1 Linux下sysfs/procfs/debugfs使用
Linux内核空间与用户空间的交互如何能透过文件系统这层关系,把需要参数写入文件中呢?
当然有办法,linux内核提供了3种 “内存文件系统”,分别是sysfs、debugfs、procfs,驱动工程师可以通过任意的一种文件系统向用户空间传递信息。
Sysfs的挂载点为/sys
Debugfs的挂载点为/sys/kernel/debug
Procfs的挂载点为/proc
内存文件系统: 一种临时文件系统,一般会利用脚本挂载到rootfs,但是这些目录都是使用RAM空间,他们中的信息只存在于内存中,下电后即消失。他们的出现旨在提供一种与用户空间交互信息的方式。
脚本如下:
[root@xxx]/etc# cat fstab
# <file system> <mount pt> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
/dev/root / ext2 rw,noauto 0 1
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
devpts /dev/pts devpts defaults,gid=5,mode=620,ptmxmode=0666 0 0
tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs mode=0777 0 0
tmpfs /tmp tmpfs mode=1777 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
nodev /sys/kernel/debug debugfs defaults 0 0
输入mount查看挂载信息:可以看到有挂载procfs, sysfs,以及debugfs
[root@xxx]~# mount
/dev/root on / type squashfs (ro,relatime)
devtmpfs on /dev type devtmpfs (rw,relatime,size=1381884k,nr_inodes=345471,mode=755)
proc on /proc type proc (rw,relatime) #procfs
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw,relatime) #sysfs
nodev on /sys/kernel/debug type debugfs (rw,relatime) #debugfs
/dev/mmcblk0p6 on /mnt/cfg type ext4 (rw,sync,relatime)
/dev/mmcblk0p7 on /mnt/data type ext4 (rw,sync,relatime)
/dev/mmcblk0p7 on /var/log type ext4 (rw,sync,relatime)
1.1 sysfs
设备驱动模型中诞生了sys这个新的虚拟文件系统。
1.1.1 sysfs举例
sysfs在linux驱动开发过程使用非常常见,比如gpio子系统 led子系统 led子系统-hexo gpio子系统-hexo
echo 256 > /sys/class/gpio/export #/sys/class/gpio会生成gpio256目录
echo 256 > /sys/class/gpio/unexport
echo 255 > /sys/class/leds/led1/brightness
cat /sys/class/leds/led1/brightness
cat /sys/class/leds/led1/max_brightness
这就是利用sysfs写入文件,这个文件是用户态和内核态共享的。方便驱动动态读取用户配置和对驱动的控制。
1.1.2 sysfs使用
[root@xxx]/sys/module/xxx_stitch/drivers# ls -l
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:00 platform:stitch -> ../../../bus/platform/drivers/stitch
[root@xxxxxx]/sys/module/xxx_stitch/parameters# ls -l
#对应驱动模块的模块参数,比如module_param(clk_sys_freq, int, 0644);module_param(gStitchDumpReg, int, 0644);
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 10:01 clk_sys_freq
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 10:01 gStitchDumpDmaCfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 10:01 gStitchDumpReg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 10:01 stitch_log_lv
/sys/module/xxx/parameters下定义了驱动xxx模块的模块参数。
1.1.2.0 syfs下的platform设备和驱动信息
[root@xxxxxx]/sys/bus/platform/devices# ls -l
...
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:06 680b8000.stitch -> ../../../devices/platform/680b8000.stitch
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:06 680ba000.dpu -> ../../../devices/platform/680ba000.dpu
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:06 680be000.sys -> ../../../devices/platform/680be000.sys
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:06 68100000.cif -> ../../../devices/platform/68100000.cif
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:06 68100000.cif_v4l2 -> ../../../devices/platform/68100000.cif_v4l2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:06 Fixed MDIO bus.0 -> ../../../devices/platform/Fixed MDIO bus.0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:06 base -> ../../../devices/platform/base
...
[root@xxxxxx]/sys/bus/platform/drivers# ls -l
...
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Jan 1 10:15 cif
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Jan 1 10:00 stitch
...
# cd /sys/bus/platform/drivers/stitch进来瞅瞅
[root@xxxxxx]/sys/bus/platform/drivers/stitch# ls -l
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:00 680b8000.stitch -> ../../../../devices/platform/680b8000.stitch
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 10:00 module -> ../../../../module/xxx_stitch
--w------- 1 root root 4096 Jan 1 10:00 uevent
可以看到只要用platform_driver_register、platform_device_register注册的驱动和设备就会建立如上的sysfs关系链。
1.1.2.1 syfs下的misc设备信息
[root@xxxxxx]/sys/class/misc# ls
miscxxxxxxadc_0 xxx-dpu xxx-stitch watchdog
miscxxxxxxadc_1 xxx-ldc xxx-sys
miscxxxxxxdac_0 xxx-mipi-rx xxx-vpss
[root@xxxxxx]/sys/class/misc# ls -l xxx-stitch
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 13:57 xxx-stitch -> ../../devices/virtual/misc/xxx-stitch
[root@xxxxxx]/sys/class/xxx-vi# ls -l
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 xxx-vi -> ../../devices/platform/68000000.vi/xxx-vi/xxx-vi
可以看到只要是misc设备注册的字符设备,都会在/sys/class/misc下。device_create函数内部会调用到device_add函数,会在/sys/device目录下生成相应的sys文件,同时会判断device结构中的devt变量是否可用,如果可用才会调用devtmpfs_create_node(dev);在/dev目录下生成对应的设备文件。所以说device_add是否会生成设备文件需要根据device结构体中是否传入了设备号来决定的。
device_create(dev->vi_class, dev->dev, dev->cdev_id, NULL, "%s", VI_DEV_NAME);
1.1.2.2 syfs API
static inline int __must_check sysfs_create_file(struct kobject *kobj,
const struct attribute *attr)//生成sysfs属性文件,此接口用于生成单个属性文件
//在参数kobj目录下面创建一个属性集合,并且显示该集合的文件。
//attribute_group *grp 中描述的是一组属性类型
int __must_check sysfs_create_group(struct kobject *kobj,
const struct attribute_group *grp);
int __must_check sysfs_create_groups(struct kobject *kobj,
const struct attribute_group **groups);
//动态生成一个struct kobject数据结构,然后将其注册到sysfs文件系统
/*
name就是要创建的文件或者目录的名称,
parent指向父目录的kobject数据结构,若parent为NULL,说明父目录就是/sys目录,
比如:kobject_create_and_add()在/sys 目录下建立一个名为“kernel”的目录,
然后sysfs_create_group()函数在该目录下面创建一些属性集合
*/
struct kobject *kobject_create_and_add(const char *name, struct kobject*parent);
//会调用到sysfs_create_file函数来生成sysfs属性文件,此接口用于生成单个属性文件
int device_create_file ( struct device * dev, const struct device_attribute * attr);
//移除组属性
void sysfs_remove_group(struct kobject *kobj,
const struct attribute_group *grp);
//Y:\linux_5.10\include\linux\sysfs.h
1.1.2.3 给驱动模块添加sysfs参数举例
- 使用
DEVICE_ATTR声明一个sys节点, 这里是一个led_status节点,申明了led_status_show,led_status_store函数。
/*
led_status:在sys接口中显示的节点名字
0600:表示操作这个led_status节点的权限
led_status_show:使用cat命令查看sys接口时调用的函数
led_status_store:使用echo命令往sys接口写入内容时调用的函数
*/
static DEVICE_ATTR(led_status, 0600, led_status_show, led_status_store);
- 完成sys节点的读写函数,执行
cat /sys/devices/platform/leds/led_status时会调用led_status_show,把buf内容显示出来。用echo命令往sys节点写入内容时调用led_status_store。led_status_show()函数和led_status_store()函数的作用分为打印led变量的值和修改led变量的值.
static unsigned int led = 0;
static ssize_t led_status_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf){
return sprintf(buf, "%s:%d.\n", "led", led);
}
static ssize_t led_status_store(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count){
//写入的内容会存放到buf中,这里将buf内容赋值给led变量
sscanf(buf, "%d", &led);
return count;
}
- 定义
struct attribute和struct attribute_group数组
static struct attribute *led_attributes[]={
/*上述使用了DEVICE_ATTR声明节点名字为led_status,
* 则struct attribute名字应为:
* dev_attr_ + (节点名) + .attr
* 所以名字为dev_attr_led_status.attr
*/
&dev_attr_led_status.attr,
NULL,
};
static const struct attribute_group led_attrs={
.attrs = led_attributes,//引用上述struct attribute数组
};
- 调用
sysfs_create_group()注册sysfs接口, 完整驱动实例如下:
static unsigned int led = 0;
static ssize_t led_status_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf){
return sprintf(buf, "%s:%d.\n", "led", led);
}
static ssize_t led_status_store(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count){
sscanf(buf, "%d", &led);
return count;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(led_status, 0600, led_status_show, led_status_store);
static struct attribute *led_attributes[]={
&dev_attr_led_status.attr,
NULL,
};
static const struct attribute_group led_attrs={
.attrs = led_attributes,
};
static int xx_led_probe(struct platform_device *pdev){
sysfs_create_group(&pdev->dev.kobj, &led_attrs);
return 0;
}
static int xx_led_remove(struct platform_device *pdev){
sysfs_remove_group(&pdev->dev.kobj, &led_attrs);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id xx_led_of_match[] = {
{.compatible = "xx,xx-led"},
};
static struct platform_driver xx_led_driver = {
.probe = xx_led_probe,
.remove = xx_led_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "xx-led",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = xx_led_of_match,
},
};
static int __init xx_led_init(void){
return platform_driver_register(&xx_led_driver);
}
static void __exit xx_led_exit(void){
platform_driver_unregister(&xx_led_driver);
}
module_init(xx_led_init);
module_exit(xx_led_exit);
1.1.3 DEVICE_ATTR宏
#define DEVICE_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) \
struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
#define __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) { \
.attr = {.name = __stringify(_name), \
.mode = VERIFY_OCTAL_PERMISSIONS(_mode) }, \
.show = _show, \
.store = _store, \
}
struct device_attribute {
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count);
};
DEVICE_ATTR宏会定义一个struct device_attribute结构体实例dev_attr_##_name和初始化。一般用device_create_file生成sysfs属性文件。
注意:属性文件的权限mode不可以随便定义,是有限制的,mode不合理会报错:
error: negative width in bit-field anonymous
1.1.3.0 DEVICE_ATTR示例
以Linux下Framebuffer子系统(cnblogs.com-fuzidage) 字符设备驱动-Framebuffer子系统 | Hexo (fuzidage.github.io) 为例,打开linux_5.10/drivers/video/fbdev/core/fbsysfs.c:
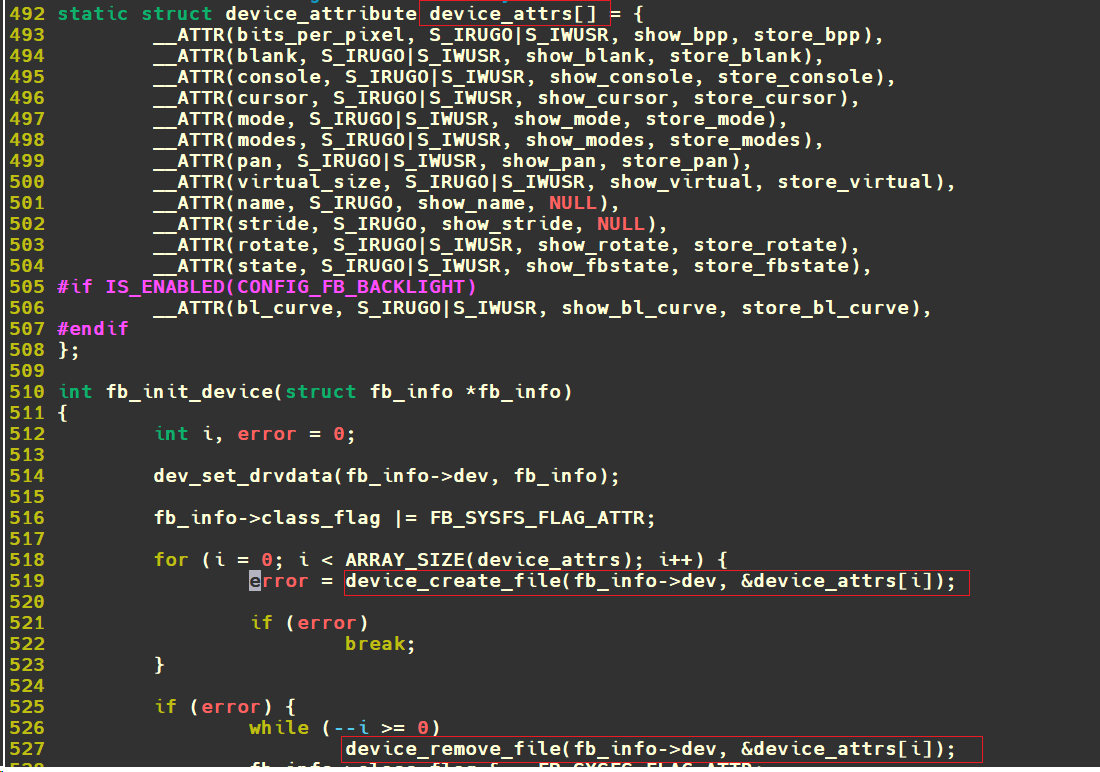
可以看到很多属性文件,都调用device_create_file建立了sysfs属性文件。
1.1.3.1 device_create_file
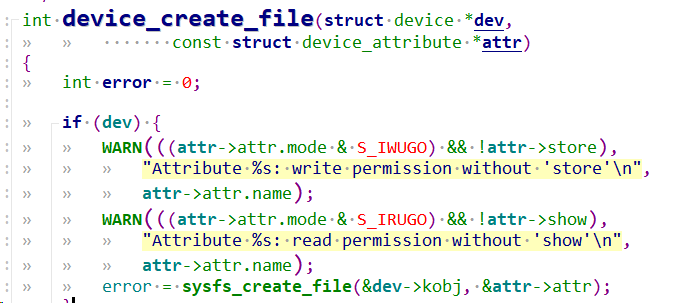
可以看到本质还是用sysfs_creat_file创建sysfs属性文件。
1.2 procfs
procfs是用户获取进程的有用信息、系统的有用信息等。可以查看某个进程的相关信息,也可以查看系统的信息,比如/proc/meminfo 用来查看内存的管理信息,/proc/cpuinfo用来观察CPU的信息。
[root@xxxxxx]~# ls -l /proc/
total 0
dr-xr-xr-x 8 root root 0 Jan 1 08:00 1
dr-xr-xr-x 8 root root 0 Jan 1 08:00 234
dr-xr-xr-x 8 root root 0 Jan 1 08:00 273
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 cmdline
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 cpuinfo
dr-xr-xr-x 3 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 dynamic_debug
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 fb
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 filesystems
dr-xr-xr-x 8 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 fs
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 interrupts
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 iomem
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 ioports
dr-xr-xr-x 92 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 irq
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 meminfo
-r-------- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 pagetypeinfo
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 partitions
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 sched_debug
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:00 self -> 291
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:00 thread-self -> 291/task/291
-r-------- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 vmallocinfo
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 vmstat
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 08:02 zoneinfo
可以看到很多信息,我们敲的命令ps、top等很多shell命令正是从proc系统中读取信息,且更具可读性。又例如free命令就是解析/proc/meminifo。
1.2.1 procfs API
procfs文件系统提供了一些常用的API,这些API函数定义在fs/proc/internal.h
struct proc_dir_entry *proc_mkdir(const char *name,struct proc_dir_entry *parent);// 如果传入的名字是null, 那么就在/proc/下创建一个目录
//添加一个proc条目, linux5.10后file_operations换成了proc_ops
#if (LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(5, 10, 0))
struct proc_dir_entry *proc_create_data(const char *name, umode_t mode,
struct proc_dir_entry *parent,
const struct proc_ops *proc_ops, void *data);
#else
struct proc_dir_entry *proc_create_data(const char *name, umode_t mode,
struct proc_dir_entry *parent,
const struct file_operations *proc_fops,
void *data);
#endif
//也可以直接用这种添加条目,支持多级目录如/proc/aaa/bbb/ccc条目
struct proc_dir_entry *proc_create_data(const char *name, umode_t mode,
struct proc_dir_entry *parent,
const struct file_operations *proc_fops,
void *data);
//删除条目
void remove_proc_entry(const char *name, struct proc_dir_entry *parent);
//删除目录
void proc_remove(struct proc_dir_entry *de);
// procfs的实现见Y:\linux_5.10\fs\proc\generic.c
// 头文件见Y:\linux_5.10\include\linux\proc_fs.h
1.2.2 使用举例
举个例子:misc杂项设备 misc杂项设备-Hexo子系统初始化时:
static int __init misc_init(void) {
int err;
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
proc_create("misc", 0, NULL, &misc_proc_fops);
#endif
misc_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "misc");
err = PTR_ERR(misc_class);
if (IS_ERR(misc_class))
goto fail_remove;
err = -EIO;
if (register_chrdev(MISC_MAJOR,"misc",&misc_fops))
goto fail_printk;
misc_class->devnode = misc_devnode;
return 0;
fail_printk:
printk("unable to get major %d for misc devices\n", MISC_MAJOR);
class_destroy(misc_class);
fail_remove:
remove_proc_entry("misc", NULL);
return err;
}
就创建了/proc/misc条目和/sys/class/misc目录。/proc/misc条目统计了包含的misc杂项字符设备:
[root@xxxx]/proc# cat misc
48 xxx-stitch
49 xxx-dpu
50 xxx-mipi-tx1
51 xxx-mipi-tx0
52 xxx-rgn
再举一个例子:透过procfs进行cif驱动的状态显示到用户,以及用户配置参数,动态调用cif驱动的流程控制。
#define CIF_PROC_NAME "v4l2/mipi-rx"
static struct proc_dir_entry *cif_proc_entry;
int dbg_hdler(struct xxx_cif_dev *dev, char const *input){//根据txt_buff做一些驱动流程控制,复位处理,时钟配置等等
struct xxx_link *link = &dev->link[0];
struct cif_ctx *ctx;
//int reset;
u32 num;
u8 str[80] = {0};
u8 t = 0;
u32 a, v, v2;
u8 i, n;
u8 *p;
num = sscanf(input, "%s %d %d %d", str, &a, &v, &v2);
if (num > 4) {
dbg_print_usage(link->dev);
return -EINVAL;
}
dev_info(link->dev, "input = %s %d\n", str, num);
/* convert to lower case for following type compare */
p = str;
for (; *p; ++p)
*p = tolower(*p);
n = ARRAY_SIZE(dbg_type);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!strcmp(str, dbg_type[i])) {
t = i;
break;
}
}
if (i == n) {
dev_info(link->dev, "unknown type(%s)!\n", str);
dbg_print_usage(link->dev);
return -EINVAL;
}
switch (t) {
case 0:
/* reset */
if (a > MAX_LINK_NUM)
return -EINVAL;
link = &dev->link[a];
ctx = &link->cif_ctx;
if (link->is_on) {
link->sts_csi.errcnt_ecc = 0;
link->sts_csi.errcnt_crc = 0;
link->sts_csi.errcnt_wc = 0;
link->sts_csi.errcnt_hdr = 0;
link->sts_csi.fifo_full = 0;
cif_clear_csi_int_sts(ctx);
cif_unmask_csi_int_sts(ctx, 0x0F);
}
break;
case 1:
/* hs-settle */
if (a > MAX_LINK_NUM)
return -EINVAL;
link = &dev->link[a];
ctx = &link->cif_ctx;
cif_set_hs_settle(ctx, v);
break;
}
int proc_cif_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v)//cat /proc/v4l2/mipi-rx会调用进行proc输出cif驱动状态信息
{
struct xxx_cif_dev *dev = (struct xxx_cif_dev *)m->private;
int i;
seq_printf(m, "\nModule: [MIPI_RX], Build Time[%s]\n",
UTS_VERSION);
seq_puts(m, "\n------------Combo DEV ATTR--------------\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_LINK_NUM; i++)
if (dev->link[i].is_on)
cif_show_dev_attr(m, &dev->link[i].attr);
seq_puts(m, "\n------------MIPI info-------------------\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_LINK_NUM; i++)
if (dev->link[i].is_on
&& (dev->link[i].attr.input_mode == INPUT_MODE_MIPI)) {
cif_show_mipi_sts(m, &dev->link[i]);
cif_show_phy_sts(m, &dev->link[i]);
}
return 0;
}
static ssize_t cif_proc_write(struct file *file, const char __user *user_buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct xxx_cif_dev *dev = PDE_DATA(file_inode(file));
#if (KERNEL_VERSION(5, 10, 0) <= LINUX_VERSION_CODE)
char txt_buff[MAX_CIF_PROC_BUF];
count = simple_write_to_buffer(txt_buff, MAX_CIF_PROC_BUF, ppos,
user_buf, count);
dbg_hdler(dev, txt_buff);
#else
dbg_hdler(dev, user_buf);//根据txt_buff做一些驱动流程控制,复位处理,时钟配置等等
#endif
return count;
}
static int proc_cif_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct xxx_cif_dev *dev = PDE_DATA(inode);
return single_open(file, proc_cif_show, dev);//proc_cif_show 输出cif驱动状态信息
}
#if (KERNEL_VERSION(5, 10, 0) <= LINUX_VERSION_CODE)
static const struct proc_ops cif_proc_fops = {
.proc_open = proc_cif_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_write = cif_proc_write,
.proc_lseek = seq_lseek,
.proc_release = single_release,
};
#else
static const struct file_operations cif_proc_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = proc_cif_open,
.read = seq_read,
.write = cif_proc_write,
.llseek = seq_lseek,
.release = single_release,
};
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
cif_proc_entry = proc_create_data(CIF_PROC_NAME, 0, NULL,
&cif_proc_fops, dev);
if (!cif_proc_entry)
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cif: can't init procfs.\n");
#endif
1.先创建proc条目:
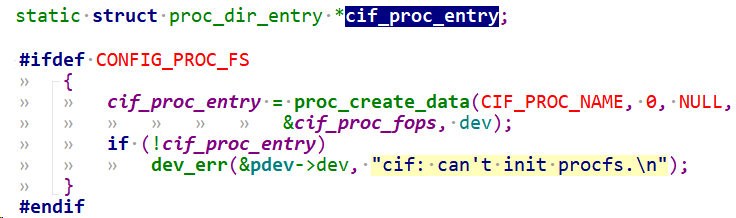
2.实现proc_ops中的成员函数,主要是.proc_open和.proc_write。注意这里当我们Linux内核版本超过5.10,叫做proc_ops, 否则还是叫做file_operations.

procfs通常会和seq_file接口一起使用。seq_file是一个序列文件接口,当我们创建的proc数据内容由一系列数据顺序组合而成或者是比较大的proc文件系统时,都建议使用seq_file接口,例如cat /proc/meminfo就会显示很多内容。
seq_file接口主要就是解决proc接口编程存在的问题,推荐在proc接口编程时使用seq_file接口,另外.read、.llseek、.release成员函数也可以直接用seq_read、seq_lseek和seq_release。
1.2.2.1 seq机制
当用户顺序读取proc接口时, 比如cat /proc/v4l2/mipi-rx, proc_cif_open被调用,然后调用seq_read。和应用程序一样,操作一个文件就是open, read, close操作...
1.2.2.1.0 sigle_open
proc_cif_open调用sigle_open,sigle_open直接调用了seq_open(file, op),该函数会创建个seq_file实例,并添加到file->private_data。
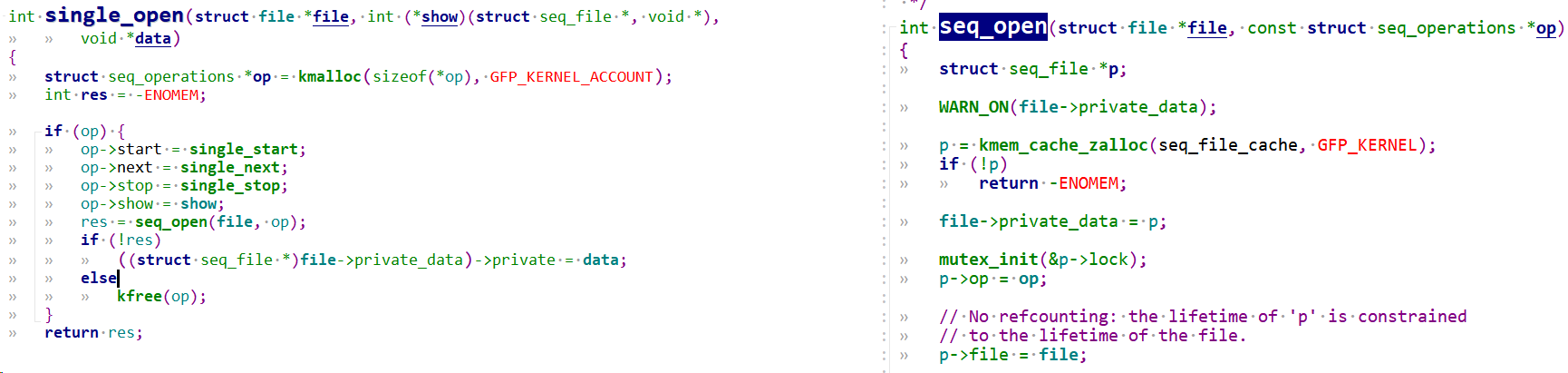
还会创建一个seq_operations *op, 可以看到驱动设置的show函数cif_proc_show被给到op的成员函数show,其余几个成员函数赋值为:
op->start = single_start;
op->next = single_next;
op->stop = single_stop;
op->show = show;
继续看seq_open,把前面的seq_operations *op实例给到seq_file *p->op。
1.2.2.1.1 seq_file基础
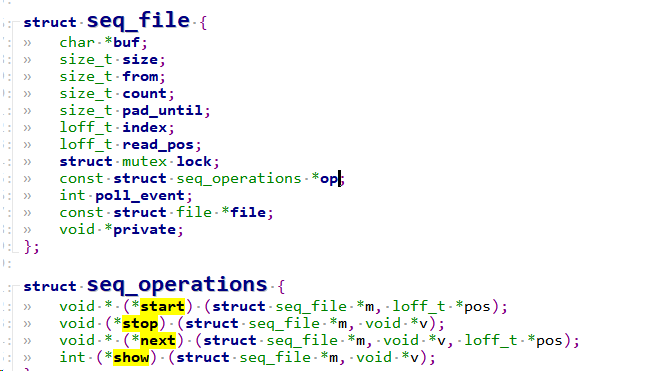
open完后,好接着调用seq_read。seq机制实现见:
Y:\linux_5.10\fs\seq_file.c
Y:\linux_5.10\include\linux\seq_file.h
1.2.2.1.2 seq_read

可以看到不就是调用sigle_open时注册的single_start, single_next函数嘛,包括驱动自己注册的show函数,我这里是cif_proc_show.
网上找了一份图总结了seq机制:
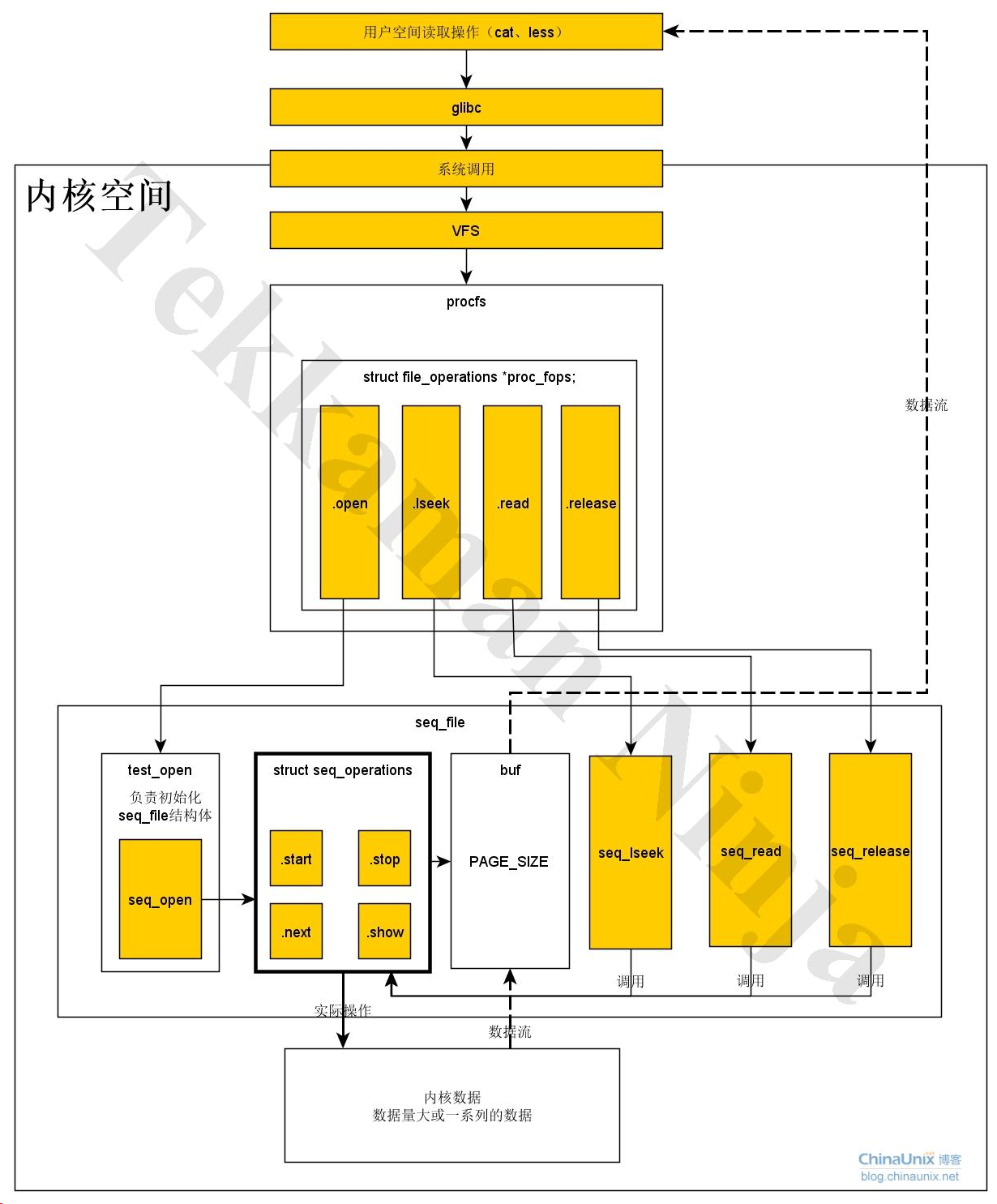
1.3 debugfs
debugfs也是一种用来调试内核的内存文件系统,内核开发者可以通过debugfs和用户空间交换数据,有点类似于前文提到的procfs和sysfs。
procfs是为了反映系统以及进程的状态信息,sysfs用于Linux设备驱动模型:
把私有的调试信息加入这两个虚拟文件系统不太合适,因此内核多添加了一个虚拟文件系统,也就是debugfs。
最常见的就是linux内核的dynamic debug dynamic_debug-hexo 可以在程序运行后动态开关模块的打印,甚至是具体某个文件,某个函数的打印。
1.3.1 debugfs API
debufs文件系统中有不少API函数可以使用,它们定义在include/linux/debugfs.h头文件中。
struct dentry *debugfs_create_dir(const char *name,struct dentry *parent)
void debugfs_remove(struct dentry *dentry)
struct dentry *debugfs_create_blob(const char *name, umode_t mode,struct dentry *parent,struct debugfs_blob_wrapper *blob)
struct dentry *debugfs_create_file(const char *name, umode_t mode,struct dentry *parent, void *data,const struct file_operations *fops)
1.3.2 debugfs 示例

#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
static ssize_t vpu_debug_read(struct file *file, char __user *user_buf,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
char buf[256];
unsigned int len;
unsigned int running, pc, vpu_to_host, host_to_vpu, wdt;
int ret;
struct device *dev = file->private_data;
struct mtk_vpu *vpu = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
ret = vpu_clock_enable(vpu);
if (ret) {
dev_err(vpu->dev, "[VPU] enable clock failed %d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
/* vpu register status */
running = vpu_running(vpu);
pc = vpu_cfg_readl(vpu, VPU_PC_REG);
wdt = vpu_cfg_readl(vpu, VPU_WDT_REG);
host_to_vpu = vpu_cfg_readl(vpu, HOST_TO_VPU);
vpu_to_host = vpu_cfg_readl(vpu, VPU_TO_HOST);
vpu_clock_disable(vpu);
if (running) {
len = snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "VPU is running\n\n"
"FW Version: %s\n"
"PC: 0x%x\n"
"WDT: 0x%x\n"
"Host to VPU: 0x%x\n"
"VPU to Host: 0x%x\n",
vpu->run.fw_ver, pc, wdt,
host_to_vpu, vpu_to_host);
} else {
len = snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "VPU not running\n");
}
return simple_read_from_buffer(user_buf, count, ppos, buf, len);
}
static struct dentry *vpu_debugfs;
static const struct file_operations vpu_debug_fops = {
.open = simple_open,
.read = vpu_debug_read,
};
vpu_debugfs = debugfs_create_file("mtk_vpu", S_IRUGO, NULL, (void *)dev,
&vpu_debug_fops);
#endif
很简单,就是调用debugfs_create_file后会在debugfs挂载目录下也就是/sys/kernel/debug/建立一个mtk_vpu文件。
当cat /sys/kernel/debug/mtk_vpu会打开该文件,也就是调用simple_open,然后调用vpu_debug_read,进一步调用simple_read_from_buffer:

你可以规定/sys/kernel/debug/mtk_vpu文件的格式和信息,这里它是dump了一些寄存器信息:
VPU_PC_REG
VPU_WDT_REG
HOST_TO_VPU
VPU_TO_HOST
当然你也可以不用simple_open这一套机制,那就要你自己去实现vpu_debug_fops中的成员函数,自己去调用copy_to_user。这里是利用simple_open, simple_read机制帮忙简化了,不需要去调用copy_to_user。
simple_open,simple_read机制见:Y:linux_5.10\fs\libfs.c




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 如何调用 DeepSeek 的自然语言处理 API 接口并集成到在线客服系统
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 2025年我用 Compose 写了一个 Todo App