yolov7模型的训练以及使用训练之后的模型通过TensorRT加速
yolov7模型的训练
训练过程与yolov5大致相同,修改cfg的yaml文件改为自己的类别,修改data的类别为自己的类别并设置数据集,验证集的目录以及类别名称
如果想从文件夹中挑选出一定数量的图片直接使用yolov7训练的话,下面提供一种方式
#pick pic with determined quantity import os import random import shutil def cpfile_rand(img, outfile, num): list_ = os.listdir(img) if num > len(list_): print('输出数量必须小于:', len(list_)) exit() numlist = random.sample(range(0,len(list_)),num) # 生成随机数列表a cnt = 0 for n in numlist: filename = list_[n] oldpath = os.path.join(img, filename) newpath = os.path.join(outfile, filename) shutil.copy(oldpath, newpath) # os.remove(oldpath) # li = os.path.splitext(filename) # txtfile = os.path.join(txtpath, li[0] + '.txt') # shutil.copy(txtfile, newpath) # os.remove(oldpath) # os.remove(txtfile) print('剩余文件:', num-cnt) cnt = cnt + 1 print('==========task OK!==========') if __name__ == "__main__": cpfile_rand('/home/dw/src/train/data/hebing', '/home/dw/src/train/data/f2', 9000) # 操作目录,输出目录,输出数量
从hebing文件夹中挑选到f2文件夹9000张图片,并生成训练依赖的txt文件。
使用训练之后的模型通过TensorRT加速
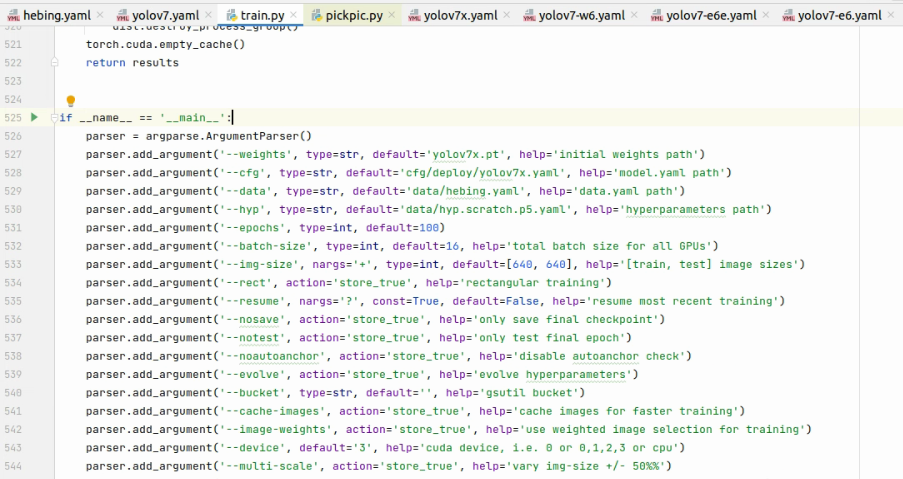
首先将yolo7的代码进行修改
修改 ./model/yolo.py 中的 Detect 类的 forward 函数如下:
def forward(self, x): # x = x.copy() # for profiling z = [] # inference output self.training |= self.export for i in range(self.nl): x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv bs, _, ny, nx = map(int, x[i].shape) # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85) x[i] = x[i].view(-1, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() if not self.training: # inference if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]: self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny).to(x[i].device) y = x[i].sigmoid() if not torch.onnx.is_in_onnx_export(): y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh else: xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh classif = y[..., 4:] y = torch.cat([xy, wh, classif], -1) z.append(y.view(-1, self.na * ny * nx, self.no)) if self.training: out = x elif self.end2end: out = torch.cat(z, 1) elif self.include_nms: z = self.convert(z) out = (z, ) else: out = torch.cat(z, 1) return out
修改 ./model/yolo.py 中的 IDetect 类的 forward 和 fuseforward 函数如下:
def forward(self, x): # x = x.copy() # for profiling z = [] # inference output self.training |= self.export for i in range(self.nl): x[i] = self.m[i](self.ia[i](x[i])) # conv x[i] = self.im[i](x[i]) bs, _, ny, nx = map(int, x[i].shape) # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85) x[i] = x[i].view(-1, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() if not self.training: # inference if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]: self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny).to(x[i].device) y = x[i].sigmoid() if not torch.onnx.is_in_onnx_export(): y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh else: xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh classif = y[..., 4:] y = torch.cat([xy, wh, classif], -1) z.append(y.view(-1, self.na * ny * nx, self.no)) return x if self.training else torch.cat(z, 1) def fuseforward(self, x): # x = x.copy() # for profiling z = [] # inference output self.training |= self.export for i in range(self.nl): x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv bs, _, ny, nx = map(int, x[i].shape) # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85) x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() if not self.training: # inference if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]: self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny).to(x[i].device) y = x[i].sigmoid() if not torch.onnx.is_in_onnx_export(): y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh else: xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh classif = y[..., 4:] y = torch.cat([xy, wh, classif], -1) z.append(y.view(-1, self.na * ny * nx, self.no)) if self.training: out = x elif self.end2end: out = torch.cat(z, 1) elif self.include_nms: z = self.convert(z) out = (z, ) else: out = torch.cat(z, 1) return out
修改 ./export.py 文件如下:
import argparse import sys import time sys.path.append('./') # to run '$ python *.py' files in subdirectories import torch import torch.nn as nn import models from models.experimental import attempt_load, End2End from utils.activations import Hardswish, SiLU from utils.general import set_logging, check_img_size from utils.torch_utils import select_device from utils.add_nms import RegisterNMS if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='./yolor-csp-c.pt', help='weights path') parser.add_argument('--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640, 640], help='image size') # height, width parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=1, help='batch size') parser.add_argument('--dynamic', action='store_true', help='dynamic ONNX axes') parser.add_argument('--grid', action='store_true', help='export Detect() layer grid') parser.add_argument('--end2end', action='store_true', help='export end2end onnx') parser.add_argument('--max-wh', type=int, default=None, help='None for tensorrt nms, int value for onnx-runtime nms') parser.add_argument('--topk-all', type=int, default=100, help='topk objects for every images') parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='iou threshold for NMS') parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='conf threshold for NMS') parser.add_argument('--device', default='cpu', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu') parser.add_argument('--simplify', action='store_true', help='simplify onnx model') parser.add_argument('--include-nms', action='store_true', help='export end2end onnx') opt = parser.parse_args() opt.img_size *= 2 if len(opt.img_size) == 1 else 1 # expand print(opt) set_logging() t = time.time() # Load PyTorch model device = select_device(opt.device) model = attempt_load(opt.weights, map_location=device) # load FP32 model labels = model.names # Checks gs = int(max(model.stride)) # grid size (max stride) opt.img_size = [check_img_size(x, gs) for x in opt.img_size] # verify img_size are gs-multiples # Input img = torch.zeros(opt.batch_size, 3, *opt.img_size).to(device) # image size(1,3,320,192) iDetection # Update model for k, m in model.named_modules(): m._non_persistent_buffers_set = set() # pytorch 1.6.0 compatibility if isinstance(m, models.common.Conv) or isinstance(m, models.common.RepConv): # assign export-friendly activations if isinstance(m.act, nn.Hardswish): m.act = Hardswish() elif isinstance(m.act, nn.SiLU): m.act = SiLU() # elif isinstance(m, models.yolo.Detect): # m.forward = m.forward_export # assign forward (optional) model.model[-1].export = not opt.grid # set Detect() layer grid export y = model(img) # dry run if opt.include_nms: model.model[-1].include_nms = True y = None # ONNX export try: import onnx print('\nStarting ONNX export with onnx %s...' % onnx.__version__) f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.onnx') # filename model.eval() output_names = ['classes', 'boxes'] if y is None else ['output'] if opt.grid and opt.end2end: print('\nStarting export end2end onnx model for %s...' % 'TensorRT' if opt.max_wh is None else 'onnxruntime') model = End2End(model,opt.topk_all,opt.iou_thres,opt.conf_thres,opt.max_wh,device) if opt.end2end and opt.max_wh is None: output_names = ['num_dets', 'det_boxes', 'det_scores', 'det_classes'] shapes = [opt.batch_size, 1, opt.batch_size, opt.topk_all, 4, opt.batch_size, opt.topk_all, opt.batch_size, opt.topk_all] else: output_names = ['output'] torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=12, input_names=['images'], output_names=output_names, dynamic_axes={'images': {0: 'batch'}, # size(1,3,640,640) 'output': {0: 'batch'}} if opt.dynamic and not opt.end2end else None) # Checks onnx_model = onnx.load(f) # load onnx model onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model) # check onnx model if opt.end2end and opt.max_wh is None: for i in onnx_model.graph.output: for j in i.type.tensor_type.shape.dim: j.dim_param = str(shapes.pop(0)) if opt.simplify: try: import onnxsim print('\nStarting to simplify ONNX...') onnx_model, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx_model) assert check, 'assert check failed' except Exception as e: print(f'Simplifier failure: {e}') # print(onnx.helper.printable_graph(onnx_model.graph)) # print a human readable model onnx.save(onnx_model,f) print('ONNX export success, saved as %s' % f) if opt.include_nms: print('Registering NMS plugin for ONNX...') mo = RegisterNMS(f) mo.register_nms() mo.save(f) except Exception as e: print('ONNX export failure: %s' % e) # Finish print('\nExport complete (%.2fs). Visualize with https://github.com/lutzroeder/netron.' % (time.time() - t))
修改完以后到 yolov7 源文件根目录下,运行
python export.py --grid --weight=./weights/yolov7best.pt --dynamic
导出onnx模型
导出之后开始使用TensorRT进行推理
仓库地址:https://github.com/shouxieai/tensorRT_Pro.git
下载到本地后使用example-simple_yolo文件夹,使用cmakelist或makefile修改配置,主要修改cuda路径、cudnn路径、opencv路径、-gencode=arch=compute_72,code=sm_72改为自己显卡的算力值,然后将导出的onnx模型文件放入workspace文件夹中,然后找到main.cpp中修改yolov7为自己的模型名称,建立和结果输出文件夹相同名称的文件夹,之后回到工作目录编译运行即可。
mkdir build cd build cmake .. make -j8 cd ../workspace ./pro




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~