Apache Hudi 源码分析 - HoodieTableSource
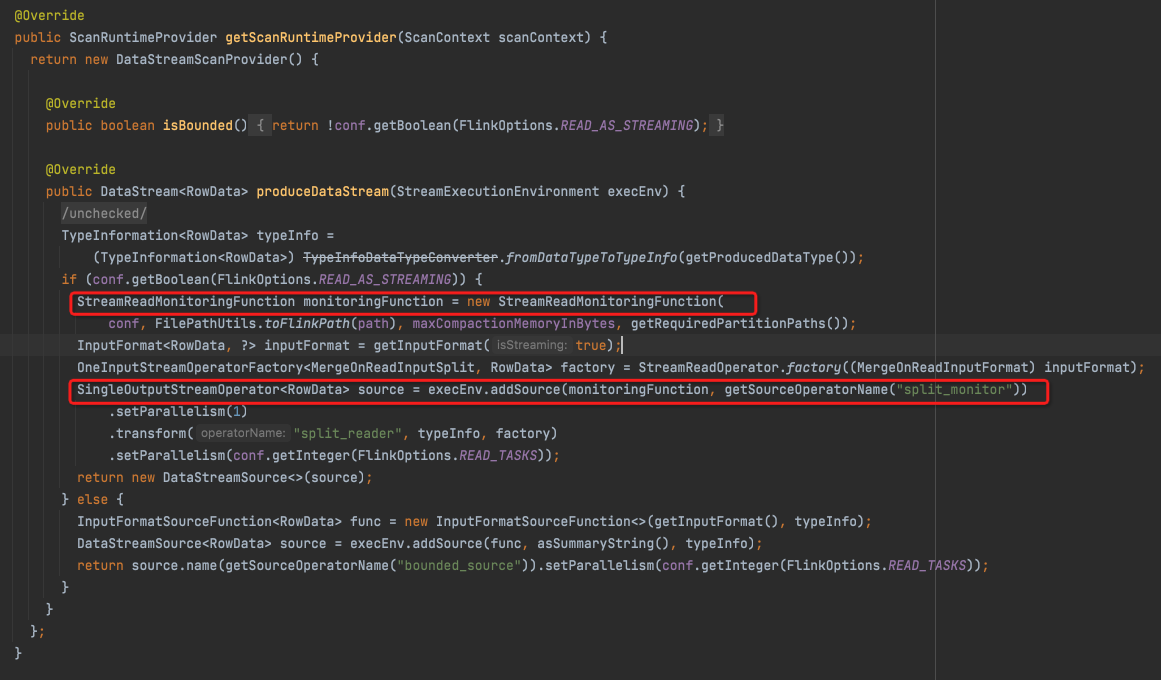
有两个核心的算子,
StreamReadMonitoringFunction ,单并发对应于一个table,读Meta,找出更新的FileSilce,生成inputSplits
StreamReadOperator,从inputSplits中读出来RowData
StreamReadMonitoringFunction
run
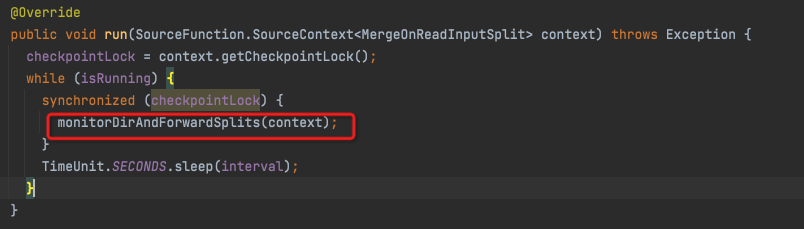
monitorDirAndForwardSplits

IncrementalInputSplits
inputSplits
a. 读到instantRange
issuedInstant,记录上次读到哪个instant
instantToIssue,没读过的instant中,默认是读最新的,如果没有指定
issuedInstant 到 instantToIssue,就形成了一个instantRange
List<HoodieInstant> instants = filterInstantsWithRange(commitTimeline, issuedInstant); //过滤出所有没有读过的instant // get the latest instant that satisfies condition final HoodieInstant instantToIssue = instants.size() == 0 ? null : instants.get(instants.size() - 1); //取出最新的instant final InstantRange instantRange; if (instantToIssue != null) { // if (issuedInstant != null) { // // the streaming reader may record the last issued instant, if the issued instant is present, // the instant range should be: (issued instant, the latest instant]. instantRange = InstantRange.getInstance(issuedInstant, instantToIssue.getTimestamp(), InstantRange.RangeType.OPEN_CLOSE); // }
private List<HoodieInstant> filterInstantsWithRange( HoodieTimeline commitTimeline, final String issuedInstant) { HoodieTimeline completedTimeline = commitTimeline.filterCompletedInstants(); //只取完成的instant,完成的instant是不会变的,未完成的不读 if (issuedInstant != null) { // returns early for streaming mode return maySkipCompaction(completedTimeline.getInstants()) //过滤掉Compaction .filter(s -> HoodieTimeline.compareTimestamps(s.getTimestamp(), GREATER_THAN, issuedInstant)) //大于issuedInstant .collect(Collectors.toList()); }
b.
Set<String> writePartitions; //需要读的partition path的集合 final FileStatus[] fileStatuses; //FileStatus,文件的相关属性,见下 if (instantRange == null) { // reading from the earliest, scans the partitions and files directly. 这个case比较简单 } else { List<HoodieCommitMetadata> activeMetadataList = instants.stream() .map(instant -> WriteProfiles.getCommitMetadata(tableName, path, instant, commitTimeline)).collect(Collectors.toList()); //读出instants的MetaData List<HoodieCommitMetadata> archivedMetadataList = getArchivedMetadata(metaClient, instantRange, commitTimeline, tableName); //如果有太老的instant,需要去读archivedTimeline List<HoodieCommitMetadata> metadataList = archivedMetadataList.size() > 0 // IMPORTANT: the merged metadata list must be in ascending order by instant time ? mergeList(archivedMetadataList, activeMetadataList) : activeMetadataList; //merge从archived里面读到的instants writePartitions = HoodieInputFormatUtils.getWritePartitionPaths(metadataList); //读出所有涉及的partition path集合 // apply partition if (this.requiredPartitions != null) { writePartitions = writePartitions.stream() .filter(this.requiredPartitions::contains).collect(Collectors.toSet()); //分区裁剪,required中是需要pruning的,过滤掉 } if (writePartitions.size() == 0) { LOG.warn("No partitions found for reading in user provided path."); return Result.EMPTY; } fileStatuses = WriteProfiles.getWritePathsOfInstants(path, hadoopConf, metadataList, metaClient.getTableType()); //获取所有涉及到的File的status }
FileStatus
public class FileStatus implements Writable, Comparable<FileStatus> { private Path path; private long length; private boolean isdir; private short block_replication; private long blocksize; private long modification_time; private long access_time; private FsPermission permission; private String owner; private String group; private Path symlink;
c. 最终得到MergeOnReadInputSplit
Split是并发处理的最小粒度,所以并发的粒度是FileSlice
HoodieTableFileSystemView fsView = new HoodieTableFileSystemView(metaClient, commitTimeline, fileStatuses); //调用addFilesToView,提前加载FileGroup final String endInstant = instantToIssue.getTimestamp(); final AtomicInteger cnt = new AtomicInteger(0); final String mergeType = this.conf.getString(FlinkOptions.MERGE_TYPE); List<MergeOnReadInputSplit> inputSplits = writePartitions.stream() .map(relPartitionPath -> fsView.getLatestMergedFileSlicesBeforeOrOn(relPartitionPath, endInstant) //根据endInstant读出相应的FileGroup最新的FileSlice .map(fileSlice -> { Option<List<String>> logPaths = Option.ofNullable(fileSlice.getLogFiles() .sorted(HoodieLogFile.getLogFileComparator()) .map(logFile -> logFile.getPath().toString()) .collect(Collectors.toList())); String basePath = fileSlice.getBaseFile().map(BaseFile::getPath).orElse(null); return new MergeOnReadInputSplit(cnt.getAndAdd(1), basePath, logPaths, endInstant, metaClient.getBasePath(), maxCompactionMemoryInBytes, mergeType, instantRange); //对于每个FileSlice生成一个MergeOnReadInputSplit,包含basePath和logPaths }).collect(Collectors.toList())) .flatMap(Collection::stream) .collect(Collectors.toList()); return Result.instance(inputSplits, endInstant);
所以最终在monitorDirAndForwardSplits,
collect出每个split,

在StreamReadMonitoringFunction中,注意他的state,
会将issuedInstant记录到ListState中,
private transient ListState<String> instantState;
@Override public void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception { this.instantState.clear(); if (this.issuedInstant != null) { this.instantState.add(this.issuedInstant); } }
StreamReadOperator
先看下Operator的State,
State只能是ListState,所以在snapshot的时候,需要把Queue转成List,然后恢复的时候再放回Queue
private transient ListState<MergeOnReadInputSplit> inputSplitsState; //在Snapshot的时候存储Queue private transient Queue<MergeOnReadInputSplit> splits; //缓存接收到InputSplits // Splits are read by the same thread that calls #processElement. Each read task is submitted to that thread by adding // them to the executor. This state is used to ensure that only one read task is in that splits queue at a time, so that // read tasks do not accumulate ahead of checkpoint tasks. When there is a read task in the queue, this is set to RUNNING. // When there are no more files to read, this will be set to IDLE. private transient volatile SplitState currentSplitState; //当前是否在处理split @Override public void initializeState(StateInitializationContext context) throws Exception { super.initializeState(context); // TODO Replace Java serialization with Avro approach to keep state compatibility. inputSplitsState = context.getOperatorStateStore().getListState( new ListStateDescriptor<>("splits", new JavaSerializer<>())); //恢复出ListState // Initialize the current split state to IDLE. currentSplitState = SplitState.IDLE; //初始化state // Recover splits state from flink state backend if possible. splits = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(); // if (context.isRestored()) { int subtaskIdx = getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask(); LOG.info("Restoring state for operator {} (task ID: {}).", getClass().getSimpleName(), subtaskIdx); for (MergeOnReadInputSplit split : inputSplitsState.get()) { splits.add(split); //将ListState中的split放回Queue } } this.sourceContext = Utils.getSourceContext( getOperatorConfig().getTimeCharacteristic(), getProcessingTimeService(), getContainingTask(), output, getRuntimeContext().getExecutionConfig().getAutoWatermarkInterval()); // Enqueue to process the recovered input splits. enqueueProcessSplits(); }
处理的主流程,比较容易理解
这里Split有个Queue
而Executor其实里面也是一个执行Queue,
因为一次调度不会做完一个Split,而且在failover的是需要管理Queue,所以两个Queue合理
@Override public void processElement(StreamRecord<MergeOnReadInputSplit> element) { splits.add(element.getValue()); //先将split放到Queue中等调度 enqueueProcessSplits(); // } private void enqueueProcessSplits() { if (currentSplitState == SplitState.IDLE && !splits.isEmpty()) { currentSplitState = SplitState.RUNNING; //设置State成running,这里同时只有一个split被process,避免冲突 executor.execute(this::processSplits, "process input split"); // } } private void processSplits() throws IOException { MergeOnReadInputSplit split = splits.peek(); //peek,因为一次可能做不完一个split if (split == null) { currentSplitState = SplitState.IDLE; return; } // 1. open a fresh new input split and start reading as mini-batch // 2. if the input split has remaining records to read, switches to another runnable to handle // 3. if the input split reads to the end, close the format and remove the split from the queue #splits // 4. for each runnable, reads at most #MINI_BATCH_SIZE number of records if (format.isClosed()) { // This log is important to indicate the consuming process, // there is only one log message for one data bucket. LOG.info("Processing input split : {}", split); format.open(split); //见下 } try { consumeAsMiniBatch(split); //对于split消费一个miniBath } finally { currentSplitState = SplitState.IDLE; //处理完设成Idle } // Re-schedule to process the next split. enqueueProcessSplits(); } /** * Consumes at most {@link #MINI_BATCH_SIZE} number of records * for the given input split {@code split}. * * <p>Note: close the input format and remove the input split for the queue {@link #splits} * if the split reads to the end. * * @param split The input split */ private void consumeAsMiniBatch(MergeOnReadInputSplit split) throws IOException { for (int i = 0; i < MINI_BATCH_SIZE; i++) { //miniBatch if (!format.reachedEnd()) { // sourceContext.collect(format.nextRecord(null)); //读出一个record split.consume(); //标记split消费一个record,这步前crash,恢复后可能读到重复数据 } else { // close the input format format.close(); // // remove the split splits.poll(); //如果消费完,remove掉这个split break; } } }
这里读数据逻辑,在MergeOnReadInputFormat
首先,先对于split生成不同的Iterator,
@Override public void open(MergeOnReadInputSplit split) throws IOException { this.currentReadCount = 0L; this.closed = false; this.hadoopConf = StreamerUtil.getHadoopConf(); if (!(split.getLogPaths().isPresent() && split.getLogPaths().get().size() > 0)) { if (split.getInstantRange() != null) { // base file only with commit time filtering,仅仅有BaseFile this.iterator = new BaseFileOnlyFilteringIterator( split.getInstantRange(), this.tableState.getRequiredRowType(), getReader(split.getBasePath().get(), getRequiredPosWithCommitTime(this.requiredPos))); // } else { // base file only this.iterator = new BaseFileOnlyIterator(getRequiredSchemaReader(split.getBasePath().get())); // } } else if (!split.getBasePath().isPresent()) { // log files only,仅仅有LogFiles if (OptionsResolver.emitChangelog(conf)) { this.iterator = new LogFileOnlyIterator(getUnMergedLogFileIterator(split)); // } else { this.iterator = new LogFileOnlyIterator(getLogFileIterator(split)); // } } else if (split.getMergeType().equals(FlinkOptions.REALTIME_SKIP_MERGE)) { this.iterator = new SkipMergeIterator( getRequiredSchemaReader(split.getBasePath().get()), getLogFileIterator(split)); } else if (split.getMergeType().equals(FlinkOptions.REALTIME_PAYLOAD_COMBINE)) { this.iterator = new MergeIterator( // hadoopConf, split, this.tableState.getRowType(), this.tableState.getRequiredRowType(), new Schema.Parser().parse(this.tableState.getAvroSchema()), new Schema.Parser().parse(this.tableState.getRequiredAvroSchema()), this.requiredPos, this.emitDelete, this.conf.getBoolean(FlinkOptions.CHANGELOG_ENABLED), this.tableState.getOperationPos(), getFullSchemaReader(split.getBasePath().get())); } else { throw new HoodieException("Unable to select an Iterator to read the Hoodie MOR File Split for " + "file path: " + split.getBasePath() + "log paths: " + split.getLogPaths() + "hoodie table path: " + split.getTablePath() + "spark partition Index: " + split.getSplitNumber() + "merge type: " + split.getMergeType()); } mayShiftInputSplit(split); //把上次已经consume过的record跳过,否则就重复读了,主要是failover的场景 }
这里一共6种Iterator,
1. BaseFileOnlyIterator和BaseFileOnlyFilteringIterator
仅仅有BaseFile的case
可以看到哪怕是读BaseFile的时候,
会根据InstantRange去过滤每条record的commit时间,来保证不重复读,所以基于COW,可以避免重复消费,但是数据仍然要读一遍
static class BaseFileOnlyFilteringIterator implements RecordIterator { // base file reader private final ParquetColumnarRowSplitReader reader; //BaseFile是Parquet格式 private final InstantRange instantRange; private final RowDataProjection projection; // private RowData currentRecord; //读到Row数据 BaseFileOnlyFilteringIterator( Option<InstantRange> instantRange, RowType requiredRowType, ParquetColumnarRowSplitReader reader) { this.reader = reader; this.instantRange = instantRange.orElse(null); int[] positions = IntStream.range(1, 1 + requiredRowType.getFieldCount()).toArray(); projection = RowDataProjection.instance(requiredRowType, positions); // } @Override public boolean reachedEnd() throws IOException { while (!this.reader.reachedEnd()) { // currentRecord = this.reader.nextRecord(); //从Parquet读一条Row if (instantRange != null) { boolean isInRange = instantRange.isInRange(currentRecord.getString(HOODIE_COMMIT_TIME_COL_POS).toString()); //判断Record的commit_Time是否满足Range的filter条件 if (isInRange) { return false; } } else { return false; } } return true; } @Override public RowData nextRecord() { // can promote: no need to project with null instant range return projection.project(currentRecord); //执行Project操作 }
2. getUnMergedLogFileIterator和getLogFileIterator
仅仅有LogFile的case
先看getLogFileIterator

logScanner -> HoodieMergedLogRecordScanner
performScan首先要将log files的数据读出,并merge,放到this.records里面,然后再用Iterator读records
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected HoodieMergedLogRecordScanner(FileSystem fs, String basePath, List<String> logFilePaths, Schema readerSchema,
String latestInstantTime, Long maxMemorySizeInBytes, boolean readBlocksLazily,
boolean reverseReader, int bufferSize, String spillableMapBasePath,
Option<InstantRange> instantRange,
ExternalSpillableMap.DiskMapType diskMapType,
boolean isBitCaskDiskMapCompressionEnabled,
boolean withOperationField, boolean forceFullScan,
Option<String> partitionName, InternalSchema internalSchema) {
super(fs, basePath, logFilePaths, readerSchema, latestInstantTime, readBlocksLazily, reverseReader, bufferSize,
instantRange, withOperationField,
forceFullScan, partitionName, internalSchema);
try {
// Store merged records for all versions for this log file, set the in-memory footprint to maxInMemoryMapSize
this.records = new ExternalSpillableMap<>(maxMemorySizeInBytes, spillableMapBasePath, new DefaultSizeEstimator(),
new HoodieRecordSizeEstimator(readerSchema), diskMapType, isBitCaskDiskMapCompressionEnabled); //缓存所有从Log读出来的Record,支持spill
this.maxMemorySizeInBytes = maxMemorySizeInBytes;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new HoodieIOException("IOException when creating ExternalSpillableMap at " + spillableMapBasePath, e);
}
if (forceFullScan) {
performScan(); //读logfile
}
}
PerformScan -> Scan -> AbstractHoodieLogRecordReader.scanInternal
AbstractHoodieLogRecordReader.scanInternal
这块逻辑对于merge,unmerge是通用的
a. log file 读准备
// Iterate over the paths //将所有log file都封装到这个Wrapper中,封装掉一个个file读,对Wrapper next读取所有的log blocks logFormatReaderWrapper = new HoodieLogFormatReader(fs, logFilePaths.stream().map(logFile -> new HoodieLogFile(new Path(logFile))).collect(Collectors.toList()), readerSchema, readBlocksLazily, reverseReader, bufferSize, enableRecordLookups, keyField, internalSchema); Set<HoodieLogFile> scannedLogFiles = new HashSet<>(); while (logFormatReaderWrapper.hasNext()) { //是否有log block可以读取 HoodieLogFile logFile = logFormatReaderWrapper.getLogFile(); LOG.info("Scanning log file " + logFile); scannedLogFiles.add(logFile); totalLogFiles.set(scannedLogFiles.size()); // Use the HoodieLogFileReader to iterate through the blocks in the log file // 读取一个logBlock,下面判断一下在某些情况下,这个logBlock可以skip HoodieLogBlock logBlock = logFormatReaderWrapper.next(); final String instantTime = logBlock.getLogBlockHeader().get(INSTANT_TIME); totalLogBlocks.incrementAndGet(); if (logBlock.getBlockType() != CORRUPT_BLOCK && !HoodieTimeline.compareTimestamps(logBlock.getLogBlockHeader().get(INSTANT_TIME), HoodieTimeline.LESSER_THAN_OR_EQUALS, this.latestInstantTime )) { // hit a block with instant time greater than should be processed, stop processing further,超出latestInstantTime,不是valid instant,可能in-flight break; } if (logBlock.getBlockType() != CORRUPT_BLOCK && logBlock.getBlockType() != COMMAND_BLOCK) { if (!completedInstantsTimeline.containsOrBeforeTimelineStarts(instantTime) || inflightInstantsTimeline.containsInstant(instantTime)) { // hit an uncommitted block possibly from a failed write, move to the next one and skip processing this one,不在completedInstant或是在inflightInstants continue; } if (instantRange.isPresent() && !instantRange.get().isInRange(instantTime)) { // filter the log block by instant range,不在这次的instantRange中 continue; } }
b. 读取LogBlock
这里每次遍历一个block放到队列中,并且读取上一个block
之所以这样,因为可能下一个block,出现rollback command,所以要多等一个block
switch (logBlock.getBlockType()) { case HFILE_DATA_BLOCK: case AVRO_DATA_BLOCK: case PARQUET_DATA_BLOCK: LOG.info("Reading a data block from file " + logFile.getPath() + " at instant " + logBlock.getLogBlockHeader().get(INSTANT_TIME)); if (isNewInstantBlock(logBlock) && !readBlocksLazily) { // If this is an avro data block belonging to a different commit/instant, // 如果这个logBlock是个新的block,就读取当前的上一个block processQueuedBlocksForInstant(currentInstantLogBlocks, scannedLogFiles.size(), keySpecOpt); } // store the current block,把当前的logBlock加入到队列中,等下次读 currentInstantLogBlocks.push(logBlock); break; case DELETE_BLOCK: LOG.info("Reading a delete block from file " + logFile.getPath()); if (isNewInstantBlock(logBlock) && !readBlocksLazily) { // If this is a delete data block belonging to a different commit/instant, // then merge the last blocks and records into the main result processQueuedBlocksForInstant(currentInstantLogBlocks, scannedLogFiles.size(), keySpecOpt); } // store deletes so can be rolled back currentInstantLogBlocks.push(logBlock); break;
processQueuedBlocksForInstant
这里一般都是调用processDataBlock
只有对于delete block,对于每个deleted的record,调用processNextDeletedRecord
而processDataBlock,就是从block里面读出数据,最终封装成HoodieRecord,调用processNextRecord


processNextRecord
分为两个版本,HoodieMergedLogRecordScanner和HoodieUnMergedLogRecordScanner
对于HoodieMergedLogRecordScanner
@Override protected void processNextRecord(HoodieRecord<? extends HoodieRecordPayload> hoodieRecord) throws IOException { String key = hoodieRecord.getRecordKey(); // if (records.containsKey(key)) { // records里面是否已经包含该record // Merge and store the merged record. The HoodieRecordPayload implementation is free to decide what should be // done when a DELETE (empty payload) is encountered before or after an insert/update. HoodieRecord<? extends HoodieRecordPayload> oldRecord = records.get(key); // HoodieRecordPayload oldValue = oldRecord.getData(); // HoodieRecordPayload combinedValue = hoodieRecord.getData().preCombine(oldValue); // Merge,将update进行merge // If combinedValue is oldValue, no need rePut oldRecord if (combinedValue != oldValue) { HoodieOperation operation = hoodieRecord.getOperation(); records.put(key, new HoodieAvroRecord<>(new HoodieKey(key, hoodieRecord.getPartitionPath()), combinedValue, operation)); //更新records } } else { // Put the record as is records.put(key, hoodieRecord); //第一次,支持insert } }
再看getUnMergedLogFileIterator

BoundedMemoryRecords
生产者-消费者模式,
public BoundedMemoryRecords( MergeOnReadInputSplit split, Schema logSchema, Configuration hadoopConf, org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration flinkConf) { this.executor = new BoundedInMemoryExecutor<>( // StreamerUtil.getMaxCompactionMemoryInBytes(flinkConf), getParallelProducers(), //产生生产者 Option.empty(), //消费者为空 Function.identity(), new DefaultSizeEstimator<>(), Functions.noop()); // Consumer of this record reader this.iterator = this.executor.getQueue().iterator(); //外部消费者,直接暴露Iterator this.scanner = FormatUtils.unMergedLogScanner(split, logSchema, hadoopConf, record -> executor.getQueue().insertRecord(record)); //最后一个参数,callback,把record放入Queue // Start reading and buffering this.executor.startProducers(); //开启Producer } public Iterator<HoodieRecord<?>> getRecordsIterator() { return this.iterator; } /** * Setup log and parquet reading in parallel. Both write to central buffer. */ private List<BoundedInMemoryQueueProducer<HoodieRecord<?>>> getParallelProducers() { List<BoundedInMemoryQueueProducer<HoodieRecord<?>>> producers = new ArrayList<>(); //加入一个producer producers.add(new FunctionBasedQueueProducer<>(buffer -> { scanner.scan(); //producer的逻辑就是调用,Scanner.scan return null; })); return producers; }
逻辑相对简单,
Producer就是调用Scanner.scan,就看看如何scan
这里逻辑大部分和merge版本一样,
Scan -> AbstractHoodieLogRecordReader.scanInternal......
唯一不同的是,
HoodieUnMergedLogRecordScanner.processNextRecord
@Override protected void processNextRecord(HoodieRecord<? extends HoodieRecordPayload> hoodieRecord) throws Exception { // Just call callback without merging callback.apply(hoodieRecord); }
这个callback就是上面传入的,
record -> executor.getQueue().insertRecord(record))
就是直接放到queue里面
所以看看,
Merge版本,是查询场景,所以基本结构是Map,要把各个Log里面的Value都merge到Map里面
UnMerge版本,是流式场景,所以基本结构是Queue,只是将读上来的record简单的放到Queue中即可
3. SkipMergeIterator
后面的场景,都是既有base file,又有log files
SkipMerge,意思是,Base file和Log files之间不会merge,
会全量的读base file,
然后读Log files,log files之间是会merge,因为这里用的是logFileIterator

static class SkipMergeIterator implements RecordIterator { // base file reader private final ParquetColumnarRowSplitReader reader; // iterator for log files private final ClosableIterator<RowData> iterator; // add the flag because the flink ParquetColumnarRowSplitReader is buggy: // method #reachedEnd() returns false after it returns true. // refactor it out once FLINK-22370 is resolved. private boolean readLogs = false; private RowData currentRecord; SkipMergeIterator(ParquetColumnarRowSplitReader reader, ClosableIterator<RowData> iterator) { this.reader = reader; this.iterator = iterator; } @Override public boolean reachedEnd() throws IOException { if (!readLogs && !this.reader.reachedEnd()) { currentRecord = this.reader.nextRecord(); //先读base return false; } readLogs = true; if (this.iterator.hasNext()) { currentRecord = this.iterator.next(); //base读完后,再读log return false; } return true; }
4. MergeIterator

对于MergeIterator,
也是要同时考虑base file和log file,
这里其实读取basefile和logfile的方式和SkipMergeIterator也是一样的,
这里虽然没有直接用logFileIterator,但是实现的方式是一样的,logScanner是会将log file merge后,再Iterate读取的

核心的逻辑在reachEnd中,
逻辑主要在于,读basefile的时候,需要考虑和logfile的merge
@Override public boolean reachedEnd() throws IOException { while (!readLogs && !this.reader.reachedEnd()) { //Base file没有读完 currentRecord = this.reader.nextRecord(); //读一条record if (instantRange != null) { boolean isInRange = instantRange.isInRange(currentRecord.getString(HOODIE_COMMIT_TIME_COL_POS).toString()); //判断一下是否在range中 if (!isInRange) { //不在range中丢弃 // filter base file by instant range continue; } } final String curKey = currentRecord.getString(HOODIE_RECORD_KEY_COL_POS).toString(); //读出record key if (scanner.getRecords().containsKey(curKey)) { //scanner的records中是否包含该key,意思是logfile中是否有这个key keyToSkip.add(curKey); //如果有,这里合并掉,那么后面再碰到就可以skip Option<IndexedRecord> mergedAvroRecord = mergeRowWithLog(currentRecord, curKey); //合并basefile和logfile中相同key的record if (!mergedAvroRecord.isPresent()) { //merged为null,为deleted // deleted continue; } else { final RowKind rowKind = FormatUtils.getRowKindSafely(mergedAvroRecord.get(), this.operationPos); //获取kind,如果kind是delete,也continue if (!emitDelete && rowKind == RowKind.DELETE) { // deleted continue; } GenericRecord avroRecord = buildAvroRecordBySchema( mergedAvroRecord.get(), requiredSchema, requiredPos, recordBuilder); this.currentRecord = (RowData) avroToRowDataConverter.convert(avroRecord); //将读出的record赋值给currentRecord,等待后续读 this.currentRecord.setRowKind(rowKind); return false; } } // project the full record in base with required positions currentRecord = projection.project(currentRecord); return false; } // read the logs readLogs = true; while (logKeysIterator.hasNext()) { //开始对logfile,遍历 final String curKey = logKeysIterator.next(); // if (!keyToSkip.contains(curKey)) { //如果这个key之前读过,就skip Option<IndexedRecord> insertAvroRecord = getInsertValue(curKey); // if (insertAvroRecord.isPresent()) { // the record is a DELETE if insertAvroRecord not present, skipping GenericRecord avroRecord = buildAvroRecordBySchema( insertAvroRecord.get(), requiredSchema, requiredPos, recordBuilder); this.currentRecord = (RowData) avroToRowDataConverter.convert(avroRecord); FormatUtils.setRowKind(this.currentRecord, insertAvroRecord.get(), this.operationPos); return false; } } } return true; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号