大数据学习14_MapReduce规约&流量统计案例
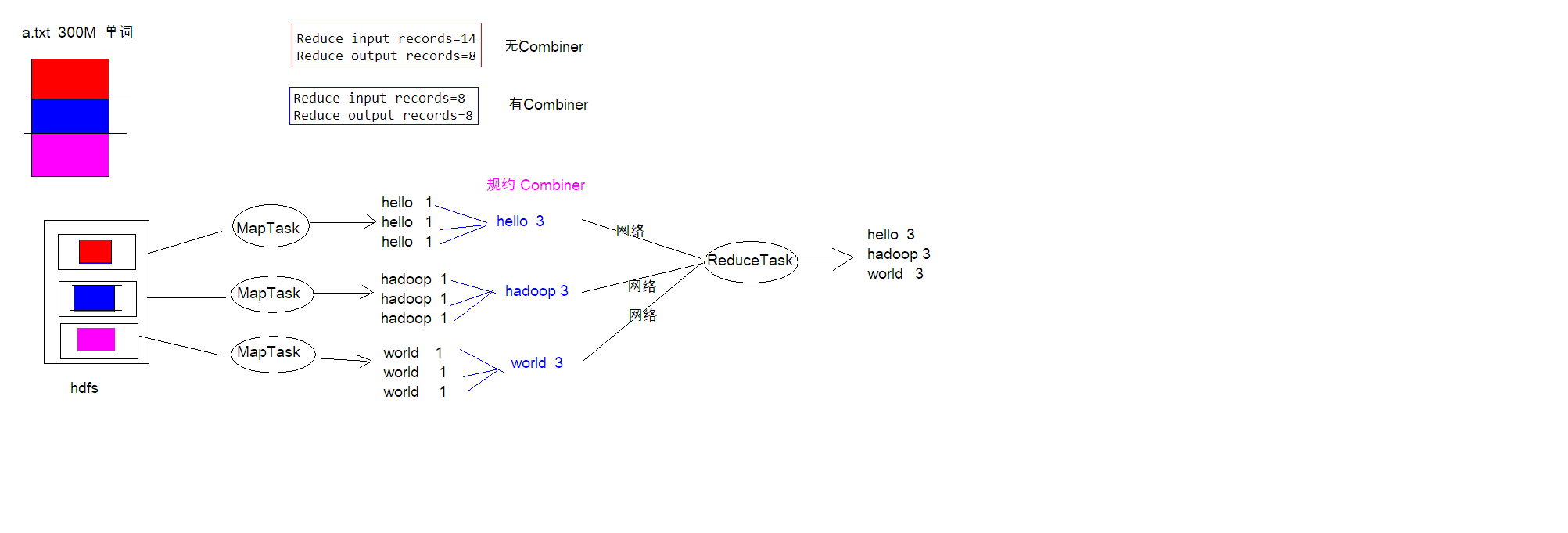
规约Combiner
概念
每一个 map 都可能会产生大量的本地输出,Combiner 的作用就是对 map 端的输出先做一次 合并,以减少在 map 和 reduce 节点之间的数据传输量,以提高网络IO 性能,是 MapReduce 的一种优化手段之一
- combiner 是 MR 程序中 Mapper 和 Reducer 之外的一种组件
- combiner 组件的父类就是 Reducer
- combiner 和 reducer 的区别在于运行的位置
Combiner 是在每一个 maptask 所在的节点运行 Reducer 是接收全局所有 Mapper 的输出结果
- combiner 的意义就是对每一个 maptask 的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量
一个图看懂规约
实现步骤
- 自定义一个 combiner 继承 Reducer,重写 reduce 方法
- 在 job 中设置 job.setCombinerClass(CustomCombiner.class)
combiner 能够应用的前提是不能影响最终的业务逻辑,而且,combiner 的输出 kv 应该跟 reducer 的输入 kv 类型要对应起来。
public class MyCombiner extends Reducer<Text,LongWritable,Text,LongWritable> {
/*
key : hello
values: <1,1,1,1>
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long count = 0;
//1:遍历集合,将集合中的数字相加,得到 V3
for (LongWritable value : values) {
count += value.get();
}
//2:将K3和V3写入上下文中
context.write(key, new LongWritable(count));
}
}
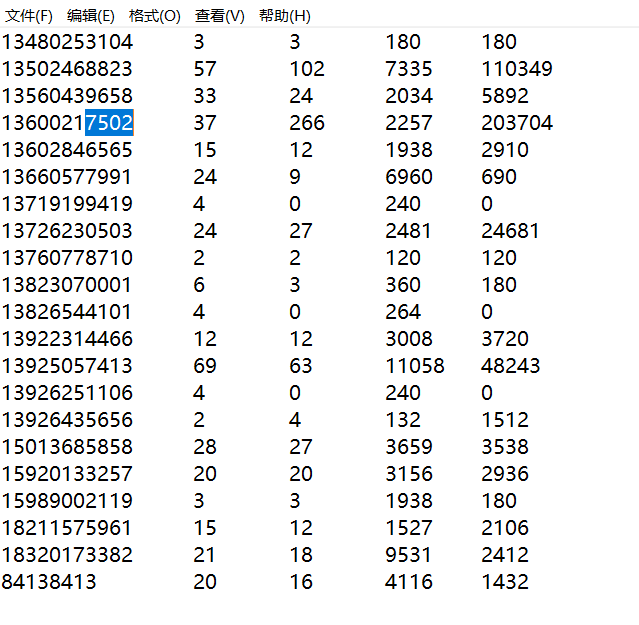
MapReduce案例-流量统计
需求:
统计每个手机号的上行数据包总和,下行数据包总和,上行总流量之和,下行总流量之和 分 析:以手机号码作为key值,上行流量,下行流量,上行总流量,下行总流量四个字段作为 value值,然后以这个key,和value作为map阶段的输出,reduce阶段的输入
一张图看懂编程流程和思路
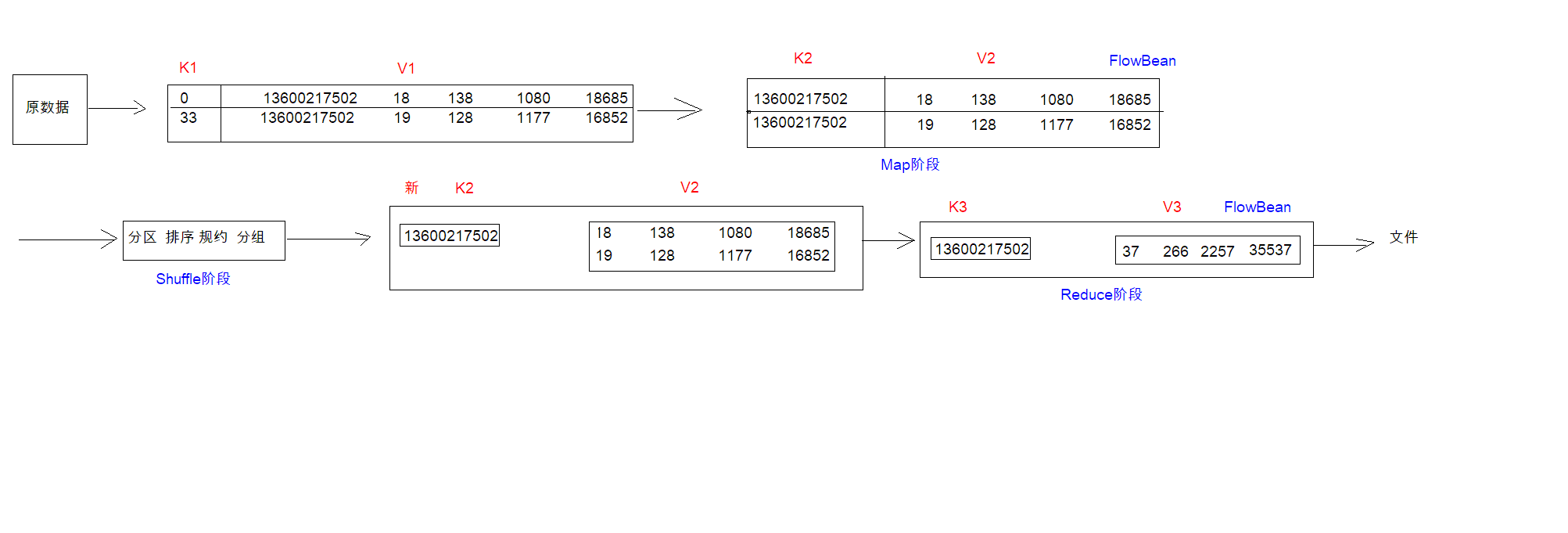
Step 1: 自定义map的输出value对象FlowBean
public class FlowBean implements Writable {
private Integer upFlow; //上行数据包数
private Integer downFlow; //下行数据包数
private Integer upCountFlow; //上行流量总和
private Integer downCountFlow;//下行流量总和
public Integer getDownFlow() {
return downFlow;
}
public void setDownFlow(Integer downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
}
public Integer getUpCountFlow() {
return upCountFlow;
}
public void setUpCountFlow(Integer upCountFlow) {
this.upCountFlow = upCountFlow;
}
public Integer getDownCountFlow() {
return downCountFlow;
}
public void setDownCountFlow(Integer downCountFlow) {
this.downCountFlow = downCountFlow;
}
public Integer getUpFlow() {
return upFlow;
}
public void setUpFlow(Integer upFlow) {
this.upFlow = upFlow;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return upFlow +
"\t" + downFlow +
"\t" + upCountFlow +
"\t" + downCountFlow;
}
//序列化方法
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(upFlow);
out.writeInt(downFlow);
out.writeInt(upCountFlow);
out.writeInt(downCountFlow);
}
//反序列化
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.upFlow = in.readInt();
this.downFlow = in.readInt();
this.upCountFlow = in.readInt();
this.downCountFlow = in.readInt();
}
}
Step 2: 定义FlowMapper类
public class FlowCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text, Text,FlowBean> {
/*
将K1和V1转为K2和V2:
K1 V1
0 1363157985059 13600217502 00-1F-64-E2-E8-B1:CMCC 120.196.100.55 www.baidu.com 综合门户 19 128 1177 16852 200
------------------------------
K2 V2
13600217502 FlowBean(19 128 1177 16852)
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//1:拆分行文本数据,得到手机号--->K2
String[] split = value.toString().split("\t");
String phoneNum = split[1];
//2:创建FlowBean对象,并从行文本数据拆分出流量的四个四段,并将四个流量字段的值赋给FlowBean对象
FlowBean flowBean = new FlowBean();
flowBean.setUpFlow(Integer.parseInt(split[6]));
flowBean.setDownFlow(Integer.parseInt(split[7]));
flowBean.setUpCountFlow(Integer.parseInt(split[8]));
flowBean.setDownCountFlow(Integer.parseInt(split[9]));
//3:将K2和V2写入上下文中
context.write(new Text(phoneNum), flowBean);
}
}
Step 3: 定义FlowReducer类
public class FlowCountReducer extends Reducer<Text,FlowBean, Text,FlowBean> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<FlowBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//1:遍历集合,并将集合中的对应的四个字段累计
Integer upFlow = 0; //上行数据包数
Integer downFlow = 0; //下行数据包数
Integer upCountFlow = 0; //上行流量总和
Integer downCountFlow = 0;//下行流量总和
for (FlowBean value : values) {
upFlow += value.getUpFlow();
downFlow += value.getDownFlow();
upCountFlow += value.getUpCountFlow();
downCountFlow += value.getDownCountFlow();
}
//2:创建FlowBean对象,并给对象赋值 V3
FlowBean flowBean = new FlowBean();
flowBean.setUpFlow(upFlow);
flowBean.setDownFlow(downFlow);
flowBean.setUpCountFlow(upCountFlow);
flowBean.setDownCountFlow(downCountFlow);
//3:将K3和V3下入上下文中
context.write(key, flowBean);
}
}
Step 4: 程序main函数入口FlowMain
public class JobMain extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] strings) throws Exception {
//1:创建一个job任务对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(super.getConf(), "mapreduce_flowcount");
//如果打包运行出错,则需要加该配置
job.setJarByClass(JobMain.class);
//2:配置job任务对象(八个步骤)
//第一步:指定文件的读取方式和读取路径
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
//TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("hdfs://node01:8020/wordcount"));
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("file:///F:\\input\\flowcount_input"));
//第二步:指定Map阶段的处理方式和数据类型
job.setMapperClass(FlowCountMapper.class);
//设置Map阶段K2的类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
//设置Map阶段V2的类型
job.setMapOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
//第三(分区),四 (排序)
//第五步: 规约(Combiner)
//第六步 分组
//第七步:指定Reduce阶段的处理方式和数据类型
job.setReducerClass(FlowCountReducer.class);
//设置K3的类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
//设置V3的类型
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
//第八步: 设置输出类型
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
//设置输出的路径
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("file:///F:\\out\\flowcount_out"));
//等待任务结束
boolean bl = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return bl ? 0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
//启动job任务
int run = ToolRunner.run(configuration, new JobMain(), args);
System.exit(run);
}
}
查看运行结果
原数据:

运行结果