { return x1 > xx2 || x2 < xx1 || y1 > yy2 || y2 < yy1; } inline bool cmp(int, int); int rt[N], psx; node tmp; struct KDT { node T[N]; int siz; int t[M], tn; inline void set() { siz = 0; T[0].siz = 0, T[0].s = 0; } inline void up(int x) { for (int i=0; i<2; ++i) { T[x].mi[i] = T[x].mx[i] = T[x].d[i]; if(ls) gmin(T[x].mi[i], T[ls].mi[i]); if(rs) gmin(T[x].mi[i], T[rs].mi[i]); if(ls) gmax(T[x].mx[i], T[ls].mx[i]); if(rs) gmax(T[x].mx[i], T[rs].mx[i]); } T[x].s = T[x].v + T[ls].s + T[rs].s; T[x].siz = 1 + T[ls].siz + T[rs].siz; } inline bool insert(int &x, int d, int dep) { if(!x) { x = ++siz; T[x].d[0] = T[x].mi[0] = T[x].mx[0] = tmp.d[0]; T[x].d[1] = T[x].mi[1] = T[x].mx[1] = tmp.d[1]; T[x].siz = 1; T[x].v = tmp.v, T[x].s = tmp.s; return dep > log(T[rt[psx]].siz)/REBUILD_LOG; } int id; bool ret; if(tmp.d[d] < T[x].d[d]) id = ls, ret = insert(ls, d^1, dep+1); else id = rs, ret = insert(rs, d^1, dep+1); up(x); if(ret) { if(T[id].siz > REBUILD_FAC * T[x].siz) { x = rebuild(x, d); return 0; } return 1; } return 0; } inline int query(int x, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { if(!x) return 0; int ret = 0; if(in(x1, y1, x2, y2, T[x].mi[0], T[x].mi[1], T[x].mx[0], T[x].mx[1])) return T[x].s; if(out(x1, y1, x2, y2, T[x].mi[0], T[x].mi[1], T[x].mx[0], T[x].mx[1])) return 0; if(in(x1, y1, x2, y2, T[x].d[0], T[x].d[1], T[x].d[0], T[x].d[1])) ret += T[x].v; ret += query(ls, x1, y1, x2, y2) + query(rs, x1, y1, x2, y2); return ret; } inline void getnode(int x) { if(!x) return ; getnode(ls); getnode(rs); t[++tn] = x; } inline int build(int l, int r, int d) { if(l>r) return 0; int mid = l+r>>1; D = d; nth_element(t+l, t+mid, t+r+1, cmp); int x = t[mid]; T[x].l = build(l, mid-1, d^1); T[x].r = build(mid+1, r, d^1); up(x); return x; } inline int rebuild(int x, int d) { tn = 0; getnode(x); return build(1, tn, d); } }T; inline bool cmp(int a, int b) { return T.T[a] < T.T[b]; } # undef ls # undef rs int xs, ys, xx, yy; int L[N], R[N]; int siz, root; inline void modify(int &x, int l, int r, int v, bool b) { if(!x) x = ++siz; if(b) { psx = x; T.insert(rt[x], 0, 0); } if(l == r) return ; int mid = l+r>>1; if(v <= mid) modify(L[x], l, mid, v, 0); else modify(R[x], mid+1, r, v, 1); } inline int sum(int x, int l, int r, int k) { if(l == r) return l; int t = T.query(rt[R[x]], xs, ys, xx, yy); int mid = l+r>>1; if(k <= t) return sum(R[x], mid+1, r, k); else return sum(L[x], l, mid, k-t); } int main() { // freopen("4605.in", "r", stdin); // freopen("4605.out", "w", stdout); int opt, v, lst = 0; n = read(), Q = read(); T.set(); while(Q--) { opt = read(); if(opt == 1) { // xs = read(), ys = read(), v = read(); xs = read() ^ lst, ys = read() ^ lst, v = read() ^ lst; tmp.d[0] = xs, tmp.d[1] = ys, tmp.v = tmp.s = 1; modify(root, 1, 1e9, v, 1); } if(opt == 2) { // xs = read(), ys = read(), xx = read(), yy = read(), v = read(); xs = read() ^ lst, ys = read() ^ lst, xx = read() ^ lst, yy = read() ^ lst, v = read() ^ lst; int t = T.query(rt[root], xs, ys, xx, yy); if(t < v) puts("NAIVE!ORZzyz."), lst = 0; else printf("%d\n", lst = sum(root, 1, 1e9, v)); } // if(Q % 10000 == 0) cerr << Q << endl; } return 0; }
贴两张lemon的测的图
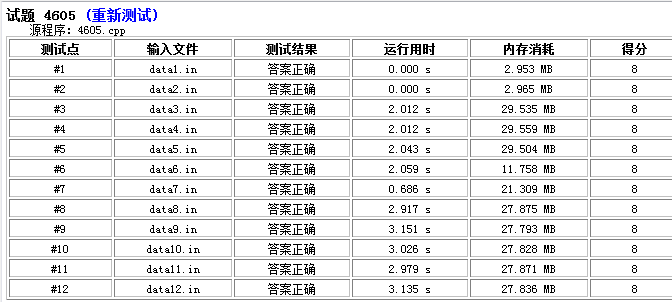
上面这张是第一份代码
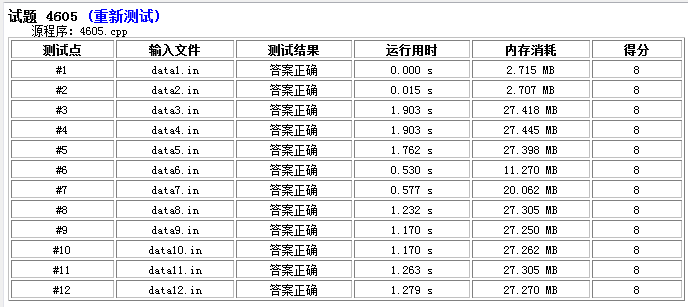
下面是第二张代码,在bzoj跑19s。
(我的老爷机比bzoj的老爷机快呀。。。)





