stat命令的实现
stat命令的实现
任务详情
- 学习使用stat(1),并用C语言实现
- 提交学习stat(1)的截图
- man -k ,grep -r的使用
- 伪代码
- 产品代码 mystate.c,提交码云链接
- 测试代码,mystat 与stat(1)对比,提交截图
一、学习过程
-
通过man命令查看stat
-
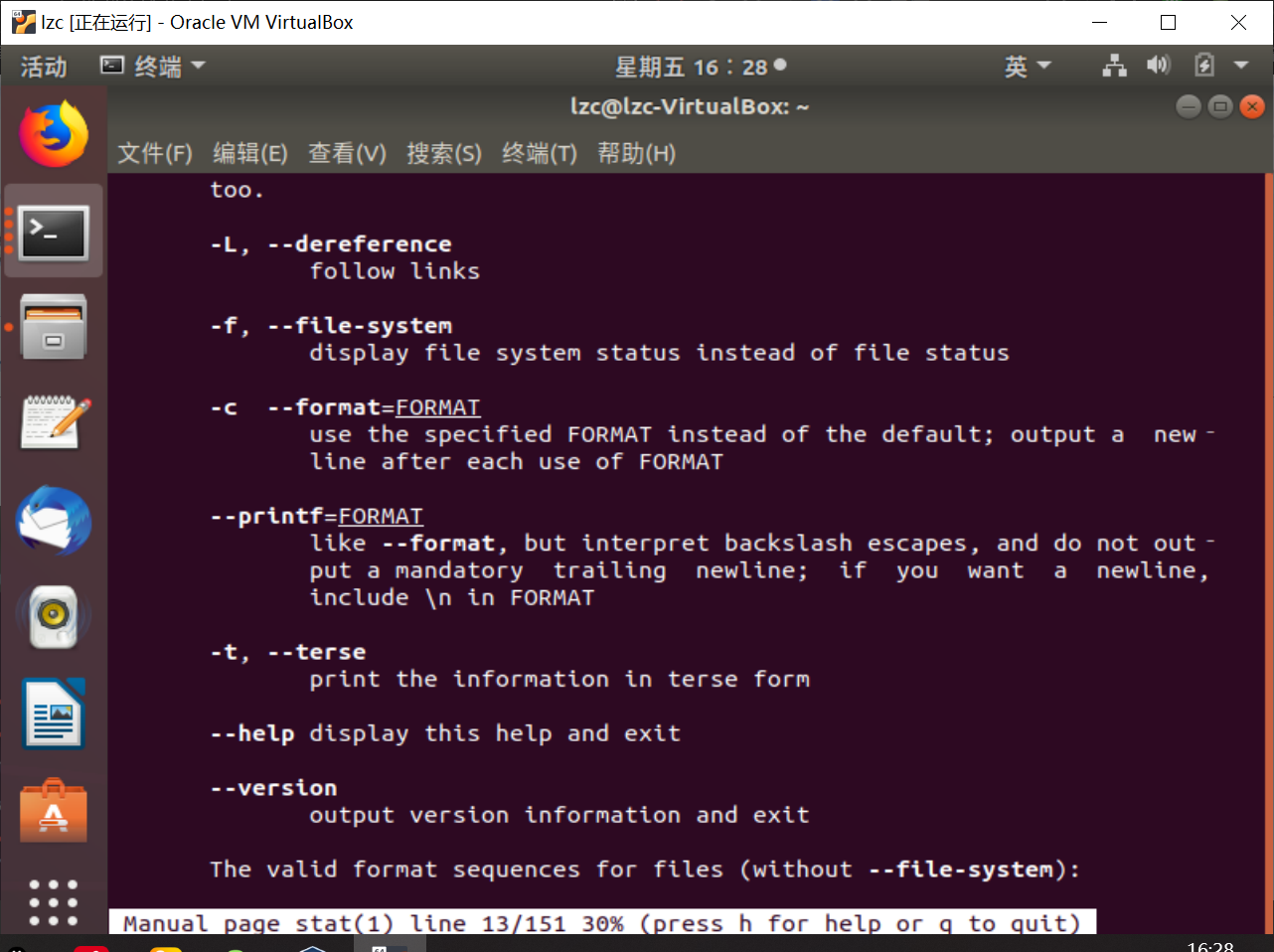
首先使用
man -k stat | grep 1或man 1 stat查看stat(1)
-
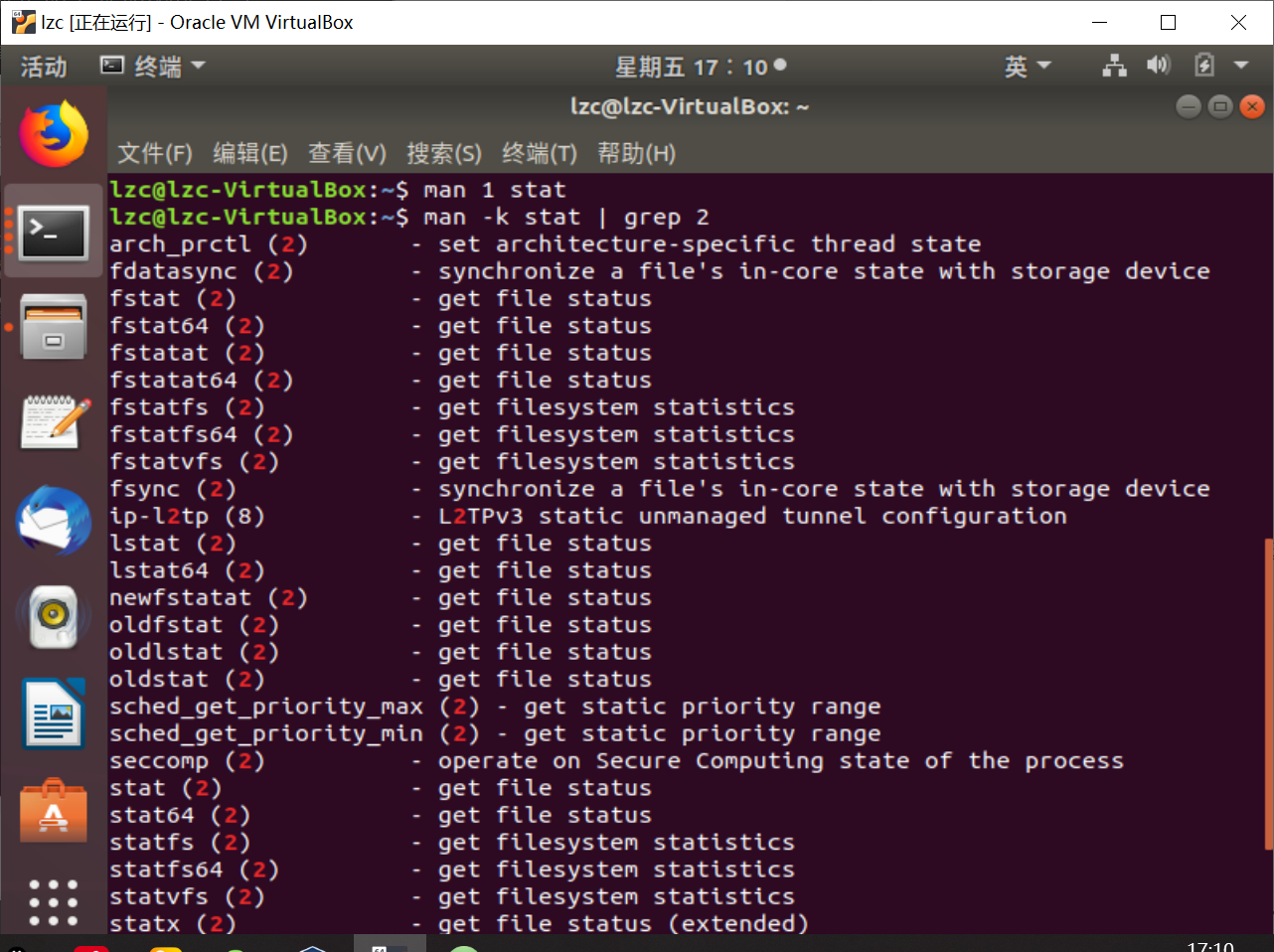
使用
man -k stat | grep 2查看相关的系统调用
二、学习使用stat
-
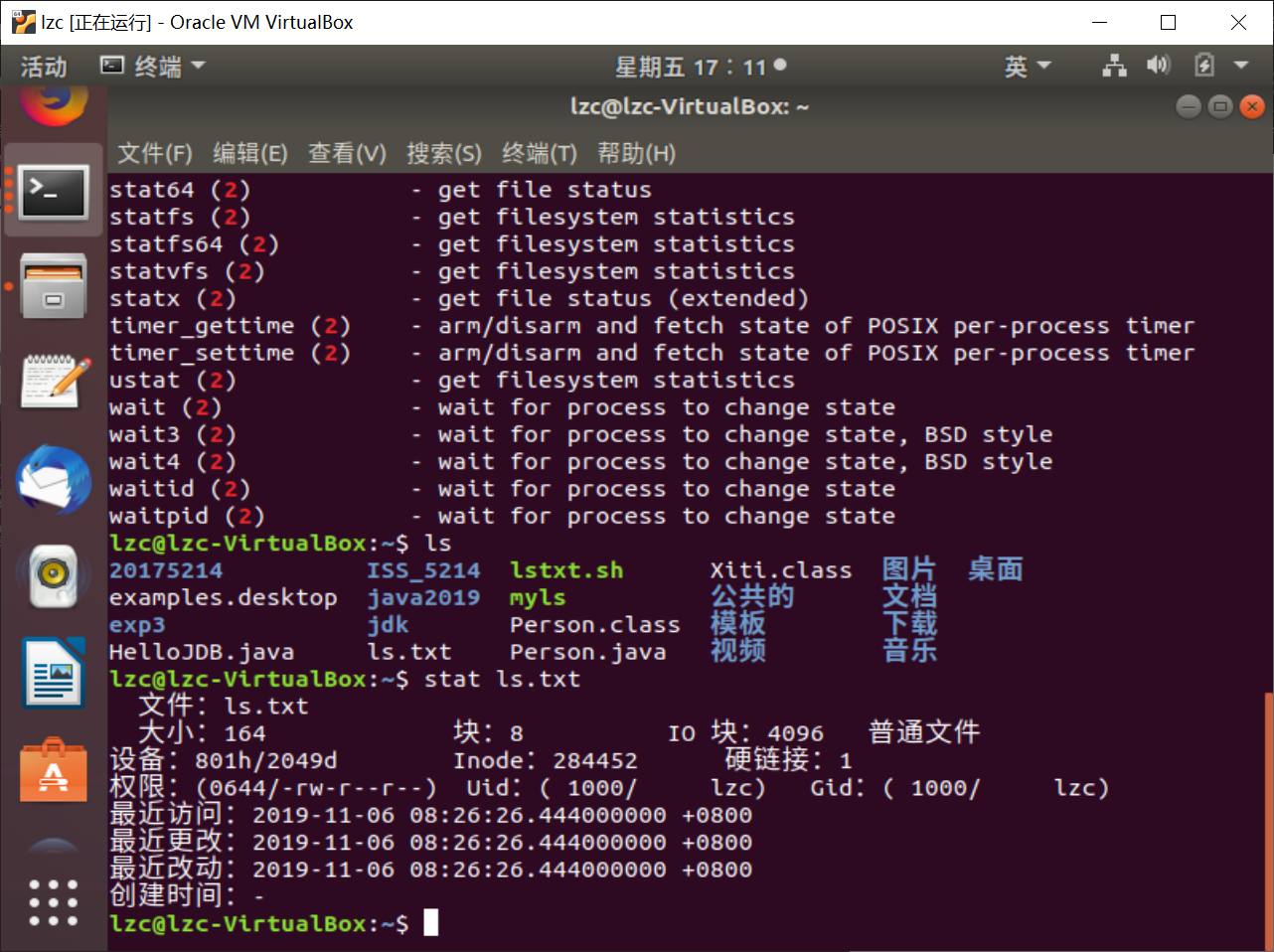
使用stat查看文件
-
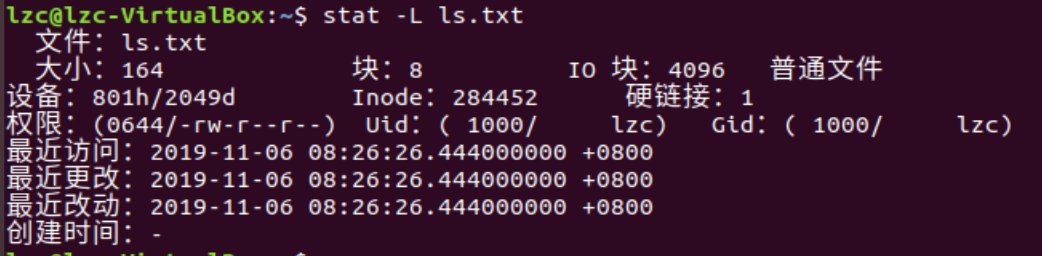
使用stat -L查看文件
-
使用stat -f查看文件
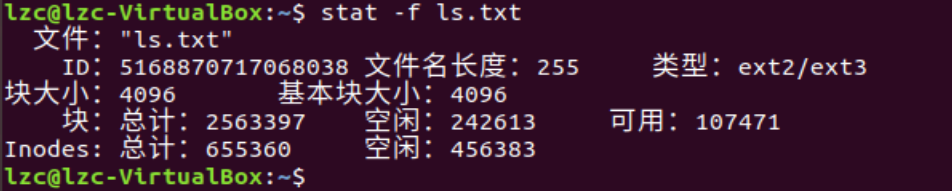
-
使用stat -t查看文件

三、伪代码
- 查看并存储文件各个属性
- 依次打印
四、实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat sb;
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <pathname>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (stat(argv[1], &sb) == -1) {
perror("stat");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("文件类型: ");
switch (sb.st_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n");
break;
case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n");
break;
case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n");
break;
case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
break;
case S_IFLNK: printf("symlink\n");
break;
case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n");
break;
case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n");
break;
default: printf("unknown?\n");
break;
}
printf("大小: %lld bytes\n",(long long) sb.st_size);
printf("块: %lld\n",(long long) sb.st_blocks);
printf("Inode: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_ino);
printf("硬链接: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_nlink);
printf("权限: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n",(long) sb.st_uid, (long) sb.st_gid);
printf("最近访问: %s", ctime(&sb.st_atime));
printf("最近更改: %s", ctime(&sb.st_ctime));
printf("最近改动: %s", ctime(&sb.st_mtime));
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
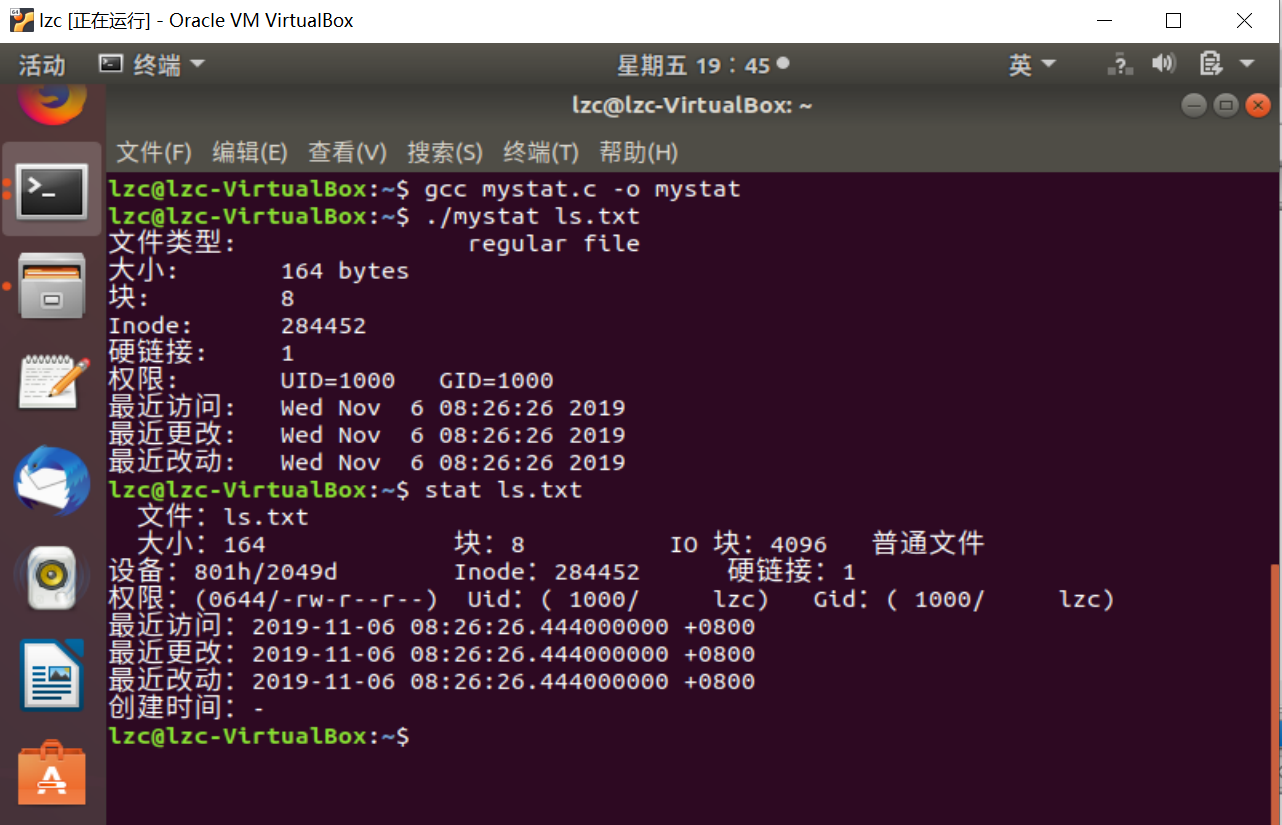
五、测试
即便不高谈理想,也要心存信仰。

