实验二:逻辑回归算法实验
实验二:逻辑回归算法实验
|博客班级|https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/czu/classof2020BigDataClass3-MachineLearning|
|----|----|----|
|作业要求|https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/czu/classof2020BigDataClass3-MachineLearning/homework/12858|
|学号|201613324|
【实验目的】
理解逻辑回归算法原理,掌握逻辑回归算法框架;
理解逻辑回归的sigmoid函数;
理解逻辑回归的损失函数;
针对特定应用场景及数据,能应用逻辑回归算法解决实际分类问题。
【实验内容】
1.根据给定的数据集,编写python代码完成逻辑回归算法程序,实现如下功能:
建立一个逻辑回归模型来预测一个学生是否会被大学录取。假设您是大学部门的管理员,您想根据申请人的两次考试成绩来确定他们的入学机会。您有来自以前申请人的历史数据,可以用作逻辑回归的训练集。对于每个培训示例,都有申请人的两次考试成绩和录取决定。您的任务是建立一个分类模型,根据这两门考试的分数估计申请人被录取的概率。
算法步骤与要求:
(1)读取数据;(2)绘制数据观察数据分布情况;(3)编写sigmoid函数代码;(4)编写逻辑回归代价函数代码;(5)编写梯度函数代码;(6)编写寻找最优化参数代码(可使用scipy.opt.fmin_tnc()函数);(7)编写模型评估(预测)代码,输出预测准确率;(8)寻找决策边界,画出决策边界直线图。
2. 针对iris数据集,应用sklearn库的逻辑回归算法进行类别预测。
要求:
(1)使用seaborn库进行数据可视化;(2)将iri数据集分为训练集和测试集(两者比例为8:2)进行三分类训练和预测;(3)输出分类结果的混淆矩阵。
【实验报告要求】
对照实验内容,撰写实验过程、算法及测试结果;
代码规范化:命名规则、注释;
实验报告中需要显示并说明涉及的数学原理公式;
查阅文献,讨论逻辑回归算法的应用场景;
实验内容及结果
问题一
1.读取数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data=pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\\86152\\Desktop\\ex2data1.txt",delimiter=',',header=None,names=['exam1','exam2','isAdmitted'])
data.head(5)
print(data)
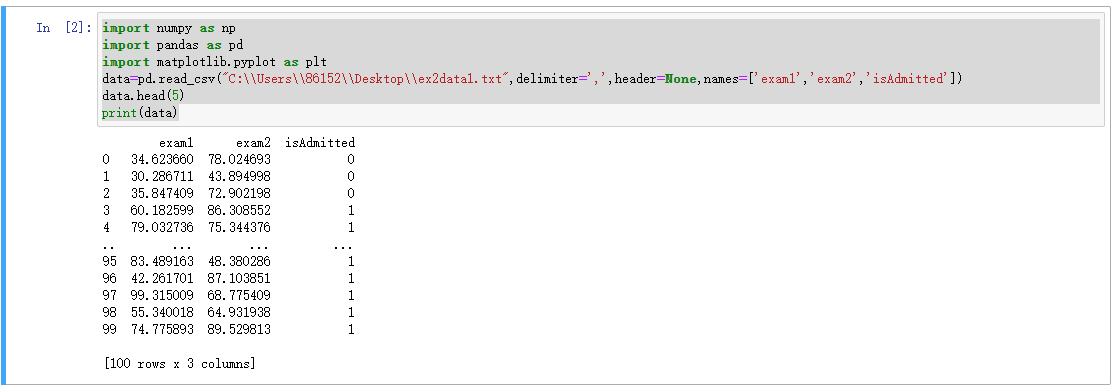
2. 数据可视化
#数据可视化
positive = data[data['isAdmitted']==1] #获取正样本
negative = data[data['isAdmitted']==0] #获取负样本
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
ax.scatter(positive['exam1'],positive['exam2'],s=30,c='g',marker='o',label='admitted')
ax.scatter(negative['exam1'],negative['exam2'],s=30,c='r',marker='x',label='not admitted')
ax.legend(loc=1) #显示标签位置
ax.set_xlabel("Exam1 Score")
ax.set_ylabel("Exam2 Score")
plt.show()
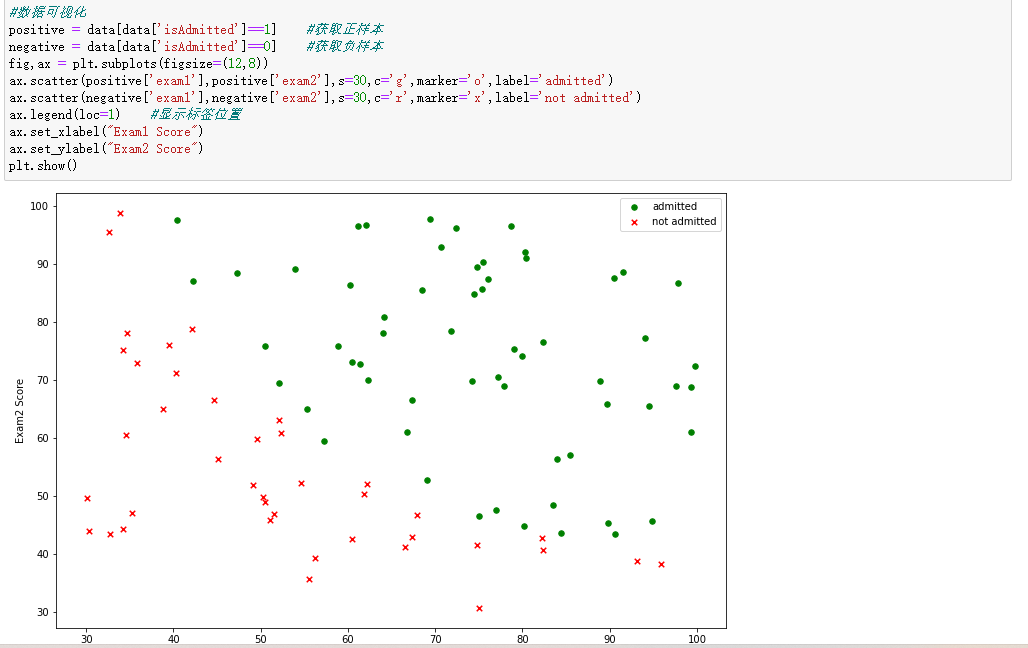
3.编写sigmoid函数代码
逻辑回归函数的定义为:
逻辑回归函数为:
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(z):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
nums = np.arange(-20,20,step=1)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
ax.plot(nums,sigmoid(nums),"r")
plt.show()
4.逻辑回归代价函数
def cost(theta, X, y):
theta = np.matrix(theta)
X = np.matrix(X)
y = np.matrix(y)
first = np.multiply(-y, np.log(sigmoid(X * theta.T)))
second = np.multiply((1 - y), np.log(1 - sigmoid(X * theta.T)))
return np.sum(first - second) / (len(X))
# 原始数据新建一列更易使用代价函数代码
data.insert(0, 'Ones', 1)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data.iloc[:,0:cols-1]#训练集
y = data.iloc[:,cols-1:cols]#label
#转换numnp数组
X = np.array(X.values)
y = np.array(y.values)
theta = np.zeros(3)
X.shape, theta.shape, y.shape
cost(theta, X, y)

5.编写梯度函数代码
def gradient(theta, X, y):
theta = np.matrix(theta)
X = np.matrix(X)
y = np.matrix(y)
parameters = int(theta.ravel().shape[1])
grad = np.zeros(parameters)
error = sigmoid(X * theta.T) - y
for i in range(parameters):
term = np.multiply(error, X[:,i])
grad[i] = np.sum(term) / len(X)
return grad
gradient(theta, X, y)

6.编写寻找最优化参数代码
import scipy.optimize as opt result = opt.fmin_tnc(func=cost, x0=theta, fprime=gradient, args=(X, y)) result

7.编写模型评估代码,输出准确率
def predict(theta, X): probability = sigmoid(X * theta.T) return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in probability] theta_min = np.matrix(result[0]) predictions = predict(theta_min, X) correct = [1 if ((a == 1 and b == 1) or (a == 0 and b == 0)) else 0 for (a, b) in zip(predictions, y)] accuracy = (sum(map(int, correct)) % len(correct)) print ('accuracy = {0}%'.format(accuracy))

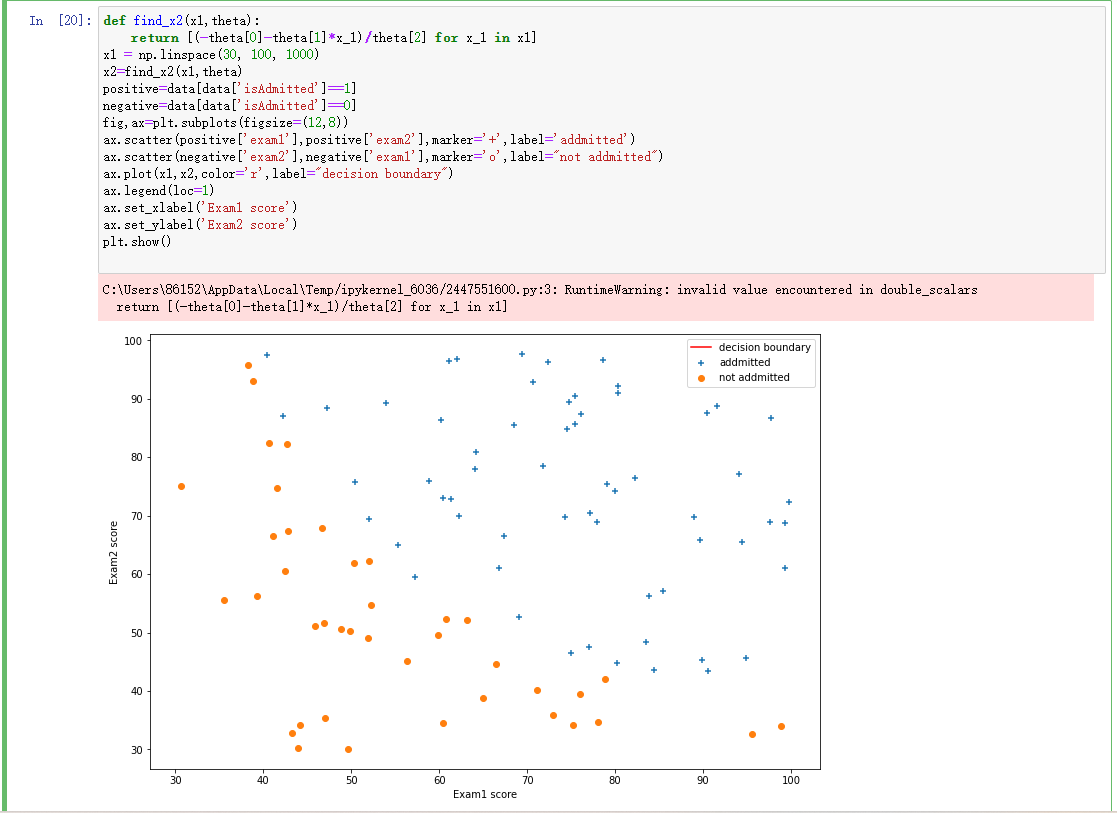
8.寻找决策边界,画出决策边界直线图
def find_x2(x1,theta):
return [(-theta[0]-theta[1]*x_1)/theta[2] for x_1 in x1]
x1 = np.linspace(30, 100, 1000)
x2=find_x2(x1,theta)
positive=data[data['isAdmitted']==1]
negative=data[data['isAdmitted']==0]
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
ax.scatter(positive['exam1'],positive['exam2'],marker='+',label='addmitted')
ax.scatter(negative['exam2'],negative['exam1'],marker='o',label="not addmitted")
ax.plot(x1,x2,color='r',label="decision boundary")
ax.legend(loc=1)
ax.set_xlabel('Exam1 score')
ax.set_ylabel('Exam2 score')
plt.show()
问题二:
(1)使用seaborn库进行数据可视化
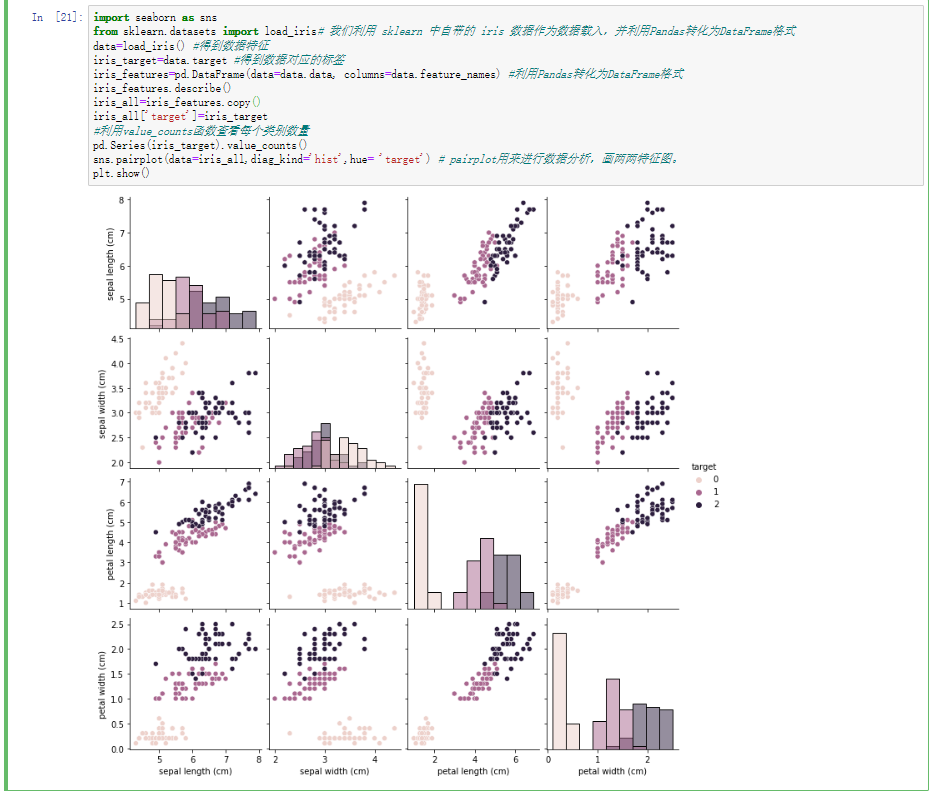
import seaborn as sns from sklearn.datasets import load_iris# 我们利用 sklearn 中自带的 iris 数据作为数据载入,并利用Pandas转化为DataFrame格式 data=load_iris() #得到数据特征 iris_target=data.target #得到数据对应的标签 iris_features=pd.DataFrame(data=data.data, columns=data.feature_names) #利用Pandas转化为DataFrame格式 iris_features.describe() iris_all=iris_features.copy() iris_all['target']=iris_target #利用value_counts函数查看每个类别数量 pd.Series(iris_target).value_counts() sns.pairplot(data=iris_all,diag_kind='hist',hue= 'target') # pairplot用来进行数据分析,画两两特征图。 plt.show()
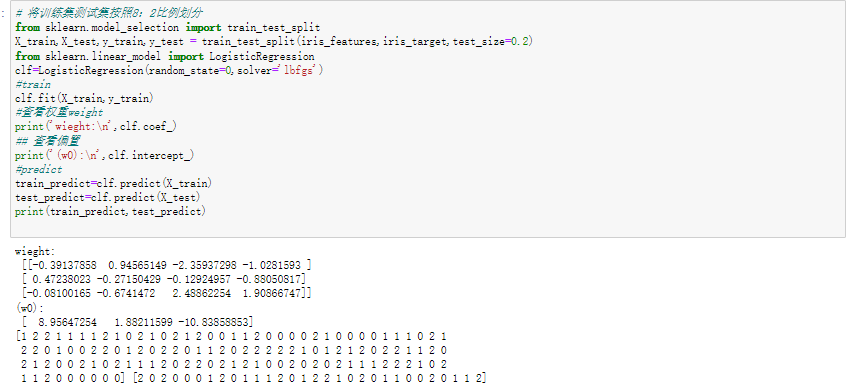
2.将iri数据集分为训练集和测试集(两者比例为8:2)进行三分类训练和预测
# 将训练集测试集按照8:2比例划分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(iris_features,iris_target,test_size=0.2)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf=LogisticRegression(random_state=0,solver='lbfgs')
#train
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
#查看权重weight
print('wieght:\n',clf.coef_)
## 查看偏置
print('(w0):\n',clf.intercept_)
#predict
train_predict=clf.predict(X_train)
test_predict=clf.predict(X_test)
print(train_predict,test_predict)
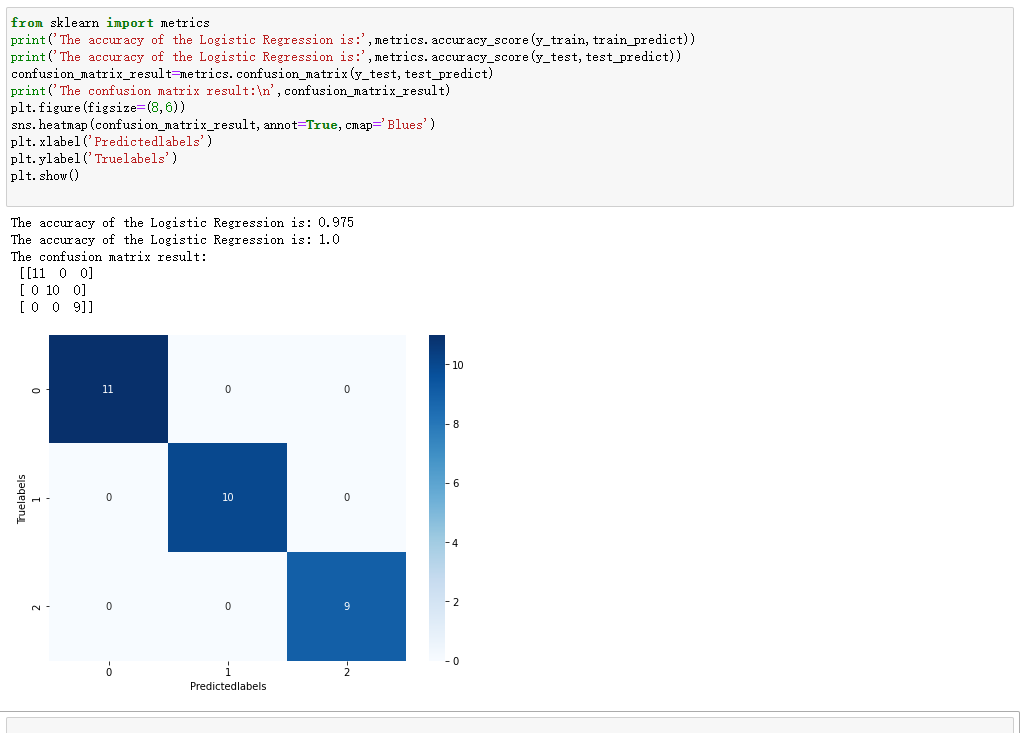
3.输出分类结果的混淆矩阵
from sklearn import metrics
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_train,train_predict))
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,test_predict))
confusion_matrix_result=metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test,test_predict)
print('The confusion matrix result:\n',confusion_matrix_result)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix_result,annot=True,cmap='Blues')
plt.xlabel('Predictedlabels')
plt.ylabel('Truelabels')
plt.show()
实验小结:
1、sigmoid函数
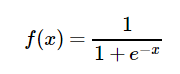
优缺点
优点:平滑、易于求导。
缺点:激活函数计算量大,反向传播求误差梯度时,求导涉及除法;反向传播时,很容易就会出现梯度消失的情况,从而无法完成深层网络的训练。
2.梯度函数

如果函数为一元函数,梯度就是该函数的导数:
如果为二元函数,梯度定义为:
梯度下降法公式:



