什么是Familywise Error Rate
1.什么是Familywise Error Rate(FWE or FWER)
定义:在一系列假设检验中,至少得出一次错误结论的概率。
换句话说,是造成至少一次Type I Error的概率。术语FWE来自测试系列,这是一系列数据测试的技术定义
2.估计FWE的公式
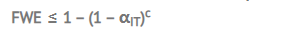
- αIT:一个独立测试的显著水平
- c : 对比次数
举个例子,对于一个10次试验的的序列,显著水平5%,FWE = ≤ 1 – (1 – .05)^10 = 0.401 ,这意味着Type I Error 发生的概率超过了40%,对于只有10次试验而言,是非常高的
3.控制FWE
单步执行,Bonferroni校正
单步程序对每个p值进行相同的调整。这保持了整个alpha水平保持在期望值(例如..05)。该方法被称为被称为Bonferroni校正。
1. 将alpha级别除以正在运行的测试的数量,并将该alpha级别应用于每个单独的测试。例如,如果您的整体alpha水平是.05,并且您正在运行5个测试,那么每个测试的alpha水平将是.05/5=.01。
2. 在每个测试中应用新的alpha级别来查找p值。在本例中,p值必须小于或等于0.01才具有统计意义。
多步执行
Similar to Bonferroni, but makes adaptive adjustments to each p-value. Several sequential methods exist. The easiest is probably the Holm-Bonferroni Method, but several others have been developed including the Sidak-Bonferroni and Holland-Copenhaver.
- Holm-Bonferroni: tests are run and then ordered from lowest to highest p-values. The individual tests are then tested (starting with the one with the lowest p-value) with an overall Bonferroni correction for all tests. See: Holm-Bonferroni Method for a step-by-step example.
- Sidak-Bonferroni (sometimes called the Boole or Dunn approximation): a variant of Bonferroni which uses a Taylor expansion (from calculus)
Type I Error
Type I Error 就是错误地拒绝了一个真实的零假设Ho(null hypothesis)(应该接受的)
null hypothesis :普遍接受的假设
Ho是一个普遍接受的假设;它与备择假设相反。研究人员提出了另一种假设,他们认为这种假设解释了一种现象,然后努力拒绝零假设。
Type II Error
Il型错误(有时称为2型错误)是拒绝虚假零假设的失败。类型ll错误的概率用符号B表示。
reference:https://www.statisticshowto.datasciencecentral.com/familywise-error-rate/

